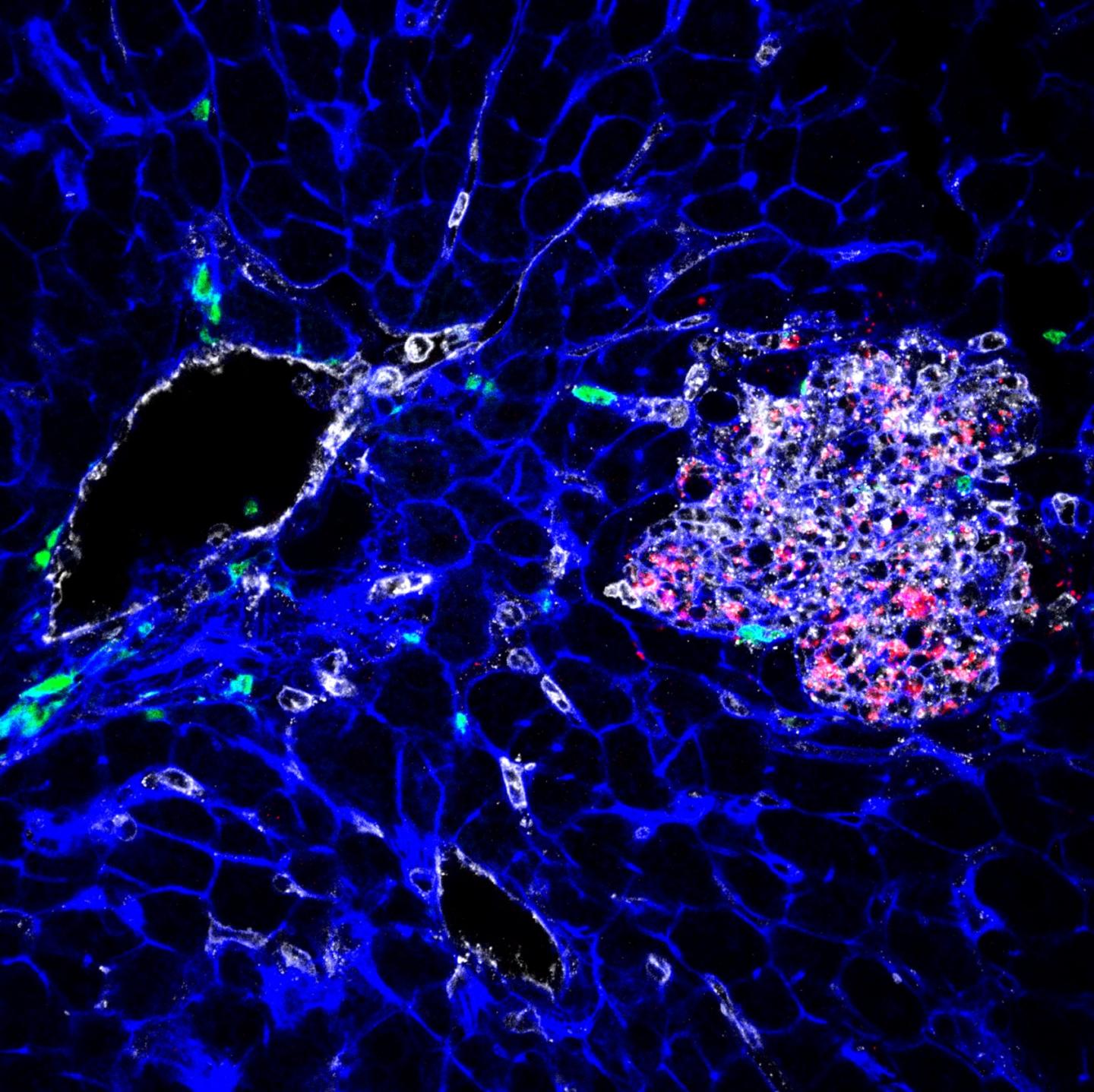
Credit: © Institut Pasteur
Listeriosis is a disease caused by eating foods that have been contaminated by the Listeria monocytogenes bacterium. It is an infrequent condition but it is a particular danger to individuals with an impaired immune system, the elderly and new-born infants. It also affects farmed livestock. The pathogenic potential of L. monocytogenesis linked to its ability to invade different cells in the body, such as epithelial cells in the intestine, liver, brain and placenta. When it reaches the cytoplasm of these cells, L. monocytogenes proliferates and uses a network of cell filaments – called the cytoskeleton – to travel and spread into neighbouring cells. This phase enablesL. monocytogenesto disseminate throughout the body's tissues.
In order to study the behaviour of L. monocytogenes during an asymptomatic infection, INRA(1) scientists, working in collaboration with their colleagues at Institut Pasteur(2), created an original in vitro experimental model using cultures of human epithelial cells. Through this model, they discovered that L. monocytogenesis able to change its lifestyle when it infects the cells of the liver and placenta for several days. The bacteria gradually stop producing the protein (ActA) that allows them to spread using the cytoskeleton of infected cells. They are then trapped in the vacuoles. In this intracellular niche, they are more tolerant of antibiotics and retain an ability to reactivate themselves in a form that can be disseminated.
The scientists also demonstrated that these bacteria can also parasite host cells during cell divisions, without it being possible to detect them on the culture media usually employed for diagnostic tests. Although viable, the bacteria are thus in a non-cultivable physiological state.
These in vitro results have revealed the ability of L. monocytogenes to generate dormant intracellular forms which may be harboured, unsuspected, by humans or animals. The asymptomatic carriage of this pathogenic bacterium may explain why the incubation period for listeriosis is sometimes long (up to three months). It also offers a possible explanation for the problems encountered in identifying the source of contamination in the case of sporadic listeriosis, if the illness occurs a long time after the ingestion of contaminated food. It is possible that dormant forms of L. monocytogenes may thus reactivate themselves. This mechanism could also lead to healthy carriage of this pathogenic agent in animals that serve as a reservoir for the bacterium.
In light of these results, their different consequences require reconsideration of the knowledge acquired on the intracellular life of this pathogen. They thus offer numerous options for investigation which may, in the longer term, result in new therapeutic and diagnostic strategies, and in improvements to managing the risks related to a microbial food contaminant.
###
(1) Institut Microbiologie de l'alimentation au service de la santé (Inra, AgroParisTech, Université Paris-Saclay)
(2) Unité Interactions bactéries-cellules (Inra, Institut Pasteur, Inserm)
Media Contact
Catherine Foucaud-Scheunemann
[email protected]
http://www.pasteur.fr
Original Source
http://presse.inra.fr/en/Press-releases/Listeria-monocytogenes-and-dormant-intracellular-forms