Credit: University of Warwick
- The UK has the highest level of obesity in Europe, in fact it’s estimated half the population could be obese by 2050. Obesity is a significant risk factor for increased morbidity and mortality
- Fasting, has been a trend in recent years to maintain a healthy weight, the body responds to fasting using autophagy, a cellular self-recycling process
- The proteins required for autophagy to work during fasting have been identified by researchers from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick
- Understanding how the proteins work means researchers can activate autophagic pathways to help people maintain a normal body weight
As modern life-styles and high calorie diets drive the UK’s obesity levels up, researchers from the University of Warwick have found how cells respond to fasting and activate the process called autophagy, which means a healthier lifestyle can be promoted to help people maintain a healthy body weight.
The UK has the highest level of obesity in Western Europe, with its levels having more than trebled in the last 30 years, it is estimated that more than half of the population could be obese by 2050 in UK. Obesity is a significant risk factor for increased morbidity and mortality. The cause of the rapid rise in obesity has been blamed on modern lifestyles, including high-calorie diet.
Intermittent fasting, alternate-day fasting, and other forms of periodic caloric restriction are beneficial to maintain a healthy body weight and have gained popularity during the last few years. To respond to fasting, cells use autophagy, a cellular self-recycling process.
A team of researchers led by Professor Ioannis Nezis from the School of Life Sciences, University of Warwick, discovered how cells activate autophagy genes during fasting. In the paper titled ‘Regulation of expression of autophagy genes by Atg8a-interacting partners Sequoia, YL-1 and Sir2 in Drosophila’, published in the journal Cell Reports on the 26th May, Dr Anne-Claire Jacomin, Dr Stavroula Petridi, PhD student Marisa Di Monaco and Professor Ioannis Nezis have discovered proteins which are required for the transcription of autophagy genes.
The proteins are called Sequoia, YL-1 and Sir2, these proteins interact with the cytoplasmic autophagy-related protein Atg8a. These interactions recruit Atg8a in the nucleus to control the transcription of autophagy genes. This is the first study that uncovers a nuclear role of the cytoplasmic protein Atg8a.
Lead author of the research Professor Ioannis Nezis, from the School of Life Sciences at the University of Warwick, comments:
“Understanding the molecular mechanisms of activation of autophagy genes during fasting will help us to use interventions to activate the autophagic pathways to maintain a normal body weight and promote healthy well-being.”
###
NOTES TO EDITORS
High-res images available credit to the University of Warwick at:
https:/
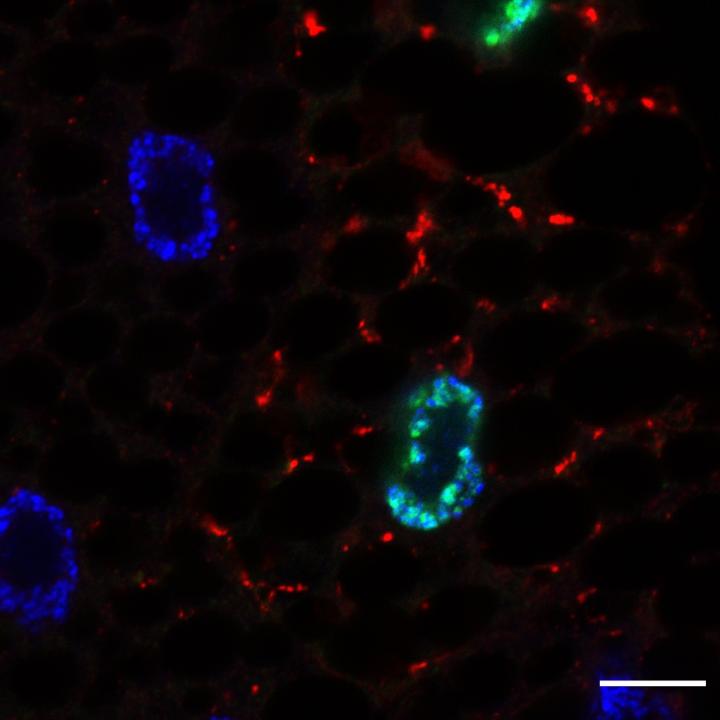
Caption: Cells expressing GFP-Sequoia-LIR mutant (green nuclei) activate autophagy (shown by red puncta)
For previous research of Nezis’ group see https:/
The paper ‘Regulation of expression of autophagy genes by Atg8a-interacting partners Sequoia, YL-1 and Sir2 in Drosophila’ by Anne-Claire Jacomin, Stavroula Petridi, Marisa Di Monaco, Zambarlal Bhujabal, Ashish Jain, Nitha Mulakkal, Anthimi Palara, Emma L. Powell, Bonita Chung, Cleidi Zampronio, Alexandra Jones, Alexander Cameron, Terje Johansen and Ioannis P. Nezis is published in Cell Reports on 26/05/2020 and is available to view at: https:/
It is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, LeverhulmeTrust and Midlands Integrative Biosciences Training Partnership.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION PLEASE CONTACT:
Alice Scott
Media Relations Manager – Science
University of Warwick
Tel: +44 (0) 7920 531 221
E-mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
Alice Scott
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




