Credit: UT Arlington
A University of Texas at Arlington researcher is working to determine how blood flow and cardiac muscle contraction affects gene development that leads to ventricular chamber development in the heart.
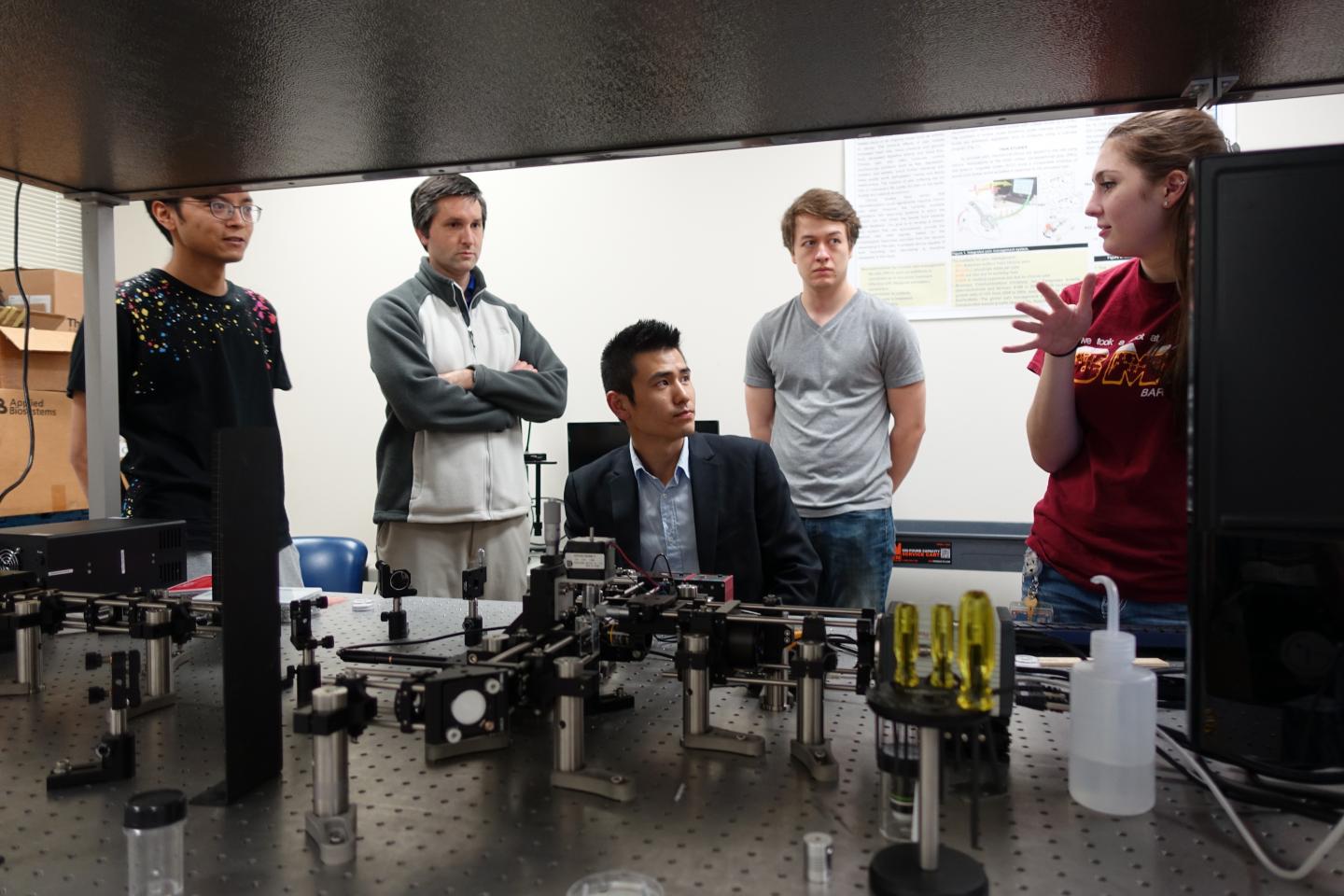
Juhyun Lee, an assistant professor in the Bioengineering Department, is using a two-year, $154,000 Institutional Research Grant from the American Heart Association to develop a new microscope that can capture 3-D motion, then add time to construct a 4-D beating heart using optical imaging techniques with fluorescent nanoparticles in a zebrafish. Victoria Messerschmidt and Zach Bailey, two doctoral students, and Richard Bryant, who is seeking his master's degree, are helping Lee on the project.
"We are trying to understand biological forces through engineering," Lee said. "This research is still in its basic stages, but what we learn now could someday allow doctors to pre-identify heart abnormalities and diagnose congenital heart conditions that could then be treated with gene therapy."
Lee must build his microscope because none are commercially available that can capture 3-D motion plus time. Once it is built, he will inject the zebrafish with nanoparticles that attach where certain genes are expressed and track how genes affect ventricular development. He is using zebrafish because their bodies are transparent in the embryonic stage, so it is easy to see the nanoparticles without the use of magnetic resonance imaging.
Lee will use his new microscope to create a 4-D model of a beating heart based on the images and genetic information collected from the fish, then apply computation models to that data to test his findings.
This will include modifying the genes and using them to modulate contraction and hemodynamics or blood flow to see how changes in biomechanical forces affect gene development and then chamber development. In response to hemodynamic forces, ridges and grooves form in a wavelike pattern called a trabecular network in the direction of the blood flow. Too much or too little trabeculation can lead to defects with high mortality rates.
"If we can understand the effects of biomechanical forces on the genes that cause ventricular chamber development, we can discern the optimized shape of the ventricle and best contraction rate. From there, it could be possible to change the levels of gene expressions," Lee said.
Lee's work is the latest example of UTA's research in cardiac health in support of health and the human condition, a key tenet of the University's Strategic Plan 2020: Bold Solutions | Global Impact, said Michael Cho, professor and Alfred R. and Janet H. Potvin Endowed Chair of the Bioengineering Department.
"Even in its early stages, Dr. Lee's work is exciting in its potential for making large strides in correcting cardiac defects in the future," Cho said. "This research will offer critical insight into how the heart forms and the biomechanical factors that affect cardiac growth, and that knowledge will allow better research into potentially life-saving techniques down the road."
Other recent examples of UTA research in cardiac health include:
- * Michael Nelson, assistant professor of kinesiology, is using a $3.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to study the link between fat storage in the heart and cardiovascular disease, as well as the influence of gender on the development of cardiac dysfunction.
* Bioengineering Professor Kytai Nguyen earned a National Institutes of Health T-32 grant totaling more than $1 million over five years to recruit and train outstanding doctoral students in nanotechnology and nanomedicine related to cardiovascular and pulmonary issues.
* Mark Haykowsky, a cardiovascular exercise scientist in the College of Nursing and Health Innovation, received a $308,000 grant from the National Institutes of Health to study exercise intolerance in older heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction, or HFpEF.
* Yi Hong, an assistant professor in the Bioengineering Department, was awarded a $211,000 R21 grant from the National Institutes of Health to develop materials that will allow doctors to use a 3-D printer to create unique new blood vessels for children with vascular defects.
###
Media Contact
Herb Booth
[email protected]
817-272-7075
@utarlington
http://www.uta.edu
Original Source
https://www.uta.edu/news/releases/2018/03/Juhyun-AHA-grant.php