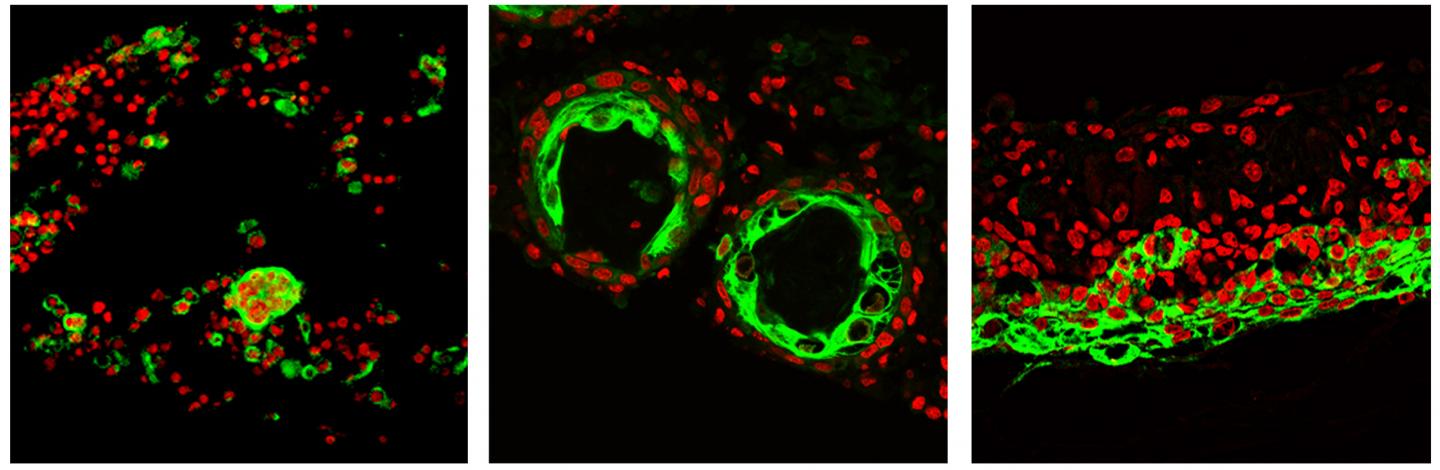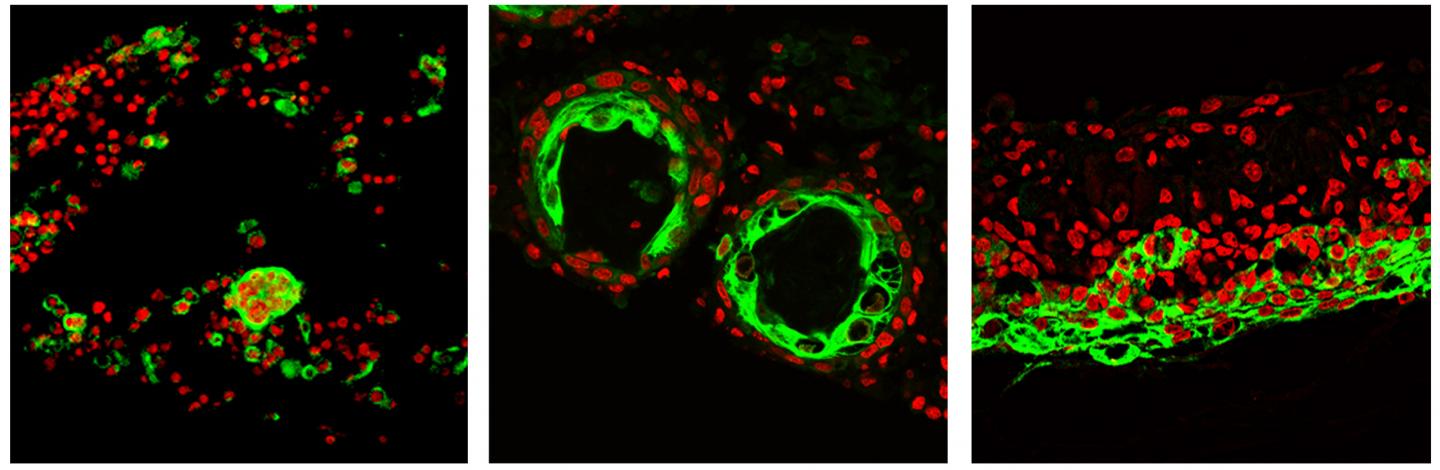
Credit: Images by Mingxing Lei/Cheng-Ming Chuong Lab
How does the skin develop follicles and eventually sprout hair? A USC-led study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), addresses this question using insights gleaned from organoids, 3D assemblies of cells possessing rudimentary skin structure and function–including the ability to grow hair.
In the study, first author Mingxing Lei, a postdoctoral scholar in the USC Stem Cell laboratory of Cheng-Ming Chuong, and an international team of scientists started with dissociated skin cells from a newborn mouse. Lei then took hundreds of timelapse movies to analyze the collective cell behavior. They observed that these cells formed organoids by transitioning through six distinct phases: 1) dissociated cells; 2) aggregated cells; 3) cysts; 4) coalesced cysts; 5) layered skin; and 6) skin with follicles, which robustly produce hair after being transplanted onto the back of a host mouse.
In contrast, dissociated skin cells from an adult mouse only reached phase 2–aggregation–before stalling in their development and failing to produce hair.
To understand the forces at play, the scientists analyzed the molecular events and physical processes that drove successful organoid formation with newborn mouse cells.
"We used a combination of bioinformatics and molecular screenings, and the core facilities at the Health Sciences Campus have facilitated my analyses," said Lei.
At various time points, they observed increased activity in genes related to: the protein collagen; the blood sugar-regulating hormone insulin; the formation of cellular sheets; the adhesion, death or differentiation of cells; and many other processes. In addition to determining which genes were active and when, the scientists also determined where in the organoid this activity took place. Next, they blocked the activity of specific genes to confirm their roles in organoid development.
By carefully studying these developmental processes, the scientists obtained a molecular "how to" guide for driving individual skin cells to self-organize into organoids that can produce hair. They then applied this "how to" guide to the stalled organoids derived from adult mouse skin cells. By providing the right molecular and genetic cues in the proper sequence, they were able to stimulate these adult organoids to continue their development and eventually produce hair. In fact, the adult organoids produced 40 percent as much hair as the newborn organoids–a significant improvement.
"Normally, many aging individuals do not grow hair well, because adult cells gradually lose their regenerative ability," said Chuong, senior author, USC Stem Cell principal investigator and professor of pathology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. "With our new findings, we are able to make adult mouse cells produce hair again. In the future, this work can inspire a strategy for stimulating hair growth in patients with conditions ranging from alopecia to baldness."
###
Additional co-authors include: Chao-Yuan Yeh, Ping Wu, Ting-Xin Jiang, and Randall Bruce Widelitz from USC; Linus J. Schumacher from the University of Oxford and Imperial College, London; Ruth E. Baker from the University of Oxford; Yung-Chi Lai from China Medical University; Wen-Tau Juan from China Medical University and Academia Sinica, Taipei; and Li Yang from Chongqing University.
Most of the experimental work was supported by U.S. federal funding from the National Institutes of Health (AR42177 and AR60306). The multi-disciplinary team members were also supported by nine non-U.S. sources: the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M590866); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (106112015CDJRC231206); Special Funding for Postdoctoral Research Projects in Chongqing (Xm2015093); the China Scholarship Council (2011605042); the Innovation and Attracting Talents Program for College and University (111 project grant B06023); the National Nature Science Foundation of China (11532004 and 31270990); the Academia Sinica Research Project on Nanoscience and Technology; the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan; and the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EP/F500394/1).
Media Contact
Zen Vuong
[email protected]
213-300-1381
@keckmedusc
Keck Home
Original Source
http://stemcell.usc.edu/2017/08/11/usc-stem-cell-scientists-obtain-how-to-guide-for-producing-hair-follicles/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700475114