In a fascinating twist in the realm of nanotechnology, researchers are delving into the potential of goji berries to pave the way for sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles. As the quest for environmentally friendly and efficient solutions to health and safety challenges continues, Kamran Alam and his team are pushing the boundaries of conventional methods. Their study, published in AIP Advances, highlights the innovative use of an organic source in producing antibacterial silver nanoparticles, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainability in scientific research.
Traditionally, the production of silver nanoparticles has heavily relied on chemical techniques, many of which pose environmental risks and complexities. However, the team at Sapienza University of Rome, alongside collaborators from King Saud University and NED University of Engineering and Technology, have introduced a green synthesis approach. This methodology leverages the inherent properties of goji berries, a popularly known health food, to produce nanoparticles that demonstrate potent antibacterial effects without the detrimental side effects associated with harsher chemical procedures.
The rationale behind using goji berries lies in their rich bioactive compounds. These compounds serve as natural reducing agents capable of transforming silver ions into nanoparticles. Unlike conventional methods that necessitate the use of toxic capping agents to stabilize nanoparticles, the biochemical makeup of goji berries fulfills this role seamlessly. This feature not only enhances safety for potential biomedical applications but also simplifies the overall production process, making it more accessible.
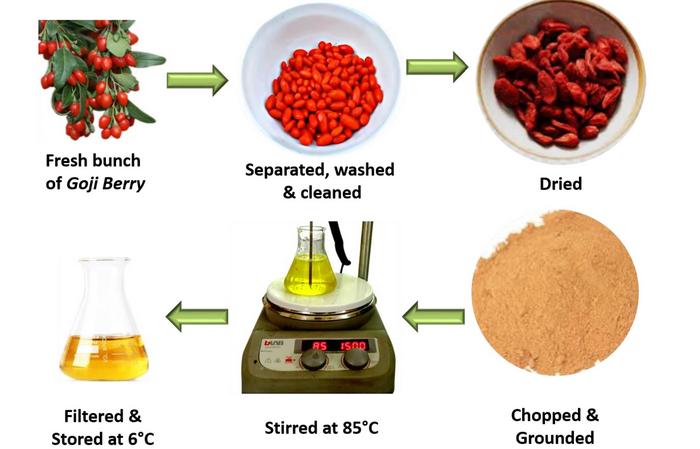
In practice, the researchers began their inquiry by sourcing common, dried goji berries. They meticulously prepared an extract through a straightforward sequence of drying and grinding, followed by filtration. This extract was then integrated with silver nitrate, allowing a reduction reaction to occur, which resulted in the formation of silver nanoparticles. This simple yet effective process is already garnering attention in circles dedicated to sustainable practices.
Alam’s research further illuminates the mechanisms behind the antibacterial properties of the synthesized nanoparticles. Silver nanoparticles possess inherent properties that allow them to disrupt bacterial cell membranes. This destabilization generates reactive oxygen species, which play a crucial role in hindering bacterial proliferation, thereby illustrating the therapeutic potential of these nanoparticles in addressing microbial infections.
One enticing aspect of this study is that it employs standard microscopy and advanced visualization techniques, such as X-ray diffraction and Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy, to analyze the structural characteristics of the synthesized nanoparticles. These techniques not only confirmed their existence but also provided insight into their size distribution and morphological attributes. Furthermore, through rigorous testing against Staphylococcus aureus—a common and dangerous pathogen—the team successfully demonstrated that the silver nanoparticles exhibit strong antibacterial activity.
Looking ahead, Alam envisions an expansive horizon for his research. One of his key goals is to investigate the cellular toxicity and biocompatibility of these silver nanoparticles. This crucial step will help ascertain the safety and efficacy of using these organic-based nanoparticles in medical applications, particularly in wound healing and as agents against various infections, thus potentially revolutionizing current therapeutic strategies.
In a landscape increasingly dominated by complex and costly processes, this approach to nanoparticle synthesis serves as a refreshing perspective on the possibilities presented by nature. The ability to harvest valuable materials from readily available resources, such as goji berries, not only emphasizes environmental consciousness but also highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration to address pressing health challenges.
Moreover, Alam and his team’s method embodies the principles of green chemistry, aiming to minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and ensure safety in the production process. By demonstrating that it is feasible to create effective antibacterial agents from natural sources, the researchers lend credibility to the broader movement advocating for sustainable scientific practices. This aligns perfectly with the current scientific zeitgeist, where eco-friendly innovations are paramount.
The path forward for the application of goji berry-derived silver nanoparticles is as promising as it is exciting. As the research team continues to explore the biocompatibility, efficacy in various medical domains, and potential scaling for industrial use, the scientific community eagerly awaits the results. The overarching goal remains clear: to integrate these findings into practical applications that could significantly enhance public health and ultimately contribute to a more sustainable future.
By bridging the gap between traditional knowledge of medicinal plants and modern scientific capabilities, Alam’s work stands as a testament to the innovative possibilities that arise from examining everyday resources. As we move towards an increasingly challenging future, embracing such forward-thinking approaches will be essential in navigating the complexities of health, sustainability, and scientific progress.
Nonetheless, while the research holds great potential, continued scrutiny through rigorous peer evaluation and validation in diverse environments will remain a critical aspect of ensuring success. The exploration of various methods and the application of nanotechnology in enhancing human health will likely be one of the most exciting frontiers of scientific inquiry in the years to come. This pioneering study on goji berries and silver nanoparticles is merely the beginning of what promises to be a transformative journey.
Subject of Research: Antibacterial silver nanoparticles synthesis using goji berries
Article Title: Ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using metallic solution-based goji berry extract for their antibacterial properties
News Publication Date: Jan. 7, 2025
Web References: AIP Advances
References: Kamran Alam et al., Ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using metallic solution-based goji berry extract for their antibacterial properties
Image Credits: Kamran Alam et al.
Keywords: Silver nanoparticles, goji berries, green synthesis, antibacterial agents, biocompatibility, sustainable materials, antimicrobial properties, nanotechnology, silver nitrate, cellular toxicity.