Credit: ICIQ
- A team of researchers at ICIQ in Tarragona (Spain) and Oregon State University (US) combine experimental and computational strategies to understand the secrets behind the crystallization of unprecedented chromium polycations.
- This is the first time ICIQ will publish a paper in the prestigious journal Chem, a division of Cell Press (http://www.cell.com/chem/home).
- Natural phenomena like photosynthesis, contaminant transport and mineral growth rely on the formation of metal-oxide clusters. Discovering how these clusters crystallize could lead to a better understanding of nature and inspire new biomimetic materials.
- Research was funded by the US National Science Foundation and the Spanish Severo Ochoa Excellence Programme.
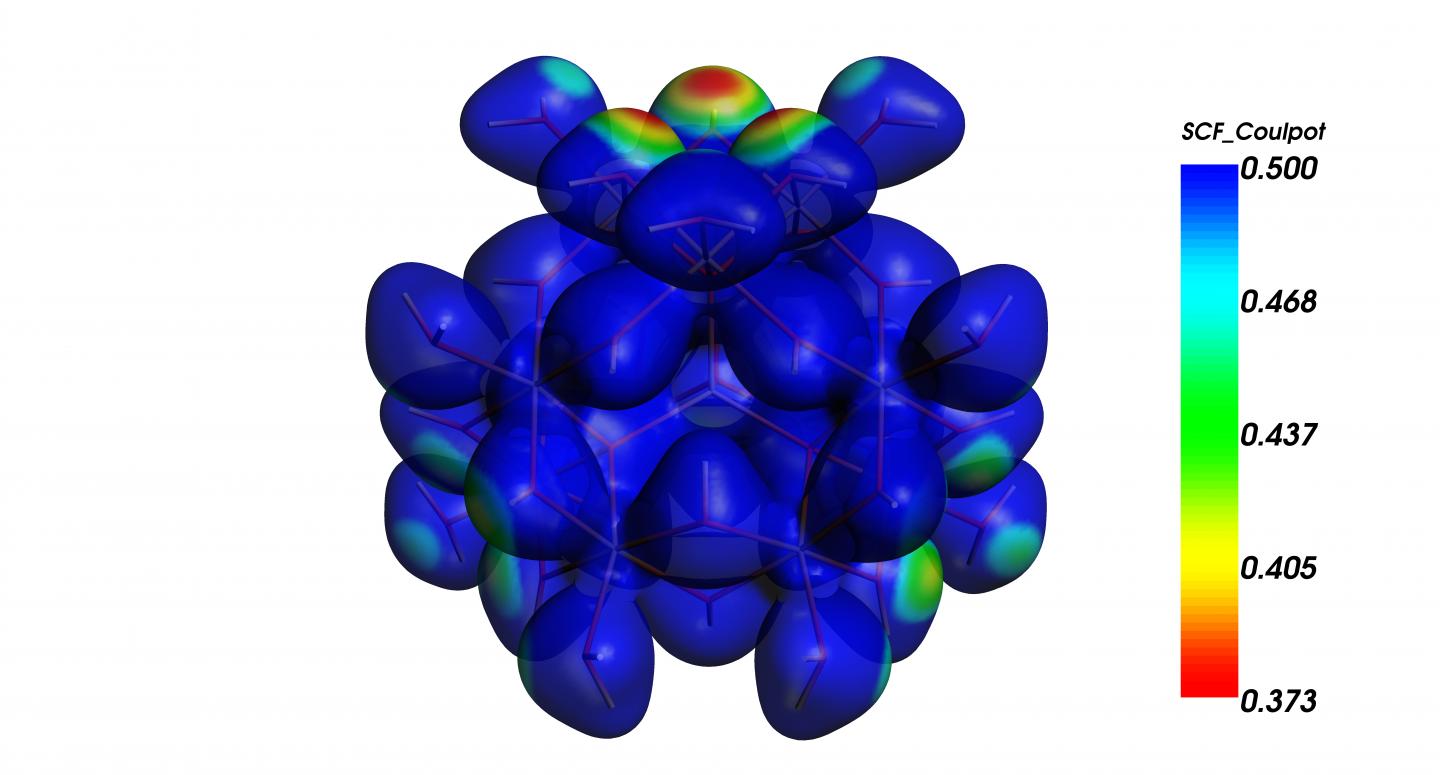
Scientists at ICIQ (Tarragona, Spain) and OSU (Oregon, US) created a new method to prepare chromium polyoxocations that, to date, represented a huge synthetic challenge. Analyzing a myriad of conditions and using all kind of state of the art techniques, researchers managed to understand and control the formation of chromium clusters.
Carles Bo, group leader at ICIQ, led the team that carried out the computational studies. These numerical experimentsconsidered all combinations, almost a thousand distinct structures, to explain the apparent disorder of the crystallographic sites and what conditions favour the formation of metallic clusters.
These findings will contribute to expand the understanding of crystallization of metal-oxide clusters and polycations. Such structures are key to many natural phenomena -photosynthesis, mineral growth- and industrial processes in material science.
###
Reference
"Crystallizing elusive chromium polycations." W. Wang, L.B. Fullmer, N.A.G. Bandeira, S. Goberna-Ferrón, L.N. Zakharov, C. Bo, D.A. Keszler and M. Nyman. Chem, 2016, DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2016.11.006
Embargoed URL: http://www.cell.com/chem/fulltext/S2451-9294(16)30233-9
Media Contact
Fernando Gomollón-Bel
[email protected]
34-977-920-200 x370
@ICIQchem
http://www.iciq.es/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag