Credit: Virginia Tech
A new machine learning approach offers important insights into catalysis, a fundamental process that makes it possible to reduce the emission of toxic exhaust gases or produce essential materials like fabric.
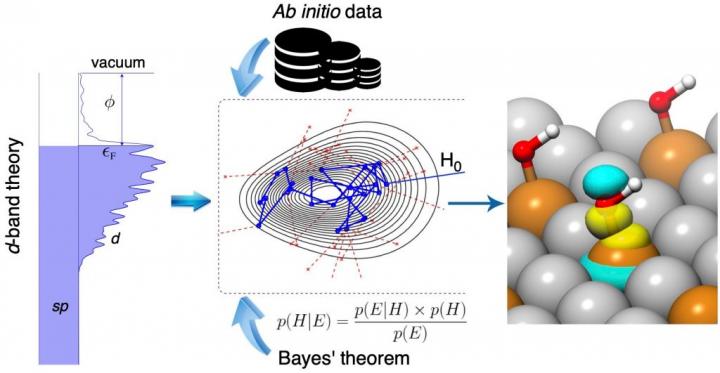
In a report published in Nature Communications, Hongliang Xin, associate professor of chemical engineering at Virginia Tech, and his team of researchers developed a Bayesian learning model of chemisorption, or Bayeschem for short, aiming to use artificial intelligence to unlock the nature of chemical bonding at catalyst surfaces.
“It all comes down to how catalysts bind with molecules,” said Xin. “The interaction has to be strong enough to break some chemical bonds at reasonably low temperatures, but not too strong that catalysts would be poisoned by reaction intermediates. This rule is known as the Sabatier principle in catalysis.”
Understanding how catalysts interact with different intermediates and determining how to control their bond strengths so that they are within that “goldilocks zone” is the key to designing efficient catalytic processes, Xin said. The research provides a tool for that purpose.
Bayeschem works using Bayesian learning, a specific machine learning algorithm for inferring models from data. “Suppose you have a domain model based on well-established physical laws, and you want to use it to make predictions or learn something new about the world,” explained Siwen Wang, a former chemical engineering doctoral student. “The Bayesian approach is to learn the distribution of model parameters given our prior knowledge and the observed, often scarce, data, while providing uncertainty quantification of model predictions.”
The d-band theory of chemisorption used in Bayeschem is a theory describing chemical bonding at solid surfaces involving d-electrons that are usually shaped like a four-leaf clover. The model explains how d-orbitals of catalyst atoms are overlapping and attracted to adsorbate valence orbitals that have a spherical or dumbbell-like shape. It has been considered the standard model in heterogeneous catalysis since its development by Hammer and Nørskov in the 1990s, and though it has been successful in explaining bonding trends of many systems, Xin said the model fails at times due to the intrinsic complexity of electronic interactions.
According to Xin, Bayeschem brings the d-band theory to a new level for quantifying those interaction strengths and possibly tailoring some knobs, such as structure and composition, to design better materials. The approach advances the d-band theory of chemisorption by extending its prediction and interpretation capabilities of adsorption properties, both of which are crucial in catalyst discovery. However, compared with the black-box machine learning models that are trained by large amounts of data, the prediction accuracy of Bayeschem is still amenable to improvement, said Hemanth Pillai, a chemical engineering doctoral student in Xin’s group who contributed equally to the study.
“The opportunity to come up with highly accurate and interpretable models that build on deep learning algorithms and the theory of chemisorption is highly rewarding for achieving the goals of artificial intelligence in catalysis,” said Xin.
###
Media Contact
Suzanne Irby
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




