Researchers from the University of Konstanz’s CRC 1214 ‘Anisotropic Particles as Building Blocks: Tailoring Shape, Interactions and Structures’ generate uniform-shape nanocrystals using direct polymerization
Credit: Stefan Mecking and Manuel Schnitte
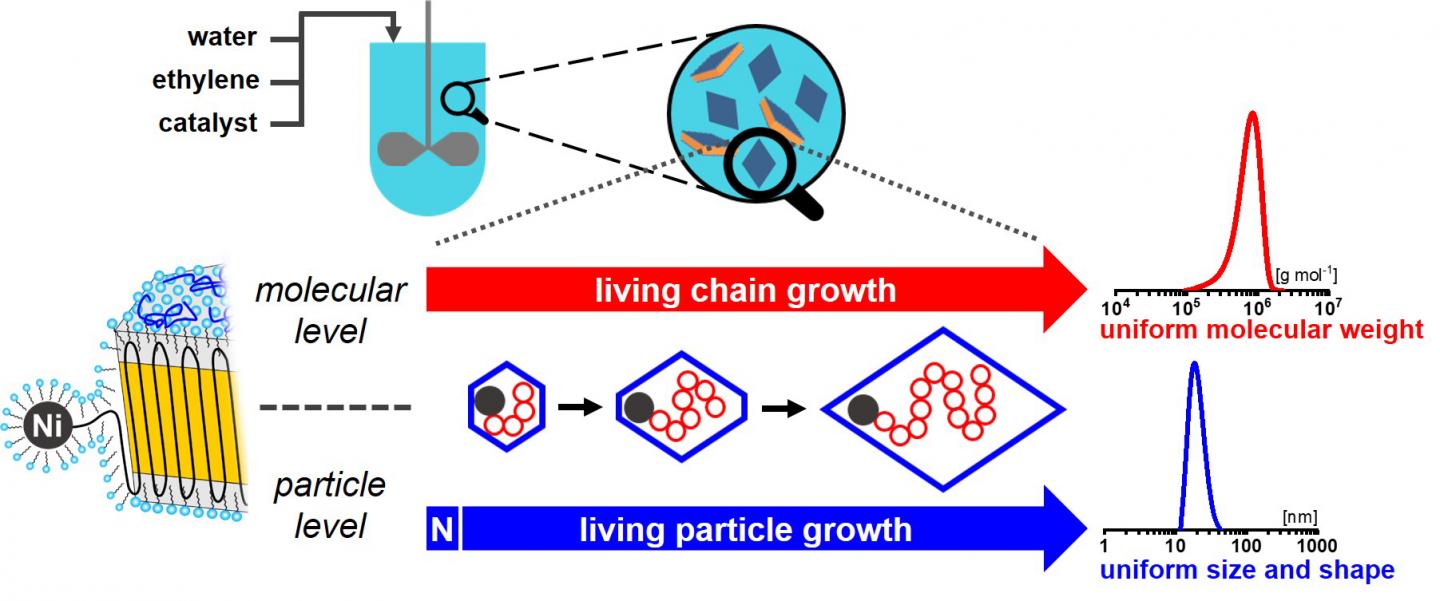
A team of researchers from the University of Konstanz’s CRC 1214 “Anisotropic Particles as Building Blocks: Tailoring Shape, Interactions and Structures”, which has been funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) since 2016, has demonstrated a new aqueous polymerization procedure for generating polymer nanoparticles with a single chain and uniform shape, which, as another difference to previous methods, involves high particle concentrations. A corresponding paper entitled “Uniform shape monodisperse single chain nanocrystals by living aqueous catalytic polymerization” is due for open access online publication in Nature Communications on 13.06.2019.
Nanoparticles are the building blocks for envisioned nanoparticle-based materials with yet unachieved optical, electronic and mechanical properties. To build nanomaterials, nanoparticles with uniform shapes and sizes are required. While inorganic metal or metal oxide nanoparticles suitable for assembly can be generated in a variety of shapes, it has been very difficult until now to manufacture polymer nanoparticles in shapes other than spheres, as Stefan Mecking, Professor of Chemical Materials Science at the University of Konstanz’s Department of Chemistry and Vice Speaker of CRC 1214, points out: “In previous approaches, single-chain particles were prepared by post-polymerization collapse or assembled from solutions of separately synthesized chains. What we have managed to do is to demonstrate direct polymerization to single-chain uniform-shape monodisperse nanocrystals for polyethylene, which is the largest and most important synthetic polymer material”.
One major challenge associated with this approach is to achieve living chain and particle growth that can be sustained for several hours and up to very high molecular weights, ideally yielding single-chain nanocrystals of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. To achieve this, the researchers developed advanced catalysts. “We then conducted a series of pressure reactor tests to identify ideal conditions for maintaining catalytic activity over longer periods of time and to gain insights into the chain and particle growth process”, explains Mecking. “In addition to the novel catalysts, control of the colloidal state of the reaction mixture is another key element in obtaining the desired aqueous particle dispersions”.
In contrast to many post-polymerization procedures, the aqueous polymerization procedure elaborated by Stefan Mecking and his team yields high particle number densities, which are comparable to commercial polymer dispersions used for coatings, paints and other applications. Using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), the researchers were able to confirm that the particles thus generated are composed of a single chain, display a uniform shape and size distribution and do not aggregate. “While our assemblies may not fully match the extensively optimized assemblies of inorganic nanoparticles, they seem to be very promising”, concludes Mecking. “In time, our insights into the creation of anisotropic polymer nanocrystals using aqueous catalytic polymerization may enable us to create polymer materials based on nanoparticle assembly”.
###
Facts:
- – Original publication: Manuel Schnitte, Anne Staiger, Larissa A. Casper, Stefan Mecking. Uniform shape monodisperse single chain nanocrystals by living aqueous catalytic polymerization. Nature Communications, 13.06.2019. DOI: https:/
– Team of University of Konstanz researchers led by Professor Stefan Mecking from the Department of Chemistry successfully demonstrates a new aqueous catalytic polymerization procedure for generating anisotropic nanocrystals with uniform shape and size
– Solution to the unresolved problem of uniform particle shape and size in the preparation of polymer nanoparticles
– Tests confirm the nanocrystals’ potential for assembly
– Part of the research carried out by the Konstanz-based Collaborative Research Centre 1214 “Anisotropic Particles as Building Blocks: Tailoring Shape, Interactions and Structures”, funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) since 2016
Note to editors:
An image is available for download here: https:/
Caption: Concept to obtain uniform size and shape particles by controlled polymerization on a molecular as well as particle level. An effective nucleation (N) ensures that particles contain only one active site, and start to grow virtually at the same time. Due to the living character of polymerization, all particles continue to grow for the entire duration of the experiment, to yield particles each composed of a chain of identical length. As the growing chains are immediately deposited on the growing single-crystal particle during this process, particle shape evolves uniformly over time during polymerization
Copyright: Stefan Mecking and Manuel Schnitte
Contact:
University of Konstanz
Communications and Marketing
Phone: + 49 7531 88-3603
Email: [email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




