Credit: Gang Huang
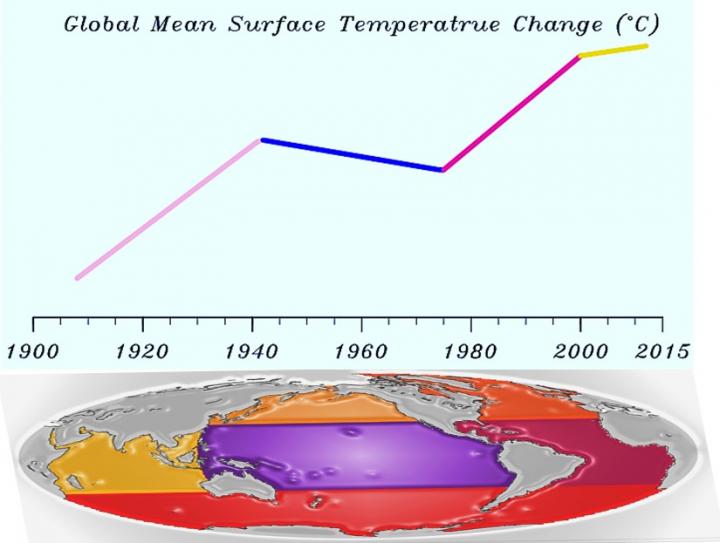
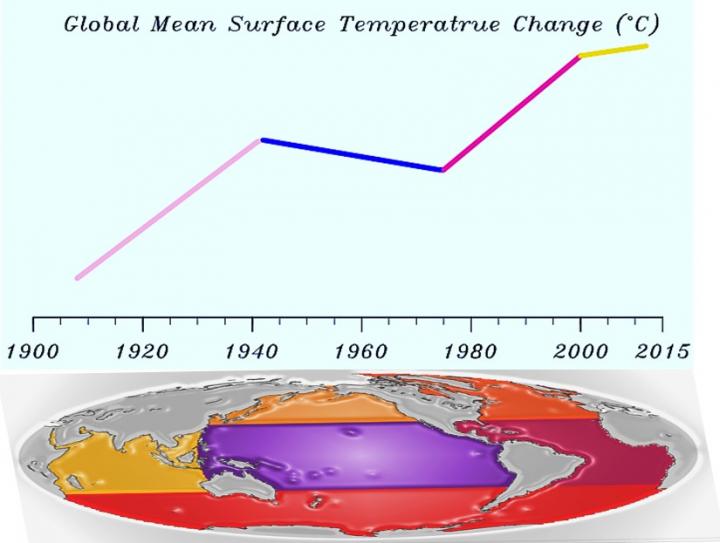
A long-standing mystery is that, despite the persistently increased greenhouse gases emissions throughout the twentieth and early twenty-first centuries, the globally-averaged surface temperature has shown distinct multi-decadal fluctuations since 1900, including two weak global warming slowdowns in the mid-twentieth century and early twenty-first century and two strong global warming accelerations in the early and late twentieth century. The multi-decadal global warming rate changes are primarily attributed to multiple ocean surface temperature changes, according to research by Institute of Atmospheric Physics and Australian Bureau of Meteorology?and It is the net impact of multiple ocean surface temperature changes, rather than a single ocean basin change, that plays a main driver for the multi-decadal global warming accelerations and slowdowns. Understanding and quantifying the respective role of individual ocean basin in the multi-decadal global warming accelerations and slowdowns, under the forcing of the sustained increase in atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations, could help achieve a more accurate estimate of the future global warming rate to better meet the global warming target of the Paris Conference reached in December 2015–no more than 1.5ºC above pre-industrial levels by 2100.
The new finding of the importance of multiple ocean surface temperature changes to the multi-decadal global warming accelerations and slowdowns is supported by a set of computer modeling experiments, in which observed sea surface temperature changes are specified in individual ocean basins, separately. The results are published in "Distinct global warming rates tied to multiple ocean surface temperature changes", in the June 12 online issue of Nature Climate Change.
"Our results identify multiple ocean surface temperature change as a major driver for global mean surface temperature changes on multi-decadal timescales. The paramount importance of multiple ocean basins in determining the global warming rates provides a new insight to improving global and regional climate projections." states the corresponding author Gang Huang from Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
"The results elucidate the relative contributions of individual ocean surface temperature changes to the multi-decadal global warming rate changes, and could help improve our understanding of global warming fluctuations under steadily increased emissions of atmospheric greenhouse gases." says Jing-Jia Luo, the corresponding author of the study and climate scientist at the Bureau of Meteorology in Australia. "It reveals a fact that we need to explore climate change in a more global perspective. This could stimulate an integrated strategy and coordinated effort toward understanding the causes of regional ocean changes."
"Our study provides a novel perspective for understanding and projecting individual ocean basin's impacts on global warming," explains co-author Dr. Shuai-Lei Yao from CAS Institute of Atmospheric Physics. "While the tropical Pacific was generally regarded as a key contributor to the multi-decadal global warming rate changes, other ocean basins, including the Indian Ocean, the Atlantic and the Southern Ocean, also exert important effects. "
###
Media Contact
Zheng Lin
[email protected]
86-108-299-5053
@aasjournal
http://english.iap.cas.cn/
Original Source
https://www.nature.com/nclimate/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nclimate3304.html http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3304
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag