Credit: KAIST
KAIST researchers have reported the detection of a picosecond electron motion in a silicon transistor. This study has presented a new protocol for measuring ultrafast electronic dynamics in an effective time-resolved fashion of picosecond resolution. The detection was made in collaboration with Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corp. (NTT) in Japan and National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the UK and is the first report to the best of our knowledge.
When an electron is captured in a nanoscale trap in solids, its quantum mechanical wave function can exhibit spatial oscillation at sub-terahertz frequencies. Time-resolved detection of such picosecond dynamics of quantum waves is important, as the detection provides a way of understanding the quantum behavior of electrons in nano-electronics. It also applies to quantum information technologies such as the ultrafast quantum-bit operation of quantum computing and high-sensitivity electromagnetic-field sensing. However, detecting picosecond dynamics has been a challenge since the sub-terahertz scale is far beyond the latest bandwidth measurement tools.
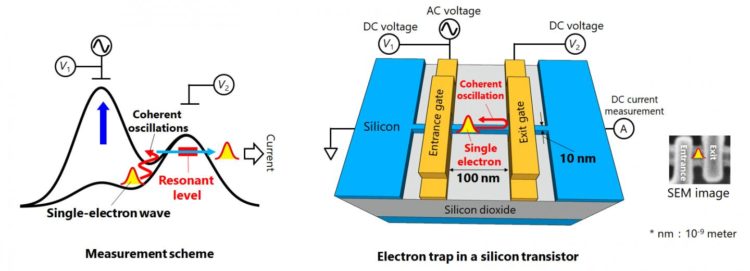
A KAIST team led by Professor Heung-Sun Sim developed a theory of ultrafast electron dynamics in a nanoscale trap, and proposed a scheme for detecting the dynamics, which utilizes a quantum-mechanical resonant state formed beside the trap. The coupling between the electron dynamics and the resonant state is switched on and off at a picosecond so that information on the dynamics is read out on the electric current being generated when the coupling is switched on.
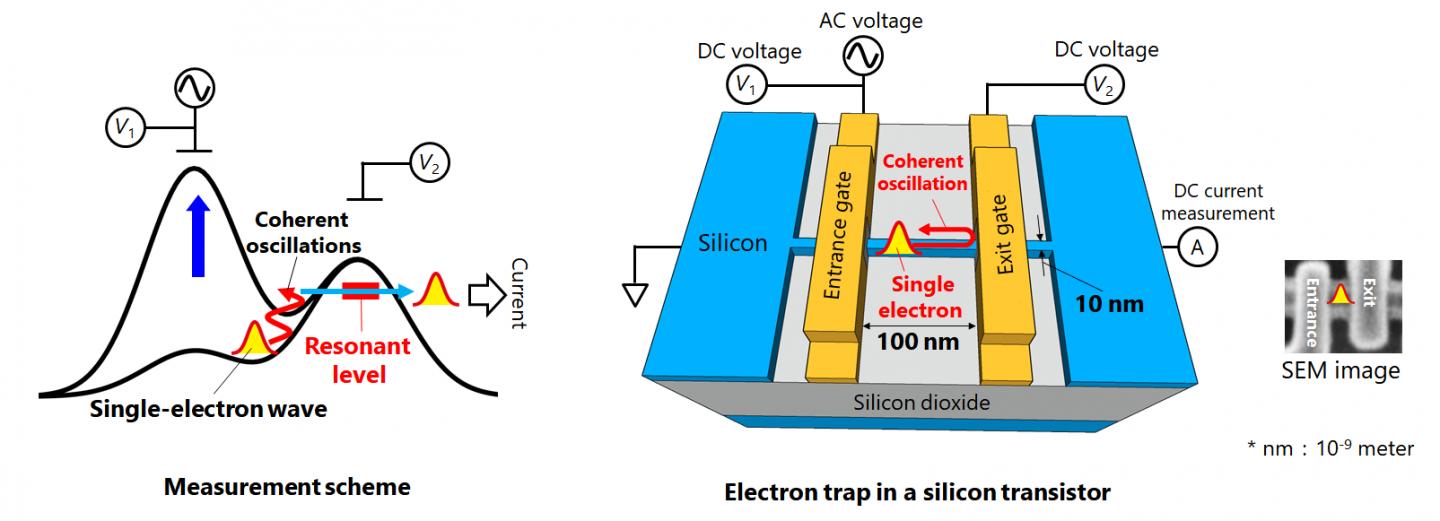
NTT realized, together with NPL, the detection scheme and applied it to electron motions in a nanoscale trap formed in a silicon transistor. A single electron was captured in the trap by controlling electrostatic gates, and a resonant state was formed in the potential barrier of the trap.
The switching on and off of the coupling between the electron and the resonant state was achieved by aligning the resonance energy with the energy of the electron within a picosecond. An electric current from the trap through the resonant state to an electrode was measured at only a few Kelvin degrees, unveiling the spatial quantum-coherent oscillation of the electron with 250 GHz frequency inside the trap.
Professor Sim said, “This work suggests a scheme of detecting picosecond electron motions in submicron scales by utilizing quantum resonance. It will be useful in dynamical control of quantum mechanical electron waves for various purposes in nano-electronics, quantum sensing, and quantum information”.
###
This work was published online at Nature Nanotechnology on November 4. It was partly supported by the Korea National Research Foundation through the SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matter. (END)
Profile: Prof. Heung-Sun Sim
[email protected]
https:/
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon 34141, Korea
About KAIST
KAIST is the first and top science and technology university in Korea. KAIST was established in 1971 by the Korean government to educate scientists and engineers committed to industrialization and economic growth in Korea.
Since then, KAIST and its 61,125 graduates have been the gateway to advanced science and technology, innovation, and entrepreneurship. KAIST has emerged as one of the most innovative universities with more than 12,000 students enrolled in five colleges and seven schools including 1,000 international students from 80 countries.
On the precipice of its 50th anniversary in 2021, KAIST continues to strive to make the world better through the pursuit in education, research, entrepreneurship, and globalization.
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-52294
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.