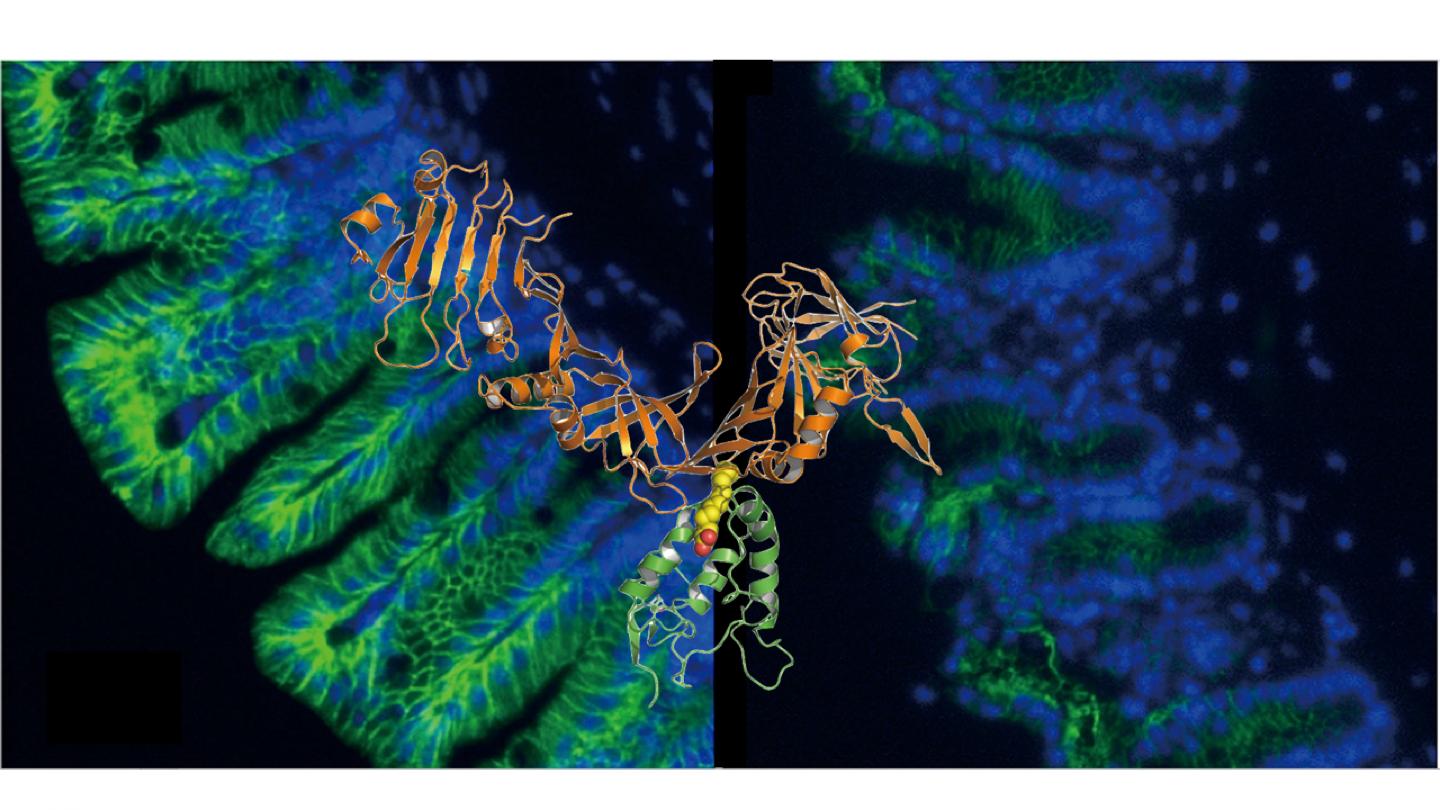
Credit: Rongsheng Jin, University of California, Irvine
Researchers from the University of California, Irvine and Harvard University have discovered how the Clostridium difficile toxin B (TcdB) recognizes the human Frizzled protein, the receptor it uses to invade intestinal cells and lead to deadly gastrointestinal infections. The findings, published today in Science, could pave the way for new C. diff antitoxins and also show potential for the development of novel anti-cancer drugs.
In a C. diff infection (CDI), TcdB targets colonic epithelia and binds to what are called Frizzled (FZD) receptors. Researchers in the labs of Rongsheng Jin, PhD, professor of physiology & biophysics from the UCI School of Medicine, and Min Dong, PhD, from Boston Children's Hospital – Harvard Medical School, found that during this binding process, the toxin locks certain lipid molecules in FZD, which block critical Wnt signaling that regulates renewal of colonic stem cells and differentiation of the colonic epithelium.
"This toxin is indeed very smart. It takes advantage of an important lipid that FZD uses for its own function, to improve its binding affinity and specificity to FZD," said Jin, "However, the need for this lipid also exposes a vulnerability of TcdB that could be exploited to develop antitoxins that block toxin-receptor recognition."
Jin and Dong believe that the novel FZD-antagonizing mechanism exploited by toxin B could be used to turn this deadly toxin into a potential pharmacological tool for research and therapeutic applications, including anti-cancer drugs.
The team's preliminary data show that a non-toxic fragment of TcdB that they identified could significantly inhibit the growth of some cancer cells with dysregulation in Wnt signaling. A patent application has been filed.
Clostridium difficile, also called "C. diff," causes severe gastrointestinal tract infections and tops the Center for Disease Control and Prevention's list of urgent drug-resistant threats. Clostridium difficile infection has become the most common cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and gastroenteritis-associated death in developed countries, accounting for half-million cases and 29,000 deaths annually in the United States. It is classified as one of the top three "urgent threats" by the CDC.
###
The research was funded with National Institute of Health grants R01AI091823, R01AI125704, and R21AI123920 to Jin, and R01 NS080833 and R01 AI132387 to Dong.
About the UCI School of Medicine
Each year, the UCI School of Medicine educates more than 400 medical students, as well as 200 doctoral and master's students. More than 600 residents and fellows are trained at UC Irvine Medical Center and affiliated institutions. The UCI School of Medicine offers an MD degree, a dual MD/PhD medical scientist training program, PhDs and master's degrees in anatomy and neurobiology, biomedical sciences, genetic counseling, epidemiology, environmental health sciences, pathology, pharmacology, physiology and biophysics, and translational sciences. Medical students also may pursue an MD/MBA program, a combined MD/Master's in Public Health or a dual MD/master's program called the Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community (PRIME-LC). UCI School of Medicine is accredited by Liaison Committee on Medical Accreditation (LCME), and ranks among the top 50 nationwide for research. For more information, visit: som.uci.edu.
About the University of California, Irvine
Founded in 1965, UCI is the youngest member of the prestigious Association of American Universities. The campus has produced three Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UCI has more than 30,000 students and offers 192 degree programs. Located in one of the world's safest and most economically vibrant communities, UCI is Orange County's second-largest employer, contributing $5 billion annually to the local economy. For more on UCI, visit http://www.uci.edu.
Media Contact
John Murray
[email protected]
310-433-8809
@UCIrvine
http://www.uci.edu
Original Source
http://www.ucirvinehealth.org/news/2018/05/uci-health-research-may-help-combat-deadly-gastrointestinal-infection