Credit: University of British Columbia
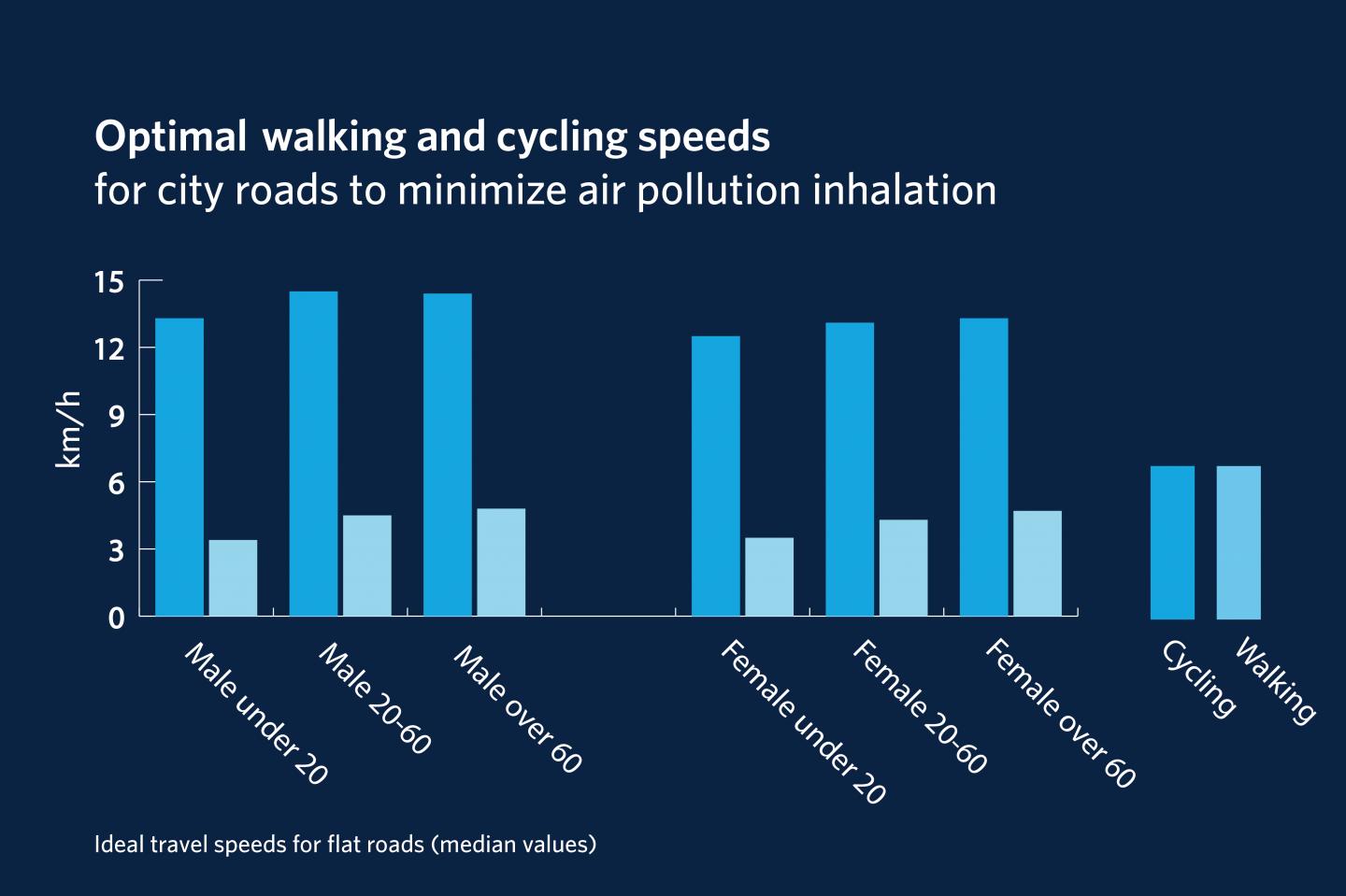
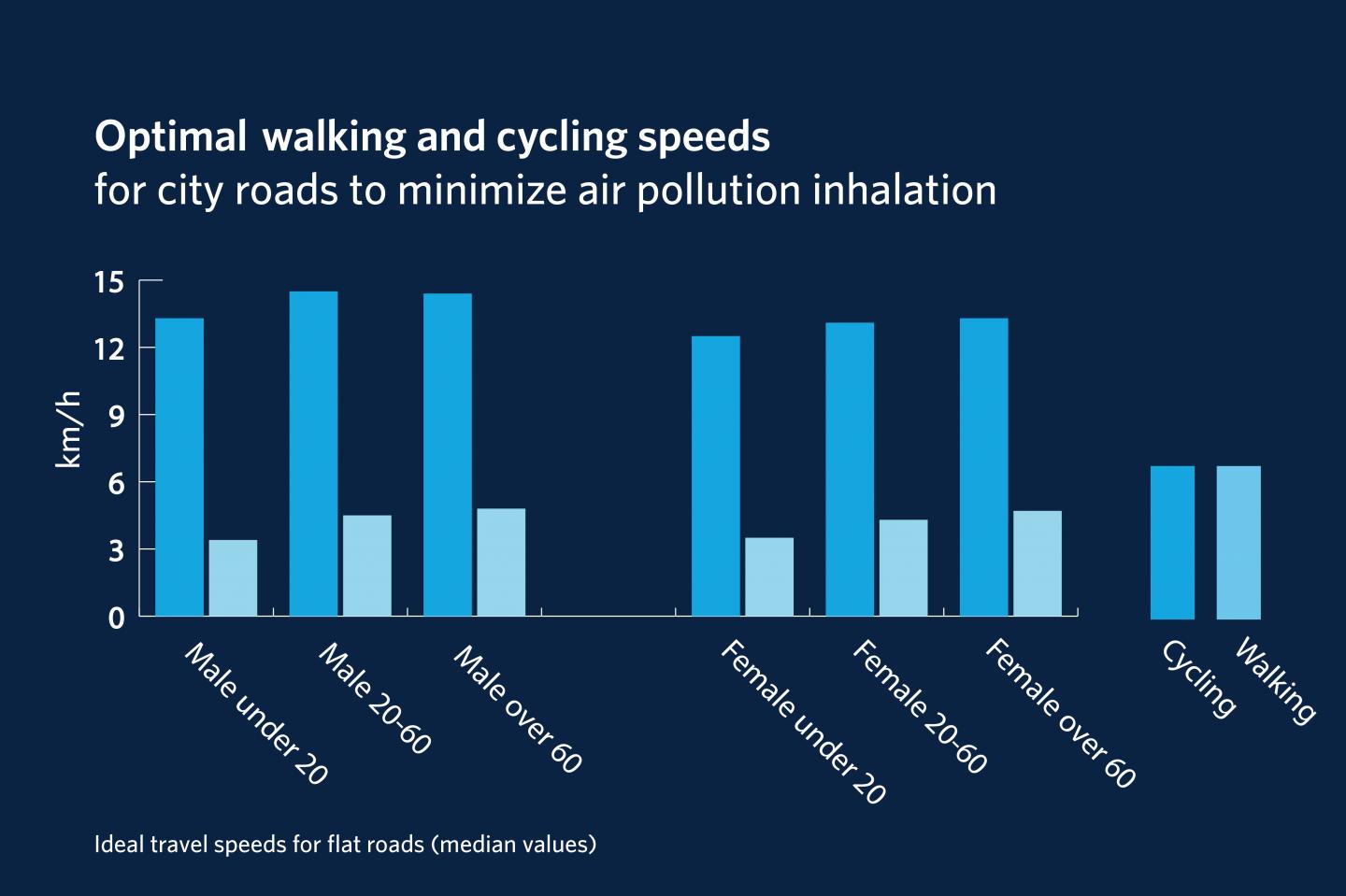
Cyclists should be riding at speeds between 12 and 20 kilometres per hour on city roads, while pedestrians should be moving at two to six kilometres per hour to minimize their inhalation of air pollution while still getting the health benefits of exercise, according to new UBC research.
"The faster you move, the harder you breathe and the more pollution you could potentially inhale, but you also are exposed to traffic for a shorter period of time. This analysis shows where the sweet spot is," said Alex Bigazzi, a UBC transportation expert in the department of civil engineering and school of community and regional planning who conducted this analysis.
Using a U.S. Census-based computer model of 10,000 people, Bigazzi calculated ideal travel speeds that he calls the minimum-dose speeds (MDS) for different age and sex groups. For female cyclists under 20, the ideal speed linked to the least pollution risk is 12.5 kilometres per hour on average on a flat road. For male cyclists in the same age group, it's 13.3 kilometres per hour. Ideal travel speeds were at 13 and 15 kilometres per hour for female and male cyclists in the 20-60 age group.
Female and male pedestrians under 20 years old should be walking at speeds around three kilometres per hour, while their older counterparts should look at reaching at least four kilometres per hour, to breathe in the least amount of pollution over a trip. Bigazzi also computed these ideal travel speeds for other road grades.
"If you move at much faster speeds than the MDS–say, cycling around 10 kilometres faster than the optimal range–your inhalation of air pollution is significantly higher," said Bigazzi. "The good news is, the MDS numbers align pretty closely with how fast most people actually travel."
The findings, which build on Bigazzi's recent research on the high amounts of toxic chemicals absorbed by cyclists on busy city streets, are described in a paper published recently in the International Journal of Sustainable Transportation.
Future research will validate the minimum-dose speed estimates with on-road data.
###
Media Contact
Lou Corpuz-Bosshart
[email protected]
604-999-0473
@UBCnews
http://www.ubc.ca