Type 2 diabetes alters the behavior of discs in the vertebral column, making them stiffer, and also causes the discs to change shape earlier than normal. As a result, the disc’s ability to withstand pressure is compromised. This is one of the findings of a new study in rodents from a team of engineers and physicians from the University of California San Diego, UC Davis, UCSF and the University of Utah.
Credit: University of California/University of Utah
Type 2 diabetes alters the behavior of discs in the vertebral column, making them stiffer, and also causes the discs to change shape earlier than normal. As a result, the disc’s ability to withstand pressure is compromised. This is one of the findings of a new study in rodents from a team of engineers and physicians from the University of California San Diego, UC Davis, UCSF and the University of Utah.
Low back pain is a major cause of disability, often associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. People with Type 2 diabetes face a higher risk of low back pain and disc-related issues. Yet the precise mechanisms of disc degeneration remain unclear.
Investigating the biomechanical properties of the intervertebral disc is crucial for understanding the disease and developing effective strategies for managing low back pain. The research team was co-led by Claire Acevedo, a faculty member in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the University of California San Diego, and Aaron Fields, faculty in the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery at UC San Francisco.
“These findings provide novel insight into the potential mechanisms underlying diabetes-related disc tissue damage and may inform the development of preventative and therapeutic strategies for this debilitating condition,” the researchers write.
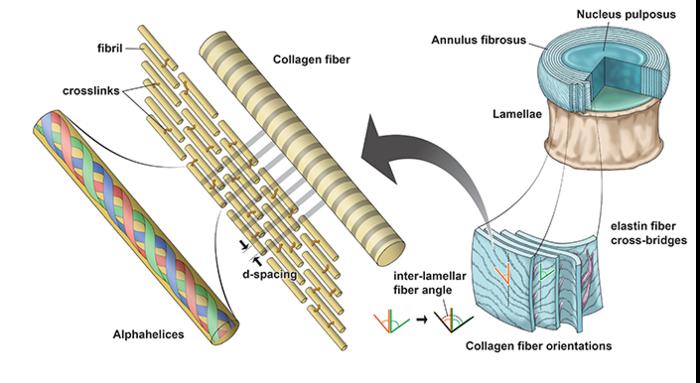
The study emphasizes that nanoscale deformation mechanisms of collagen fibrils accommodate compressive loading of the intervertebral disc. In the context of type 2 diabetes, these mechanisms are compromised, resulting in collagen embrittlement. These findings provide novel insight into the potential mechanisms underlying diabetes-related disc tissue damage and may inform the development of preventative and therapeutic strategies for this debilitating condition.
Researchers employed synchrotron small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS), an experimental technique that looks at collagen fibril deformation and orientation at the nanoscale. They wanted to explore how alterations in collagen behavior contribute to changes in the disc’s ability to withstand compression.
They compared discs from healthy rats to those from rats with Type 2 diabetes (UC Davis rat model). The healthy rats showed that collagen fibrils rotate and stretch when discs are compressed, allowing the disc to dissipate energy effectively.
“In diabetic rats, the way vertebral discs dissipate energy under compression is significantly impaired: diabetes reduces the rotation and stretching of collagen fibrils, indicating a compromised ability to handle pressure,” the researchers write.
Further analysis showed that the discs from diabetic rats exhibited a stiffening of collagen fibrils, with a higher concentration of non-enzymatic cross-links. This increase in collagen cross-linking, induced by hyperglycemia, limited plastic deformations via fibrillar sliding. These findings highlight that fibril reorientation, straightening, stretching, and sliding are crucial mechanisms facilitating whole-disc compression. Type 2 diabetes disrupts these efficient deformation mechanisms, leading to altered whole-disc biomechanics and a more brittle (low-energy) behavior.
The team published their findings in the December 2023 issue of PNAS Nexus.
This research was supported by the Research Allocation Committee at UCSF (A.J.F.), the Core Center for Musculoskeletal Biology and Medicine at UCSF (A.J.F.), the University of California Office of the President (P.J.H.), the National Institutes of Health (R01 DK095980, R01 HL107256, R01 HL121324, P30 AR066262, R01 AR070198), the University of Utah (J.L.R.), and the Advanced Light Source (ALS07392; T.N.A., C.A.).
Type 2 diabetes impairs annulus fibrosus fiber deformation and rotation under disc compression in the University of California Davis type 2 diabetes mellitus (UCD-T2DM) rat model
Claire Acevedo Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, University of California San Diego and James L. Rosenberg Departments of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, University of Utah
Eric Schaible Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory
Alan Bostrom Ann A. Lazar Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of California San Francisco
James L. Graham Department of Molecular Biosciences and Department of Nutrition
Robert O. Ritchie Materials Science Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of California, Berkeley
Aaron J. Fields, Jeffrey C. Lotz, Tamara N. Alliston Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California, San Francisco
*To whom correspondence should be addressed: Email: [email protected](C.A.); [email protected](A.J.F.)
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Type 2 diabetes impairs annulus fibrosus fiber deformation and rotation under disc compression in the University of California Davis type 2 diabetes mellitus (UCD-T2DM) rat model
Article Publication Date
1-Dec-2023




