Researchers at University of Tsukuba clarify the molecular mechanisms involved in the early stage of lung cancer, and identify two drugs with other clinical uses that could also be applied effectively in this disease
Credit: University of Tsukuba
Tsukuba, Japan – Lung adenocarcinoma is the most common type of lung cancer. Although various targeted drugs have been developed to treat it, they do not markedly improve the survival of patients. Part of the explanation for this impasse is a poor understanding of the molecular causes of this disease during the early stages.
A new study reported in the journal Clinical Cancer Research has raised hopes in this field by revealing how a cancer-promoting protein called stratifin causes lung adenocarcinoma to emerge. This finding by researchers at University of Tsukuba also enabled the identification of two drugs, currently used for treating other health conditions, which are promising for treating this type of lung cancer.
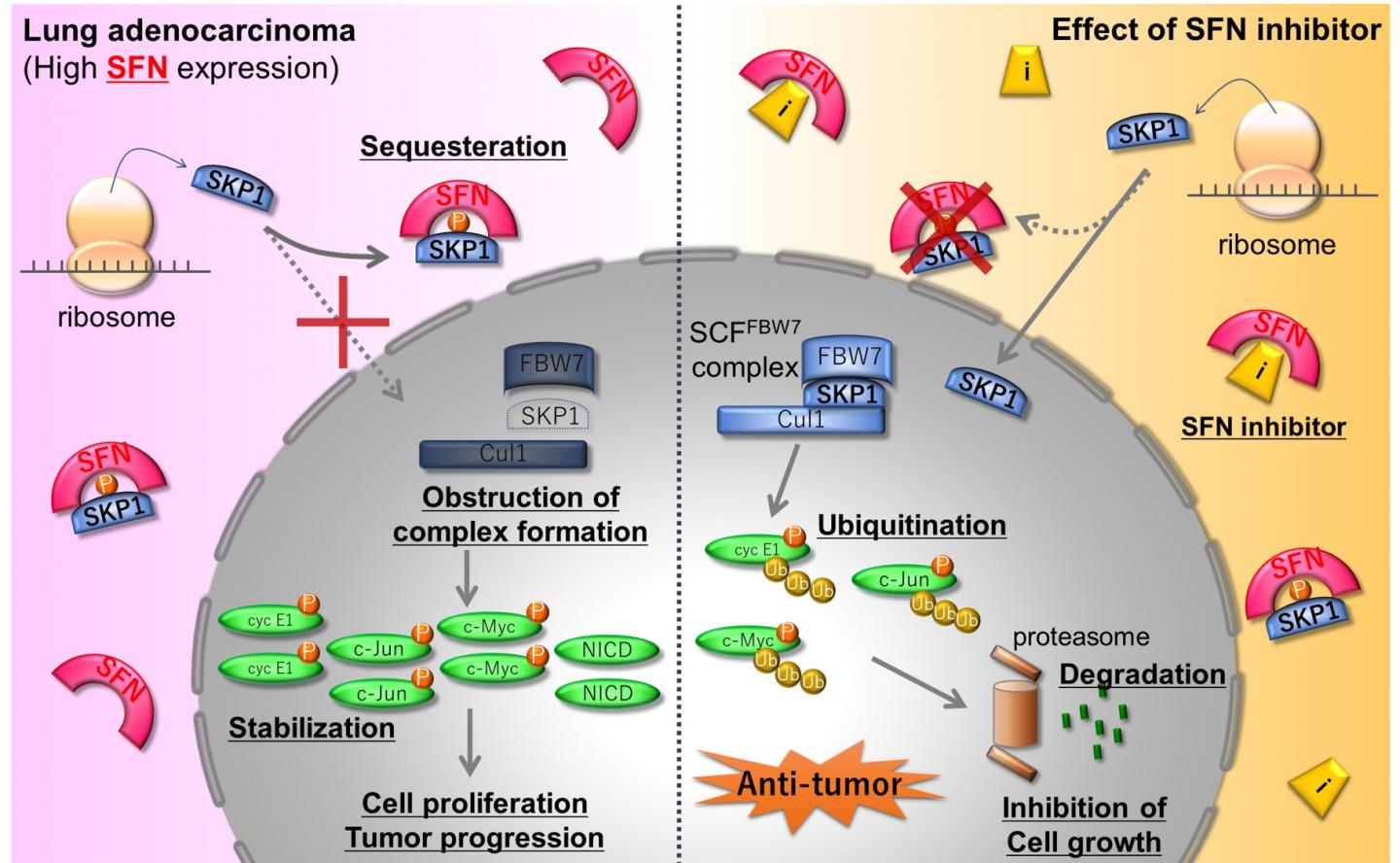
Building on previous work, the team analyzed how and when stratifin binds to SKP1. SKP1 is one component of a larger cellular complex that normally labels molecules in a process called ubiquitination, which condemns these labeled molecules to degradation. The researchers showed that a reversible modification of SKP1 promotes its binding to stratifin, rather than its typical inclusion within the ubiquitination-related complex.
“We used the overexpression of stratifin as well as its blocking by siRNA to clarify the effects on SKP1 in a lung adenocarcinoma cell line,” Masayuki Noguchi says. “The blocking of stratifin meant that SKP1 remained stable and could function in promoting the ubiquitination of errant proteins, some of which could be cancerous if not degraded by this process.”
Based on these findings, the team then undertook computer-based drug screening to find plausible candidates that could inhibit stratifin and prevent its binding to SKP1 and consequent disruption of ubiquitination. This screening of a database of drugs already in clinical use identified four promising candidates that were then narrowed down to two after testing their efficacy on lung cancer cells.
“We then performed additional testing of these two drugs on mice that had been injected with lung cancer cells,” lead author Aya Shiba-Ishii says. “We administered each of these drugs either the day after this injection or once tumor establishment had been confirmed. Our findings showed their success at blocking tumor formation or stopping or reversing the progression of tumors once they had formed.”
This novel approach of focusing on epigenetic changes early in adenocarcinogenesis raises hopes about more powerful tools to treat this condition. This work also shows the value of drug repositioning for lung cancer, given that such drugs have already passed through clinical trials and had their safety in humans confirmed.
###
Media Contact
Masataka Watanabe
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




