Transition metal selenides have been considered to be a good choice for electrocatalytic water splitting. In addition, Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have been used to make catalysts with good electrocatalytic capabilities. Traditionally, the MOF-derived selenides are produced via the self-sacrificing MOF template methods. However, this strategy is high-energy consuming, and it is difficult to precisely control the structure and component homogeneity of the product during pyrolysis.
Credit: HIGHER EDUCATION PRESS
Transition metal selenides have been considered to be a good choice for electrocatalytic water splitting. In addition, Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have been used to make catalysts with good electrocatalytic capabilities. Traditionally, the MOF-derived selenides are produced via the self-sacrificing MOF template methods. However, this strategy is high-energy consuming, and it is difficult to precisely control the structure and component homogeneity of the product during pyrolysis.
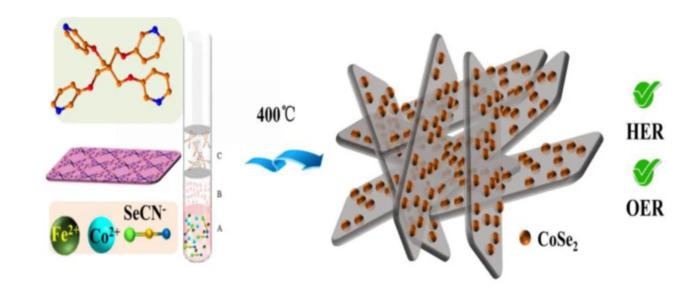
A research group of Wang-ting Lu, Fan Yu, and Yun Zheng from Jianghan University and Fuzhou University used two-dimensional (2D) layered metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as self-sacrificial templates to create high-efficiency Selenium (Se)-containing electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. They adopted two strategies to introduce Se element into the Co–Fe MOF, one being the etching of as-prepared MOF by SeO2 solution and the other, the replacing of SCN− with SeCN− as the construction unit. The electrochemical activity of Se-containing electrocatalysts for catalyzing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is evaluated and further discussed.
It is found that both two Se introducing approaches can obviously improve the HER performance during overall water splitting. The high electrochemical performance may be resulted from the unique 2D hierarchical porous structure and strong synergistic effect between different components in the material.
This work reveals that the rational design of layered MOFs with S- or Se-containing linkers as water splitting catalysts is a feasible option for the development of economical and low-energy-consuming electrocatalysts. Meanwhile, it provides an innovative approach for the synthesis of MOF-based metallic selenides.
Journal
Frontiers in Energy
DOI
10.1007/s11708-024-0924-x
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Two-dimensional bimetallic selenium-containing metal-organic frameworks and their calcinated derivatives as electrocatalysts for overall water splitting
Article Publication Date
29-Feb-2024




