Credit: Chloe Berland et al.
Energy-dense food, obesity and compulsive food intake bordering addiction: the scientific literature has been pointing to connections between these for years. Scientists at the CNRS and Université de Paris have just shown for the first time how fatty nutrients act on the brain in the reward circuit. Published in Cell Metabolism on 5 March 2020, these results shed new light on the connection between food and eating disorders.
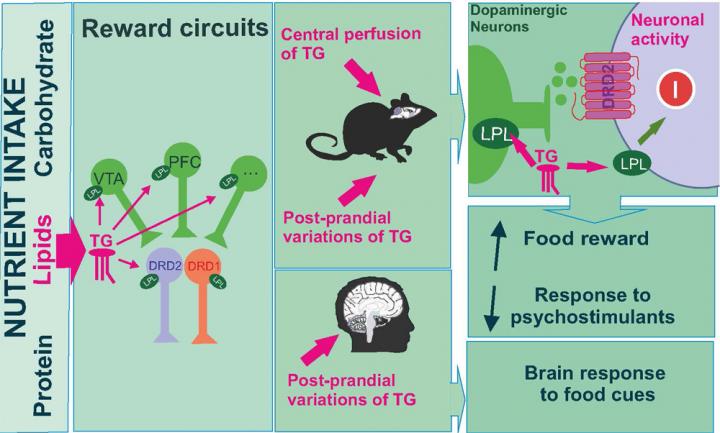
This recent work, directed by scientists at the Unité de biologie fonctionnelle et adaptative (CNRS/Université de Paris)*, show that triglycerides, the nutrients that constitute animal fats, vegetable oils and dairy products, interact with certain neurons in the reward circuit and reduce their excitability in mice, both in vitro and in vivo. These neurons carry a specific type of dopamine-receptor, and their activity strengthens reward-seeking behaviour. The scientists also observed that the manipulation of triglyceride levels in the brain of mice changes many behaviours associated with dopamine, like pleasure and motivation to collect food.
The study is completed by observations of brain activity in humans in response to a food odour compared with their blood triglyceride level after a meal. The research team has shown that activity in the prefrontal cortex, one of the regions of the reward circuit that makes connections between a food’s odour, its taste and the pleasure that it causes, is directly correlated with the quantity of triglycerides circulating in the blood. The higher it is, the lower the prefrontal cortex’s response to a food odour. This suggests that the activity of important brain structures in the reward system can be directly modified by a lipid nutrient.
Usually, triglycerides only circulate in the blood after a meal. The exception is obese patients, for whom doctors often observe abnormally high triglyceride levels all day long. In this context, this study offers a new framework for potentially explaining why ever-wider access to rich foods may contribute to the establishment of compulsive dietary problems and increase obesity rates.
###
*- Researchers at the Centre interdisciplinaire de recherche en biologie (CNRS/INSERM/Collège de France), of the Institut de neurosciences cognitives et intégratives d’Aquitaine (CNRS/Université de Bordeaux) and Laboratoire neurosciences Paris-Seine (CNRS/INSERM/Sorbonne Université) participated in this work, and outside France, from the Helmholtz Diabetes Center in Munich, Yale University, the University of California San Diego and Novo Nordisk.
Media Contact
Francois Maginiot
[email protected]
33-144-964-309
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




