Credit: Yuki Nagashima
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology developed a new strategy for producing a wide range of organotin compounds, which are the building blocks of many organic synthesis methods. Their approach is based on the photoexcitation of stannyl anions, which alters their electronic state and increases their selectivity and reactivity to form useful compounds. This protocol will be helpful for the efficient synthesis of many bioactive products, novel drugs, and functional materials.
Organotin compounds, also known as stannanes, are made of tin (Sn), hydrocarbons, and sometimes other elements like nitrogen and oxygen. During the 1970s, stannanes rapidly took the spotlight as building blocks in the field of organic synthesis mainly because of their use as reagents in the Stille reaction, which remains essential for chemists to combine various organic molecules.
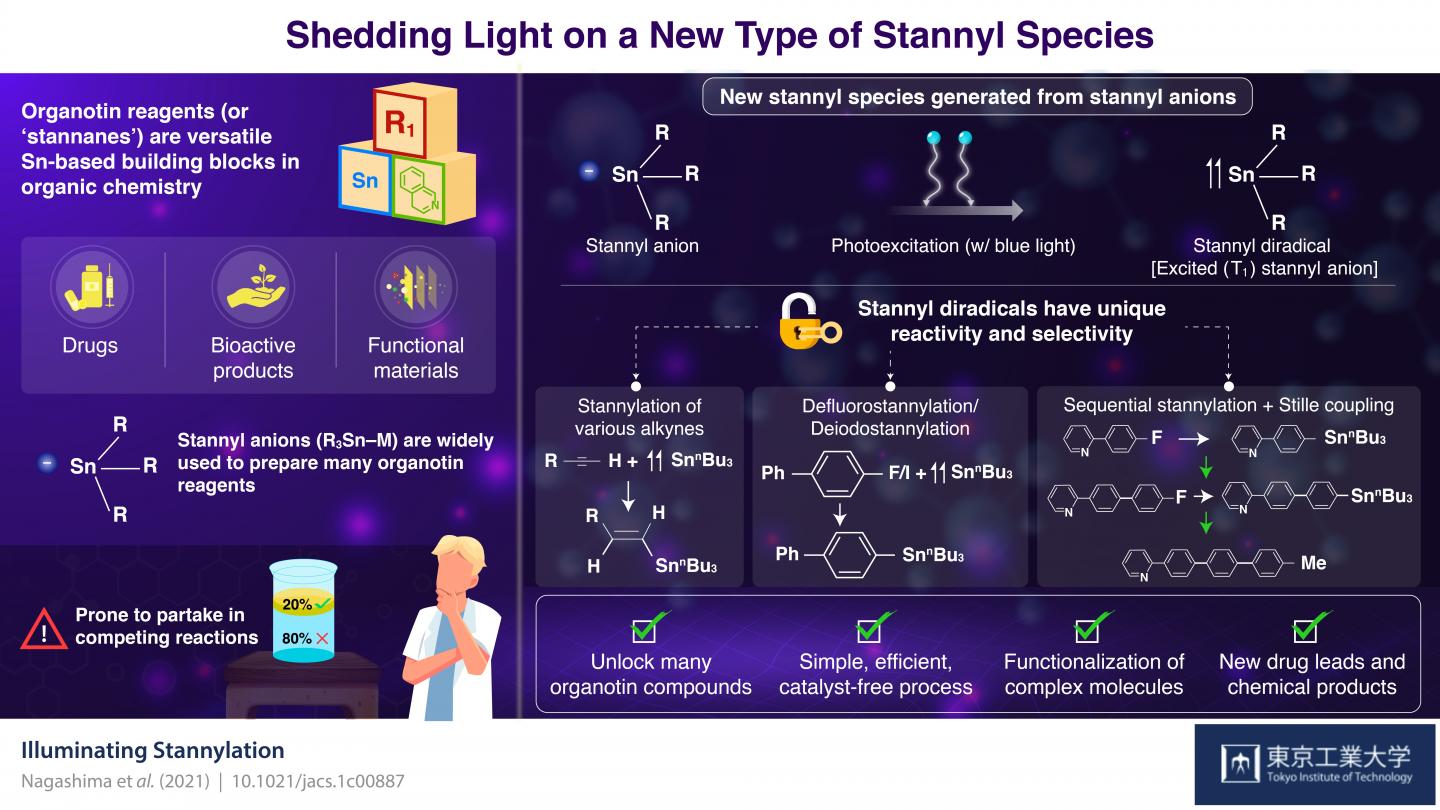
Equally important to the organotin reagents are the techniques and molecules that we rely on to make them. Stannyl anions have gained their place as the most widely used precursor for organotin reagents. However, their chemical properties make them prone to partake in unwanted reactions that compete with the synthesis of the target organotin reagent. This decreases yield and puts constraints on the main reaction, restricting the possible organotin reagents that can be produced in practice.
Surprisingly, in a recent collaborative study by Tokyo Institute of Technology and The University of Tokyo, Japan, scientists discovered a new type of stannyl species useful for producing organotin reagents. In their paper, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, they explain that this new stannyl species was first theorized to exist based on small anomalies observed in previous works. “During our studies involving stannyl anions, we occasionally detected small amounts of compounds called distannanes that were probably generated by the irradiation of stannyl anions with light. Inspired by these observations, we became interested in exploring the synthesis applications of these theoretical photoexcited stannyl anion species,” explains Assistant Professor Yuki Nagashima, lead researcher from Tokyo Tech.
Through density functional theory calculations, the team determined that trimethyltin anion (Me3Sn), a model stannyl anion, has a special affinity for blue light, which energizes the molecule to an excited ‘single’ state. From this state, the system naturally progresses to another state known as excited ‘triplet,’ where two electrons are unpaired. This easy-to-induce progression from a stannyl anion to a stannyl radical in an excited ‘triplet’ state gives the stannyl species vastly different chemical properties, including enhanced reactivity and selectivity towards certain compounds.
The scientists explored reactions between photoexcited stannyl anions and several compounds, including alkynes, aryl fluorides, and aryl halides. They found that the photoexcited stannyl species had unprecedented selectivity for the synthesis of various useful reagents that conventional stannyl anions could not easily produce. Moreover, these photoexcited anions had a remarkable ability for the defluorostannylation and dehalostannylation of aryl molecules. In simpler terms, this means that if you have an aryl fluoride or halide (an organic molecule with a fluorine or halide group, respectively), it is easy to set up a reaction that substitutes the fluorine or halide group with a stannyl group. This allowed the researchers to create a wide variety of organotin reagents useful for Stille reactions.
Excited about the results, Prof. Nagashima remarks: “Although many stannylation methods and reagents have been established over almost two centuries, our protocol using photoexcited anion species provides a new and complementary tool for preparing a wide range of organotin compounds.”
This new method will certainly be helpful for synthesizing many bioactive products, novel drugs, and functional materials, and further studies are already underway to see how far it will take us.
###
About Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tokyo Tech stands at the forefront of research and higher education as the leading university for science and technology in Japan. Tokyo Tech researchers excel in fields ranging from materials science to biology, computer science, and physics. Founded in 1881, Tokyo Tech hosts over 10,000 undergraduate and graduate students per year, who develop into scientific leaders and some of the most sought-after engineers in industry. Embodying the Japanese philosophy of “monotsukuri,” meaning “technical ingenuity and innovation,” the Tokyo Tech community strives to contribute to society through high-impact research.
https:/
Media Contact
Emiko Kawaguchi
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.