Credit: Faraon lab/Caltech
Engineers at Caltech have shown that atoms in optical cavities–tiny boxes for light–could be foundational to the creation of a quantum internet. Their work was published on March 30 by the journal Nature.
Quantum networks would connect quantum computers through a system that also operates at a quantum, rather than classical, level. In theory, quantum computers will one day be able to perform certain functions faster than classical computers by taking advantage of the special properties of quantum mechanics, including superposition, which allows quantum bits to store information as a 1 and a 0 simultaneously.
As they can with classical computers, engineers would like to be able to connect multiple quantum computers to share data and work together–creating a “quantum internet.” This would open the door to several applications, including solving computations that are too large to be handled by a single quantum computer and establishing unbreakably secure communications using quantum cryptography.
In order to work, a quantum network needs to be able to transmit information between two points without altering the quantum properties of the information being transmitted. One current model works like this: a single atom or ion acts as a quantum bit (or “qubit”) storing information via one if its quantum properties, such as spin. To read that information and transmit it elsewhere, the atom is excited with a pulse of light, causing it to emit a photon whose spin is entangled with the spin of the atom. The photon can then transmit the information entangled with the atom over a long distance via fiber optic cable.
It is harder than it sounds, however. Finding atoms that you can control and measure, and that also aren’t too sensitive to magnetic or electric field fluctuations that cause errors, or decoherence, is challenging.
“Solid-state emitters that interact well with light often fall victim to decoherence; that is, they stop storing information in a way that’s useful from the prospective of quantum engineering,” says Jon Kindem (MS ’17, PhD ’19), lead author of the Nature paper. Meanwhile, atoms of rare-earth elements–which have properties that make the elements useful as qubits–tend to interact poorly with light.
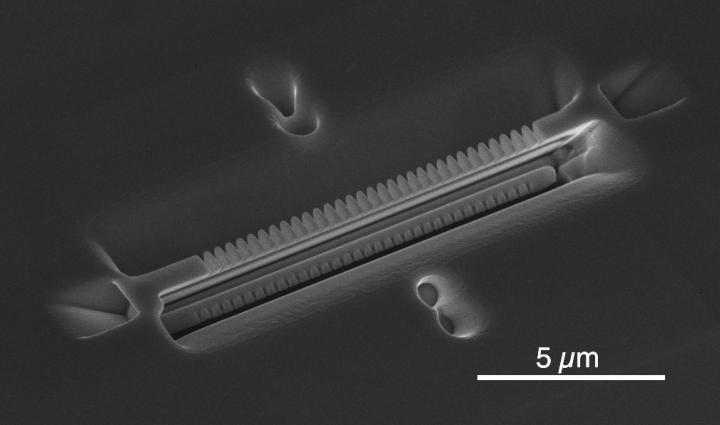
To overcome this challenge, researchers led by Caltech’s Andrei Faraon (BS ’04), professor of applied physics and electrical engineering, constructed a nanophotonic cavity, a beam that is about 10 microns in length with periodic nano-patterning, sculpted from a piece of crystal. They then identified a rare-earth ytterbium ion in the center of the beam. The optical cavity allows them to bounce light back and forth down the beam multiple times until it is finally absorbed by the ion.
In the Nature paper, the team showed that the cavity modifies the environment of the ion such that whenever it emits a photon, more than 99 percent of the time that photon remains in the cavity, where scientists can then efficiently collect and detect that photon to measure the state of the ion. This results in an increase in the rate at which the ion can emit photons, improving the overall effectiveness of the system.
In addition, the ytterbium ions are able to store information in their spin for 30 milliseconds. In this time, light could transmit information to travel across the continental United States. “This checks most of the boxes. It’s a rare-earth ion that absorbs and emits photons in exactly the way we’d need to create a quantum network,” says Faraon, professor of applied physics and electrical engineering. “This could form the backbone technology for the quantum internet.”
Currently, the team’s focus is on creating the building blocks of a quantum network. Next, they hope to scale up their experiments and actually connect two quantum bits, Faraon says.
###
Their paper is titled “Control and single-shot readout of an ion embedded in a nanophotonic cavity.” Co-authors include graduate students Andrei Ruskuc and Jake Rochman (MS ’19), former postdoctoral researcher John Bartholomew, and Yan Qi Huan (BS ’19). This research was funded by the National Science Foundation and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
The study can be found here: https:/
Media Contact
Robert Perkins
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




