Researchers review promising new nanomaterials that can be used in cancer diagnosis and as MRI contrast agents
Credit: Celia Sousa
WASHINGTON, January 28, 2020 — Small magnetic objects, which have been used successfully in technological applications such as data storage, are showing promise in the biomedical field. Magnetic nanostructures have interesting properties that enhance novel applications in medical diagnosis and allow the exploration of new therapeutic techniques.
In this week’s Applied Physics Review, by AIP Publishing, researchers review the state of the art in this field. One especially interesting advance involves an exotic nanodisc configuration, known as a vortex state, where magnetic moments arrange into a curly geometry.
Isolating and separating cells from a blood or tissue sample is crucial for a variety of medical applications, such as gene therapy or cancer diagnosis and treatment. Standard procedures involve filtration and centrifugation, but cells of similar sizes or densities cannot be separated this way.
One approach to this problem has been to coat spherical iron oxide beads with antibodies that specifically bind the cells of interest. The desired cells are then separated with applied magnetic fields. However, this can require high magnetic field strengths, so a second approach using nanowires has been tried.
A third way involves nanodiscs, either in a vortex state or a synthetic antiferromagnetic configuration, consisting of two ferromagnetic layers separated by one nonmagnetic layer. The surface of the small structures can be treated with fluorescent probes, allowing the investigators to observe motion of the particles in response to an applied field.
Another biomedical application that can benefit from magnetic nanostructures is MRI. Because the basic technique has low sensitivity, contrast agents are usually needed. The most widely used agents are gadolinium complexes, but these have raised toxicity concerns. Both nanodiscs and nanowires coated with biocompatible substances have properties that would make them good MRI contrast agents.
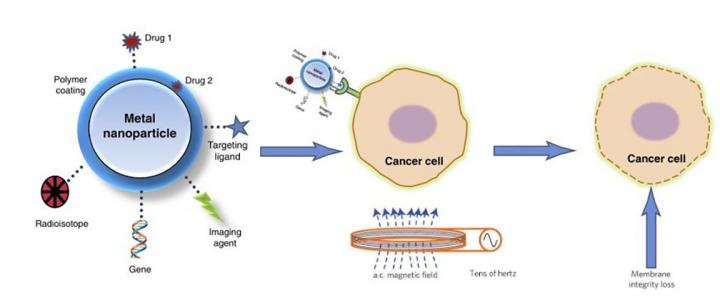
An innovative application area of magnetic nanostructures involves targeted cell annihilation for cancer treatment. Nanodiscs created in a spin vortex state or synthetic antiferromagnetic configuration show great promise for this use.
High tumor cell death rates, up to 90%, were observed when relatively weak magnetic fields were used with them. The mechanism leading to cell death is a strong mechanical force that results when a rotating magnetic field spins the nanodiscs, destroying tumor cells from the inside.
Most of these studies have been carried out in the lab, so some situations, such as retention or excretion by internal organs or transport through capillaries, could still be an issue. Further study is required to address these real-world effects.
###
The article, “Magnetic nanostructures for emerging biomedical applications,” is authored by L. Peixoto, R. Maglhäes, D. Navas, S. Moraes, C. Redondo, R. Morales, J. P. Araújo and C. T. Sousa. The article will appear in Applied Physics Reviews on Jan. 28, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5121702). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
301-209-3090
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




