A compact, lightweight sensor system with infrared imaging capabilities developed by an international team of engineers could be easily fitted to a drone for remote crop monitoring.
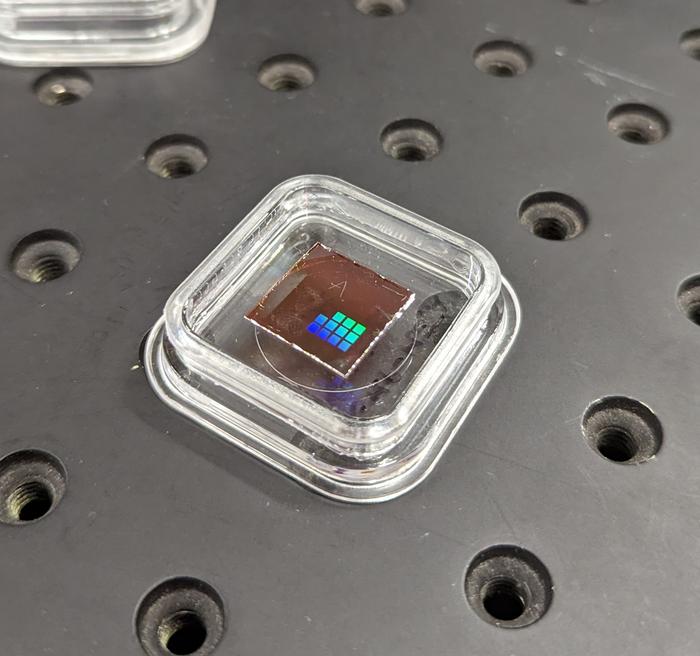
Credit: Lincoln Clark, ARC Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optical Systems (TMOS)
A compact, lightweight sensor system with infrared imaging capabilities developed by an international team of engineers could be easily fitted to a drone for remote crop monitoring.
This flat-optics technology has the potential to replace traditional optical lens applications for environmental sensing in a range of industries.
This innovation could result in cheaper groceries as farmers would be able to pinpoint which crops require irrigation, fertilisation and pest control, instead of taking a one-size-fits-all approach, thereby potentially boosting their harvests.
The sensor system can rapidly switch between edge detection – imaging the outline of an object, such as a fruit – and extracting detailed infrared information, without the need for creating large volumes of data and using bulky external processors.
The capability to switch to a detailed infrared image is a new development in the field and could allow farmers to collect more information when the remote sensor identifies areas of potential pest infestations.
This research by engineers at the City University of New York (CUNY), the University of Melbourne, RMIT University and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optical Systems (TMOS) is published in Nature Communications.
How does the sensor system work?
The prototype sensor system, which comprises a filter made with a thin layer of a material called vanadium dioxide that can switch between edge detection and detailed infrared imaging, was engineered by TMOS Chief Investigator Professor Madhu Bhaskaran and her team at RMIT in Melbourne.
“Materials such as vanadium dioxide add a fantastic tuning capability to render devices ‘smart’”, she said.
“When the temperature of the filter is changed, the vanadium dioxide transforms from an insulating state to a metallic one, which is how the processed image shifts from a filtered outline to an unfiltered infrared image.”
“These materials could go a long way in futuristic flat-optics devices that can replace technologies with traditional lenses for environmental sensing applications – making them ideal for use in drones and satellites, which require low size, weight and power capacity.
RMIT holds a granted US patent and has a pending Australian patent application for its method of producing vanadium dioxide films, which may be suitable for a broad range of applications.
Lead author Dr Michele Cotrufo said the system’s ability to switch between processing operations, from edge detection to capturing detailed infrared images, was significant.
“While a few recent demonstrations have achieved analogue edge detection using metasurfaces, most of the devices demonstrated so far are static. Their functionality is fixed in time and cannot be dynamically altered or controlled,” said Corufo, who conducted his research at CUNY.
“Yet, the ability to dynamically reconfigure processing operations is key for metasurfaces to be able to compete with digital image processing systems. This is what we have developed.”
Next steps
Co-author Shaban Sulejman from the University of Melbourne said the design and materials used make the filter amenable to mass-manufacturing.
“It also operates at temperatures compatible with standard manufacturing techniques, making it well-placed to integrate with commercially available systems and therefore move from research to real-world usage rapidly.”
TMOS Chief Investigator Ann Roberts, also from the University of Melbourne, said flat optics technologies had the potential to transform countless industries.
“Traditional optical elements have long been the bottleneck preventing the further miniaturisation of devices. The ability to replace or complement traditional optical elements with thin-film optics breaks through that bottleneck.”
‘Reconfigurable image processing metasurfaces with phase-change materials’ is published in Nature Communications (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-48783-3).
MULTIMEDIA FOR MEDIA USE
Media are free to use images available via this link in relation to this story: https://spaces.hightail.com/space/QTc4nTmecD
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-024-48783-3
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Reconfigurable image processing metasurfaces with phase-change materials
Article Publication Date
27-May-2024




