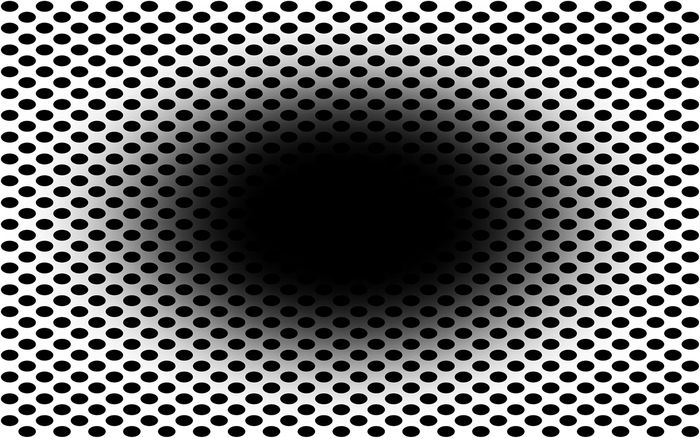
Have a look at this image. Do you perceive that the central black hole is expanding, as if you’re moving into a dark environment, or falling into a hole? If so, you’re not alone: a new study shows that this ‘expanding hole’ illusion, which is new to science, is perceived by approximately 86% of people.
Credit: Laeng, Nabil, and Kitaoka
Have a look at this image. Do you perceive that the central black hole is expanding, as if you’re moving into a dark environment, or falling into a hole? If so, you’re not alone: a new study shows that this ‘expanding hole’ illusion, which is new to science, is perceived by approximately 86% of people.
Dr Bruno Laeng, a professor at the Department of Psychology of the University of Oslo and the study’s first author, said: “The ‘expanding hole’ is a highly dynamic illusion: The circular smear or shadow gradient of the central black hole evokes a marked impression of optic flow, as if the observer were heading forward into a hole or tunnel.”
Optical illusions aren’t mere gimmicks without scientific interest: researchers in the field of psychosociology study them to better understand the complex processes our visual system uses to anticipate and make sense of the visual world – in a far more roundabout way than a photometer device, which simply registers the amount of photonic energy.
In the new study, published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, Laeng and colleagues show that the ‘expanding hole’ illusion is so good at deceiving our brain that it even prompts a dilation reflex of the pupils to let in more light, just as would happen if we were really moving into a dark area.
Pupil reflex depends on perception, not necessarily reality
“Here we show based on the new ‘expanding hole’ illusion that that the pupil reacts to how we perceive light – even if this ‘light’ is imaginary like in the illusion – and not just to the amount of light energy that actually enters the eye. The illusion of the expanding hole prompts a corresponding dilation of the pupil, as it would happen if darkness really increased,” said Laeng.
Laeng and colleagues explored how the color of the hole (besides black: blue, cyan, green, magenta, red, yellow, or white) and of the surrounding dots affect how strongly we mentally and physiologically react to the illusion. On a screen they presented variations of the ‘expanding hole’ image to 50 women and men with normal vision, asking them to rate subjectively how strongly they perceived the illusion. While participants gazed at the image, the researchers measured their eye movements and their pupils’ unconscious constrictions and dilations. As controls, the participants were shown ‘scrambled’ versions of the expanding hole image, with equal luminance and colors, but without any pattern.
The illusion appeared most effective when the hole was black. Fourteen percent of participants didn’t perceive any illusory expansion when the hole was black, while 20% didn’t if the hole was in color. Among those who did perceive an expansion, the subjective strength of the illusion differed markedly.
The researchers also found that black holes promoted strong reflex dilations of the participants’ pupils, while colored holes prompted their pupils to constrict. For black holes, but not for colored holes, the stronger individual participants subjectively rated their perception of the illusion, the more their pupil diameter tended to change.
Minority not susceptible
The researchers don’t yet know why a minority seem unsusceptible to the ‘expanding hole’ illusion. Nor do they know whether other vertebrate species, or even nonvertebrate animals with camera eyes such as octopuses, might perceive the same illusion as we do.
“Our results show that pupils’ dilation or contraction reflex is not a closed-loop mechanism, like a photocell opening a door, impervious to any other information than the actual amount of light stimulating the photoreceptor. Rather, the eye adjusts to perceived and even imagined light, not simply to physical energy. Future studies could reveal other types of physiological or bodily changes that can ‘throw light’ onto how illusions work,” concluded Laeng.
Journal
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience
DOI
10.3389/fnhum.2022.877249
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
The eye pupil adjusts to illusorily expanding holes
Article Publication Date
30-May-2022
COI Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest




