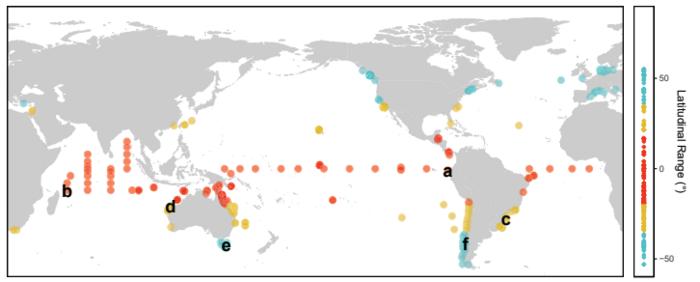
Tropical waters are not as thermally stable as once thought. Ocean waters vary widely in temperature over space and time, but the spatial and temporal resolution of remotely sensed sea surface temperature data is insufficient to capture the fine-scale variability that is relevant for marine organisms. Darren Li Shing Hiung and colleagues investigated whether ocean temperatures measured at high temporal scales are more stable in the tropics (often termed the “climate variability hypothesis”) by assembling a global array of in situ ocean temperature data with hourly or better temporal resolutions. The authors found that the long-held pattern of tropical ocean temperature stability was only valid at annual scales. At finer temporal scales, tropical waters were as variable as temperate regions—and subtropical waters were the most variable of all. This unexpected tropical and subtropical variability suggests correspondingly high variation in temperature-dependent biological rates, such as metabolism and photosynthesis, which may help to elucidate previously unexplained macroecological patterns. For instance, the results may help explain why tropical fish are more thermally tolerant than temperate fish when both are living in an overlapping subtropical range. The authors call for consideration of ocean weather in research on species’ vulnerability to future ocean climate change.
Credit: Li Shing Hiung et al
Tropical waters are not as thermally stable as once thought. Ocean waters vary widely in temperature over space and time, but the spatial and temporal resolution of remotely sensed sea surface temperature data is insufficient to capture the fine-scale variability that is relevant for marine organisms. Darren Li Shing Hiung and colleagues investigated whether ocean temperatures measured at high temporal scales are more stable in the tropics (often termed the “climate variability hypothesis”) by assembling a global array of in situ ocean temperature data with hourly or better temporal resolutions. The authors found that the long-held pattern of tropical ocean temperature stability was only valid at annual scales. At finer temporal scales, tropical waters were as variable as temperate regions—and subtropical waters were the most variable of all. This unexpected tropical and subtropical variability suggests correspondingly high variation in temperature-dependent biological rates, such as metabolism and photosynthesis, which may help to elucidate previously unexplained macroecological patterns. For instance, the results may help explain why tropical fish are more thermally tolerant than temperate fish when both are living in an overlapping subtropical range. The authors call for consideration of ocean weather in research on species’ vulnerability to future ocean climate change.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
Ocean weather, biological rates, and unexplained global ecological patterns
Article Publication Date
6-Aug-2024




