Researchers have linked US household income data to greenhouse gas emissions generated in creating that income, and found that 40% of total emissions are associated with income for the highest 10% of households. The paper, published in PLOS Climate suggests that an income or shareholder-based carbon tax focused on investments may have equity advantages over traditional consumer-facing cap-and-trade or carbon tax options.
Human created climate change is an existential threat, and there is a disconnect between those facing the worst impacts and those that drive the greatest greenhouse gas emissions.
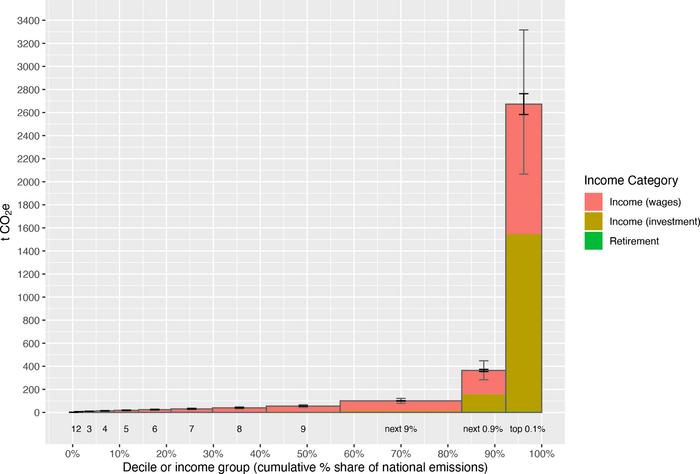
Credit: Starr et al., 2023, PLOS Climate, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Researchers have linked US household income data to greenhouse gas emissions generated in creating that income, and found that 40% of total emissions are associated with income for the highest 10% of households. The paper, published in PLOS Climate suggests that an income or shareholder-based carbon tax focused on investments may have equity advantages over traditional consumer-facing cap-and-trade or carbon tax options.
Human created climate change is an existential threat, and there is a disconnect between those facing the worst impacts and those that drive the greatest greenhouse gas emissions.
Jared Starr of the University of Massachusetts Amherst, and colleagues, took 30 years of US household-level income data, from 1990-2019, and linked it to the emissions generated in that income. They look at both income from direct emissions, such as industries like power plants, and income related to industries supplying services or commodities to those industries – such as finance or fossil fuel suppliers.
In general, white non-Hispanic households had the highest emissions linked to income, and Black households had the lowest, predominantly because of the racial inequity of income distribution. In terms of age, emissions tend to increase with age until peaking within the 45 – 54 age group before declining again.
Among the highest earning 1% of households, whose income is linked to 15 – 17% of national emissions, investment holdings account for 38 – 43% of their emissions. The team also identifies “super emitters” with extremely high overall emissions, and these are almost exclusively among the top 0.1% of households, which are overrepresented in finance, real estate, and insurance; manufacturing; mining and quarrying.
The research offers a new perspective on emissions responsibility and climate finance and could be a useful policy tool to encourage decarbonization while raising revenue for climate finance.
Starr adds: “The scale of emission disparity is quite striking. Just fifteen days of income-based emissions from an average top 0.1% household is equal to a lifetime of emissions from a bottom decile household. I find that morally troubling, especially since low-income households face disproportionate climate harms.
I think we need to make sure that our climate policies take these disparities into account. One way to do that is to make sure that those who are financially benefitting thanks to emissions are properly incentivized to both reduce their emissions and pay for the damage caused by those emissions. I believe that an income or asset-based carbon tax would focus the minds of corporate executives, board members, and large shareholders to decarbonize their industries in order to reduce their taxes. In essence it is decarbonization and divestment out of self-interest. At the same time it would generate much needed revenue for climate finance. While no tool is perfect, I think this could be a useful new approach to encourage the most economically and politically powerful in our society to focus their minds on decarbonization.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Climate: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000190
Citation: Starr J, Nicolson C, Ash M, Markowitz EM, Moran D (2023) Income-based U.S. household carbon footprints (1990–2019) offer new insights on emissions inequality and climate finance. PLOS Clim 2(8): e0000190. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pclm.0000190
Author Countries: Norway, US
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Journal
PLOS Climate
DOI
10.1371/journal.pclm.0000190
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Income-based U.S. household carbon footprints (1990–2019) offer new insights on emissions inequality and climate finance
Article Publication Date
17-Aug-2023
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.




