Intracranial aneurysm is the leading cause of nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage, with a prevalence of 7% in China. More than 70% intracranial aneurysms are unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs). Although aneurysm rupture is associated with high morbidity and mortality, previous studies revealed the rupture rate of UIAs as low as 1% per year. Notably, aggressive empirical surgical treatment carries the risk of complications, including ischemic stroke and accidental aneurysm rupture. Evaluating the unstable (rupture and growth) risk of aneurysms is helpful to guild decision-making for UIAs.
Credit: ©Science China Press
Intracranial aneurysm is the leading cause of nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage, with a prevalence of 7% in China. More than 70% intracranial aneurysms are unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs). Although aneurysm rupture is associated with high morbidity and mortality, previous studies revealed the rupture rate of UIAs as low as 1% per year. Notably, aggressive empirical surgical treatment carries the risk of complications, including ischemic stroke and accidental aneurysm rupture. Evaluating the unstable (rupture and growth) risk of aneurysms is helpful to guild decision-making for UIAs.
Metabolites and cytokines influence the environment of the vessels and are essential for the development of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. However, there are few longitudinal studies on the natural history of UIA rupture or growth, the relationship between metabolic-cytokine features and UIA instability was unclear. Moreover, there is a lack of large-scale multi-center longitudinal data in the Chinese population.
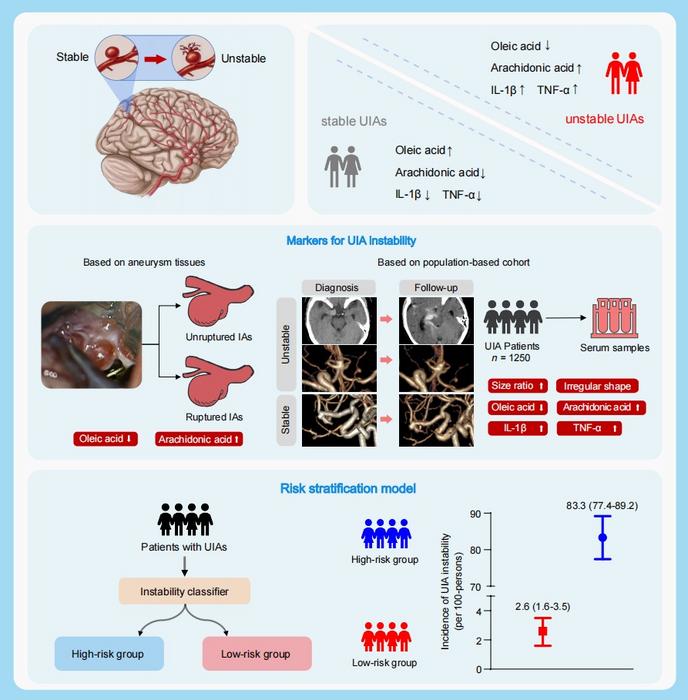
Firstly, based on the intracranial aneurysm samples and serums from 20 patients, and the dynamic change of metabolites and cytokines during 2-year follow-up, this study revealed that the abnormity of lipid metabolism is related to intracranial aneurysm rupture, and oleic acid (OA) and arachidonic (AA), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were reliable biomarkers to evaluate the risk of UIA instability.
Subsequently, incorporating radiological features and biomarkers related to UIA instability, this team established a risk stratification model using the machine-learning algorithm. Based on 1250 UIA patients who were regularly followed up for two years by radiology, this stratification model performed well to classifying unstable UIAs and stable UIAs (area under curve (AUC) as 0.94 within the derivation cohort, and as 0.89 within the validation cohort), which was superior to the existing clinical models (PHASES score and ELAPSS score).
Finally, this team investigated whether in vivo intervention of OA, IL-1β, and TNF-α could prevent IA from rupture. The in vivo study based on the rat model of intracranial aneurysms showed supplementation of OA and inhibition of IL-1β and TNF-α could prevent aneurysms from rupturing and relieve the inflammation activation in the aneurysm wall.
This study performed the first and largest multi-omics analysis based on two longitudinal multi-center Chinese cohort, and revealed that OA, AA, IL-1β, and TNF-α were revealed as biomarkers for UIA instability. These findings could help clinicians to understand the pathological characteristics of ruptured and growing intracranial aneurysms.
This team provided a risk stratification model incorporating radiological features and biomarkers with high accuracy to evaluate the 2-year risk of UIA instability, which may guide treatment decision-making for UIAs.
Journal
Science Bulletin
DOI
10.1016/j.scib.2023.05.001




