Credit: Paul Scherrer Institute/Jörg Roth
In a joint research project of five Swiss competence centres for energy research, scientists of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and colleagues have prepared a white paper on “Power-to-X” for consideration by the Swiss Federal Energy Research Commission (CORE). The goal of the white paper is to gather together the most important insights available on Power-to-X technologies. Among other things, the study sheds light on contributions that could be made to Switzerland’s energy strategy by different technologies based on conversion and storage of various forms of energy. The experts are presenting the findings of this study on July 8th at ETH Zurich.
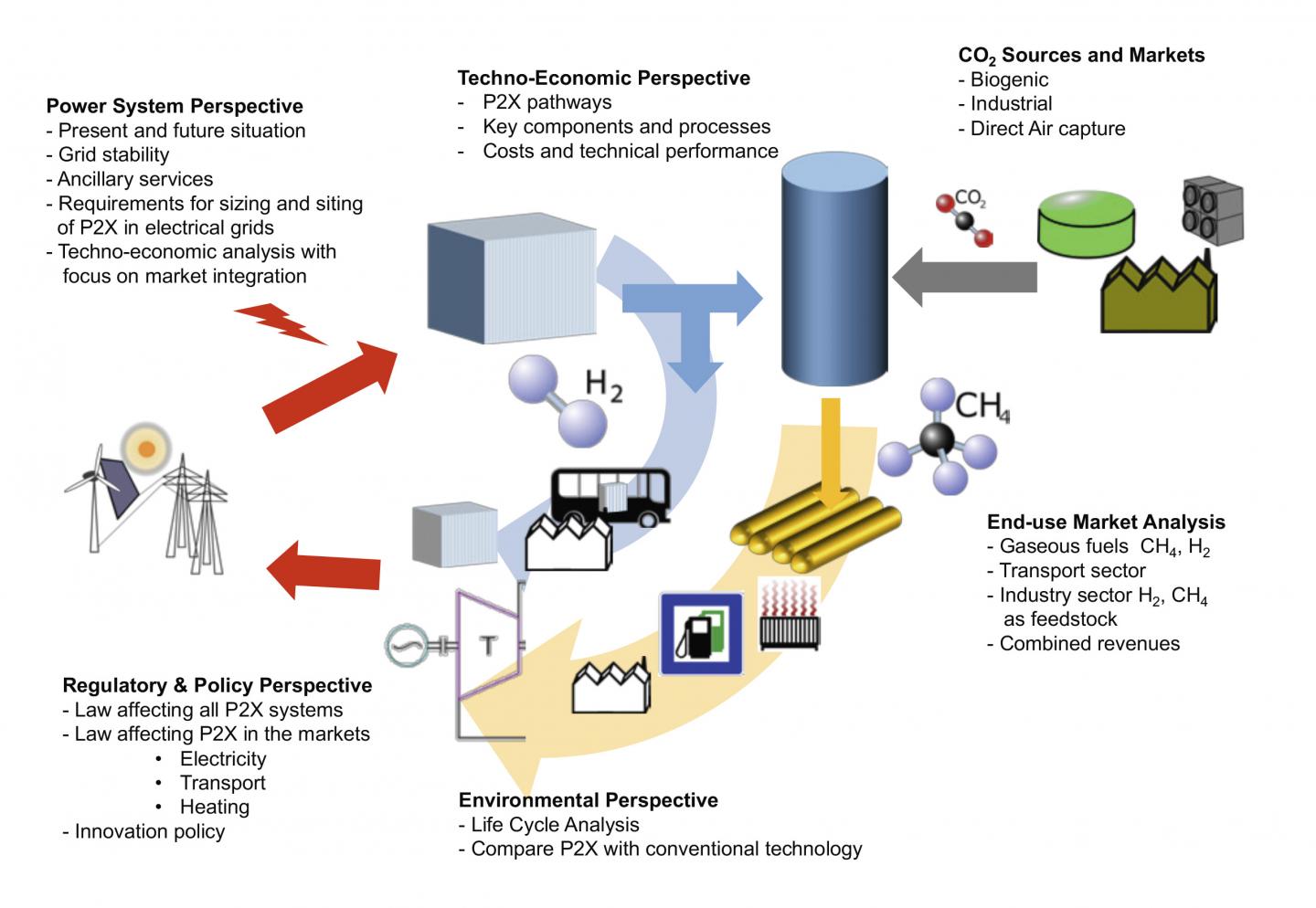
Switzerland has set itself the goal of drastically reducing its direct emissions of greenhouse gases. According to its Energy Strategy 2050, by 2030 emissions of greenhouse gases should decrease by 50 percent compared to 1990, and up to a maximum of 85 percent by 2050. After 2050, the energy supply in Switzerland should be climate-neutral, that is, without emissions of greenhouse gases such as CO2. One component of the effort to achieve this goal could be so-called Power-to-X techniques. Here surplus electricity from new renewable energy sources is used to produce, through electrochemical conversion, liquid or gaseous energy carriers such as hydrogen, methane, or methanol. These are then used in the consumer sectors to power vehicles or to generate heat or electricity again. The advantage is that the liquid or gaseous energy sources can be stored for a longer time.
Within the framework of Energy Strategy 2050, the Power-to-X techniques are of interest because new sources of renewable energy from photovoltaics or wind power are not available continuously, but rather with fluctuating intensity. To compensate for phases of low power generation, energy from production-intensive phases is expected to be temporarily stored with the help of Power-to-X techniques. Thus Power-to-X processes can contribute to balancing energy supply and demand over a longer period of time, increase the short-term flexibility of the electric grid through intelligent load management, and create substitutes for fossil fuels as well as raw materials for industry.
A flexibility option and a link between energy production and consumption
Scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, together with colleagues from six other Swiss universities and research institutions, have amassed extensive information on various aspects of Power-to-X technologies, including their potential to contribute to Energy Strategy 2050, what challenges each technology faces, and what key factors could promote their widespread use. Tom Kober, head of the Energy Economics Group at PSI and one of the lead authors of the white paper commissioned by the Swiss Federal Energy Research Commission, summarises one of the findings: “In comparison to other new renewable energy sources, there is a particularly high potential in Switzerland for electricity from solar facilities, which makes Power-to-X an important flexibility option and a link between energy production and consumption in a sustainable, low-CO2 energy system.”
The contributions Power-to-X can make in individual energy sectors such as transportation and heating or through reconversion are very different. Thus, the recovery of electricity from energy sources such as hydrogen or methane produced with Power-to-X methods is currently still very expensive. “But the costs of such so-called Power-to-Power processes could decrease by as much as two-thirds by 2030, thanks to advances in technology and increasing experience with these new technologies”, Kober estimates. It remains to be seen to what extent Power-to-Power technologies can prevail over other flexibility options in the electricity system, not least because it also depends on developments in the European market and associated conditions for Switzerland’s foreign trade in electricity.
System integration plays a key role
Fuels produced with electricity from renewable sources in Power-to-X processes can replace fossil fuels such as heating oil, natural gas, petrol, and diesel, thus helping to reduce CO2 emissions. But this will only be economically viable if appropriate environmental incentive mechanisms come into play. Conversion processes must be realised as efficiently as possible, on the one hand to minimise costs and on the other hand to preserve resources. This has implications not only for the selection of sites for Power-to-X plants, but also how the technology can be integrated into different markets.
Therefore, the study concludes that, for Power-to-X to be applied successfully within the framework of Energy Strategy 2050, it is essential to concentrate research and innovation on the optimal integration of Power-to-X into the overall energy system of Switzerland.
The white paper commissioned by the Swiss Federal Energy Research Commission (CORE) was prepared by the partners of five Swiss competence centres for energy research (SCCER) – Heat and Electricity Storage, BIOSWEET, CREST, FURIES, and Mobility – and financed by Innosuisse as well as the Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE).
The researchers will present the results of the analyses for the white paper “Power-to-X: Perspectives in Switzerland” on July 8th at an event held at ETH Zurich.
Location: ETH Zurich (Zentrum) HG D 7.1; Rämistrasse 101, 8092 ZurichStart of the event: Monday July 8th, 2019, 5:00 p.m.
###
Further information: https:/
Text: Paul Scherrer Institute/Sebastian Jutzi
Images are available to download at https:/
About PSI
The Paul Scherrer Institute PSI develops, builds and operates large, complex research facilities and makes them available to the national and international research community. The institute’s own key research priorities are in the fields of matter and materials, energy and environment and human health. PSI is committed to the training of future generations. Therefore about one quarter of our staff are post-docs, post-graduates or apprentices. Altogether PSI employs 2100 people, thus being the largest research institute in Switzerland. The annual budget amounts to approximately CHF 407 million. PSI is part of the ETH Domain, with the other members being the two Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology, ETH Zurich and EPFL Lausanne, as well as Eawag (Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology), Empa (Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology) and WSL (Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research).
Contact
Dr. Tom Kober
Head of the Energy Economics Group
Paul Scherrer Institute, Forschungsstrasse 111, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland
Telephone: +41 56 310 26 31, e-mail: [email protected] [German, English]
Media Contact
Dagmar Baroke
41-563-102-111
Original Source
https:/




