Credit: Prof. Ido Kanter
The brain is a complex network containing billions of neurons, where each of these neurons communicates simultaneously with thousands of other via their synapses (links). However, the neuron actually collects its many synaptic incoming signals through several extremely long ramified "arms" only, called dendritic trees.
In 1949 Donald Hebb's pioneering work suggested that learning occurs in the brain by modifying the strength of the synapses, whereas neurons function as the computational elements in the brain. This has remained the common assumption until today.
Using new theoretical results and experiments on neuronal cultures, a group of scientists, led by Prof. Ido Kanter, of the Department of Physics and the Gonda (Goldschmied) Multidisciplinary Brain Research Center at Bar-Ilan University, has demonstrated that the central assumption for nearly 70 years that learning occurs only in the synapses is mistaken.
In an article published today in the journal Scientific Reports, the researchers go against conventional wisdom to show that learning is actually done by several dendrites, similar to the slow learning mechanism currently attributed to the synapses.
"The newly discovered process of learning in the dendrites occurs at a much faster rate than in the old scenario suggesting that learning occurs solely in the synapses. In this new dendritic learning process, there are a few adaptive parameters per neuron, in comparison to thousands of tiny and sensitive ones in the synaptic learning scenario," said Prof. Kanter, whose research team includes Shira Sardi, Roni Vardi, Anton Sheinin, Amir Goldental and Herut Uzan.
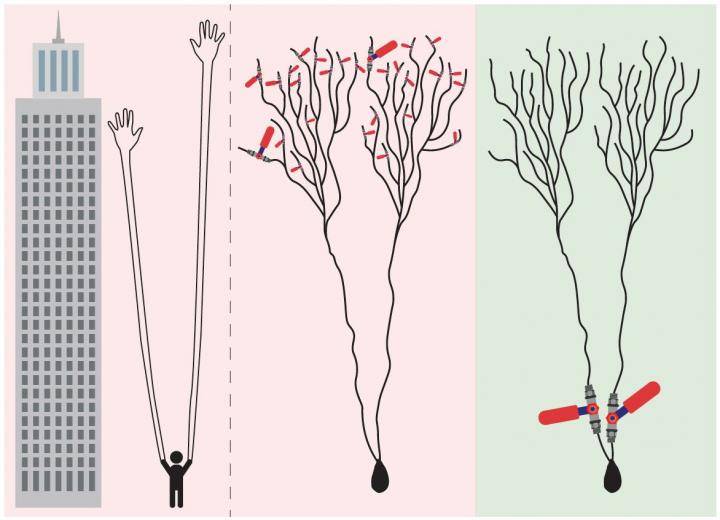
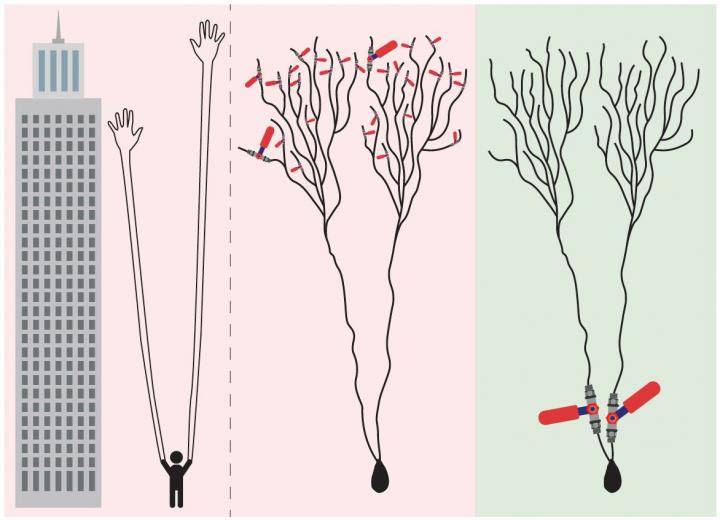
The newly suggested learning scenario indicates that learning occurs in a few dendrites that are in much closer proximity to the neuron, as opposed to the previous notion. "Does it make sense to measure the quality of air we breathe via many tiny, distant satellite sensors at the elevation of a skyscraper, or by using one or several sensors in close proximity to the nose? Similarly, it is more efficient for the neuron to estimate its incoming signals close to its computational unit, the neuron," says Kanter. Hebb's theory has been so deeply rooted in the scientific world for 70 years that no one has ever proposed such a different approach. Moreover, synapses and dendrites are connected to the neuron in a series, so the exact localized site of the learning process seemed irrelevant.
Another important finding of the study is that weak synapses, previously assumed to be insignificant even though they comprise the majority of our brain, play an important role in the dynamics of our brain. They induce oscillations of the learning parameters rather than pushing them to unrealistic fixed extremes, as suggested in the current synaptic learning scenario.
The new learning scenario occurs in different sites of the brain and therefore calls for a reevaluation of current treatments for disordered brain functionality. Hence, the popular phrase "neurons that fire together wire together", summarizing Donald Hebb's 70-year-old hypothesis, must now be rephrased. In addition, the learning mechanism is at the basis of recent advanced machine learning and deep learning achievements. The change in the learning paradigm opens new horizons for different types of deep learning algorithms and artificial intelligence based applications imitating our brain functions, but with advanced features and at a much faster speed.
###
On publication, the paper will be available online at www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-23471-7.
Media Contact
Elana Oberlander
[email protected]
@ubarilan
http://www.biu.ac.il
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23471-7