“Our study demonstrated that the VitD/VDR [vitamin D/vitamin D receptor] pathway is required for intestinal homeostasis during normal differentiation and aging.”
Credit: 2024 Park et al.
“Our study demonstrated that the VitD/VDR [vitamin D/vitamin D receptor] pathway is required for intestinal homeostasis during normal differentiation and aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 27, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “The anti-aging effect of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor in Drosophila midgut.”
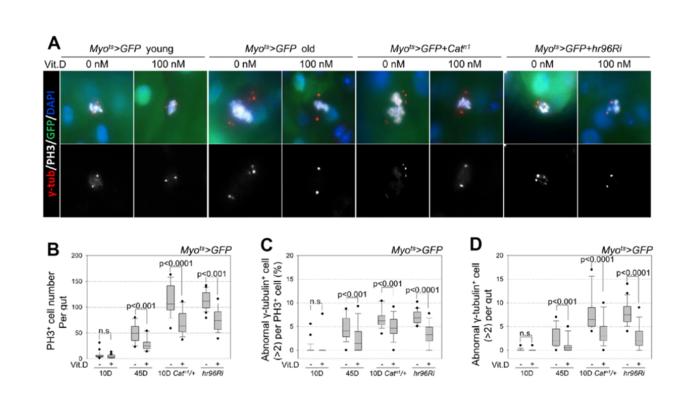
Adult stem cells are pivotal for maintaining tissue homeostasis, and their functional decline is linked to aging and its associated diseases, influenced by the niche cells’ environment. Age- and cancer-related reduction of vitamin D and its receptor levels are well documented in human clinical studies. However, the mechanisms through which the vitamin D/vitamin D receptor (VitD/VDR) pathway contributes to anti-aging and extends life expectancy are not well understood. In this new study, researchers Joung-Sun Park, Hyun-Jin Na and Yung-Jin Kim from Pusan National University and Korea Food Research Institute aimed to determine the protective role of the vitamin D/vitamin D receptor pathway in differentiated enterocytes (ECs) during intestinal stem cell (ISC) aging.
“This study aimed to determine the protective role of VitD/VDR in differentiated ECs during ISC aging using the adult Drosophila intestine model.”
By utilizing a well-established Drosophila midgut model for stem cell aging biology, the researchers revealed that vitamin D receptor knockdown in ECs induced ISC proliferation, EC death, ISC aging, and enteroendocrine cell differentiation. Additionally, age- and oxidative stress-induced increases in ISC proliferation and centrosome amplification were reduced by vitamin D treatment. In conclusion, this study provides direct evidence of the anti-aging role of the VitD/VDR pathway, involving protecting ECs during aging, and provides valuable insights for exploring the molecular mechanisms underlying enhanced healthy aging in Drosophila.
“Our findings suggest a direct evidence of the anti-aging role of the vitamin D/vitamin D receptor pathway and provides insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying healthy aging in Drosophila.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205518
Corresponding Author: Joung-Sun Park
Corresponding Email: [email protected]
Keywords: Drosophila, vitamin D, vitamin D receptor, anti-aging, intestinal stem cell
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- X, formerly Twitter
- YouTube
- Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205518
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
The anti-aging effect of vitamin D and vitamin D receptor in Drosophila midgut
Article Publication Date
7-Feb-2024




