From ‘The Terminator’ to ‘The Matrix’, Hollywood has taught us to be wary of artificial intelligence. But rather than sealing our doom on the big screen, algorithms could be the solution to at least one issue presented by the climate crisis.
Credit: Shutterstock/LuYago
From ‘The Terminator’ and ‘Blade Runner’ to ‘The Matrix’, Hollywood has taught us to be wary of artificial intelligence. But rather than sealing our doom on the big screen, algorithms could be the solution to at least one issue presented by the climate crisis.
Researchers at the ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science have successfully created a new type of machine learning model to predict the power-conversion efficiency (PCE) of materials that can be used in next-generation organic solar cells, including ‘virtual’ compounds that don’t exist yet.
Unlike some time-consuming and complicated models, the latest approach is quick, easy to use and the code is freely available for all scientists and engineers.
The key to developing a more efficient and user-friendly model was to replace complicated and computationally expensive parameters, which require quantum mechanical calculations, with simpler and chemically interpretable signature descriptors of the molecules being analysed. They provide important data about the most significant chemical fragments in materials that affect PCE, generating information that can be used to design improved materials.
The new approach could help to significantly speed up the process of designing more efficient solar cells at a time when the demand for renewable energy, and its importance in reducing carbon emissions, is greater than ever. The results have been published in the Nature journal Computational Materials.
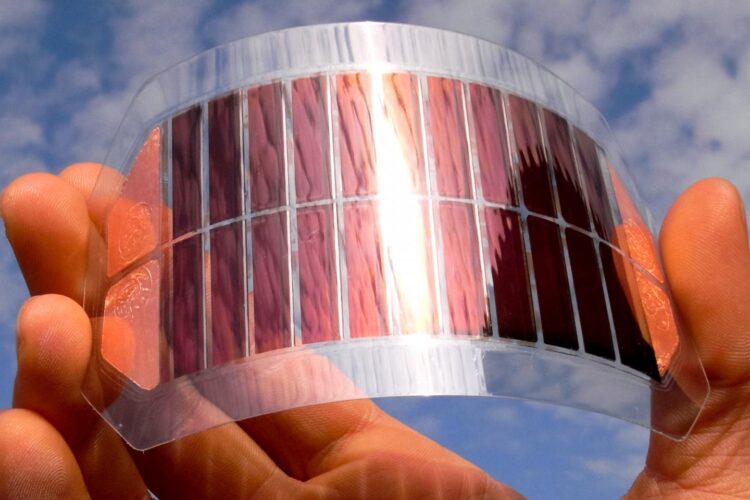
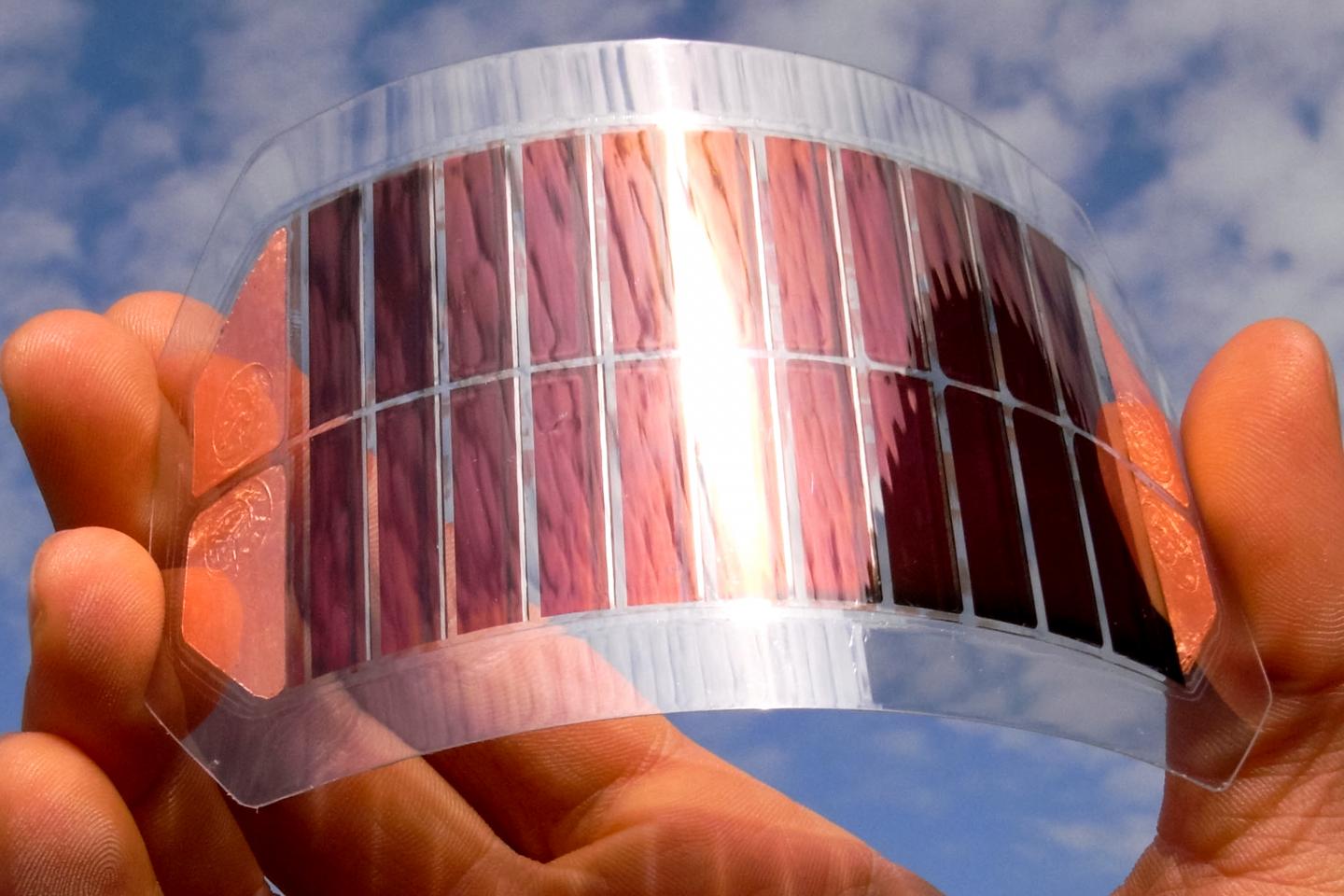
After decades of relying on silicon, which is relatively expensive and lacks flexibility, attention is increasingly turning to organic photovoltaic (OPV) solar cells, which will be cheaper to make by using printing technologies, as well as being more versatile and easier to dispose of.
A major challenge is sorting through the huge volume of potentially suitable chemical compounds that can be synthesised (tailor-made by scientists) for use in OPVs.
Researchers have tried using machine learning before to address this issue, but many of those models were time consuming, required significant computer processing power and were difficult to replicate. And, crucially, they did not provide enough guidance for the experimental scientists seeking to build new solar devices.
Now, work led by Dr Nastaran Meftahi and Professor Salvy Russo of RMIT University, in conjunction with Professor Udo Bach’s team at Monash University, has successfully addressed many of those challenges.
“The majority of the other models use electronic descriptors which are complicated and computationally expensive, and they’re not chemically interpretable,” Nastaran said.
“It means that the experimental chemist or scientist can’t get ideas from those models to design and synthesise materials in the lab. If they look at my models, because I used simple, chemically interpretable descriptors, they can see the important fragments.”
Nastaran’s work was strongly supported by her co-author Professor Dave Winkler of CSIRO’s Data 61, Monash University, La Trobe University, and the University of Nottingham. Professor Winkler co-created the BioModeller program which provided the basis for the new, open source model.
By using it, the researchers have been able produce results that are robust and predictive, and generate, among other data, quantitative relationships between the molecular signatures under examination and the efficiency of future OPV devices.
Nastaran and her colleagues now intend to extend the scope of their work to include bigger and more accurate computed and experimental datasets.
###
Media Contact
Iain Strachan
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.