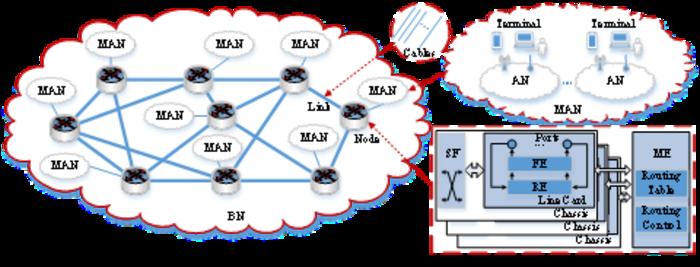
Most of the researches concentrated their efforts on power-aware networking under the non-bundled link scenarios by leveraging the dynamic power management based Low Power Idle (LPI) policy which was defined and standardized in the IEEE 802.3az standard. However, in modern backbone networks, pairs of routers are typically connected, for each traffic direction, by multiple physical links that form one logical bundled link, which is the link aggregation technique defined and standardized in IEEE 802.1AX.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Jinhong Zhang published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed the power-saving potential of the LPI policy and Traffic Engineering (TE) based green routing solution under the bundled link scenarios.
In the research, they achieved a fine-grained port-level optimization to address the problem of optimizing the total power consumption (PC) of the bundled link-based backbone network under the QoS constraints. Targeting the bundled link-based power-saving routing from a TE perspective, they devised the two-stage novel TE based Power-ware Greedy routing algorithm (TEPG). They split TEPG into two parts: the Hop-by-hop greedy routing stage (HHR) and the Traffic Assignment stage inside the Bundled links (TAB).
Firstly, In order to obtain a minimum network subset with as few powered-on elements as possible, they elaborated greedy routing by an available capacity of neighbor nodes based hop-by-hop routing stage (ACNN) and a greedy pruning stage (GP), then further power savings can be obtained by the Traffic Assignment stage inside the BLs (TAB). Experiments were carried out over a real backbone network topology-GéANT with 45 nodes and 73 links, and used the traffic profiles on links provided by SNDlib. Compared with the existing representative schemes, the proposed greedy heuristics exhibit significant network power savings and improved performance.
Future work can focus on building power-aware network architectures, and devising more effective routing algorithms to reduce the power consumption over the backbone networks.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2066-4
Credit: Jinhong ZHANG, Xingwei WANG, Ruixia LI, Bo YI, Min HUANG, Dongxing SHUI
Most of the researches concentrated their efforts on power-aware networking under the non-bundled link scenarios by leveraging the dynamic power management based Low Power Idle (LPI) policy which was defined and standardized in the IEEE 802.3az standard. However, in modern backbone networks, pairs of routers are typically connected, for each traffic direction, by multiple physical links that form one logical bundled link, which is the link aggregation technique defined and standardized in IEEE 802.1AX.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Jinhong Zhang published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed the power-saving potential of the LPI policy and Traffic Engineering (TE) based green routing solution under the bundled link scenarios.
In the research, they achieved a fine-grained port-level optimization to address the problem of optimizing the total power consumption (PC) of the bundled link-based backbone network under the QoS constraints. Targeting the bundled link-based power-saving routing from a TE perspective, they devised the two-stage novel TE based Power-ware Greedy routing algorithm (TEPG). They split TEPG into two parts: the Hop-by-hop greedy routing stage (HHR) and the Traffic Assignment stage inside the Bundled links (TAB).
Firstly, In order to obtain a minimum network subset with as few powered-on elements as possible, they elaborated greedy routing by an available capacity of neighbor nodes based hop-by-hop routing stage (ACNN) and a greedy pruning stage (GP), then further power savings can be obtained by the Traffic Assignment stage inside the BLs (TAB). Experiments were carried out over a real backbone network topology-GéANT with 45 nodes and 73 links, and used the traffic profiles on links provided by SNDlib. Compared with the existing representative schemes, the proposed greedy heuristics exhibit significant network power savings and improved performance.
Future work can focus on building power-aware network architectures, and devising more effective routing algorithms to reduce the power consumption over the backbone networks.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2066-4
Journal
Frontiers of Computer Science
DOI
10.1007/s11704-023-2066-4
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
TEPG: a traffic engineering based power-aware greedy routing algorithm in backbone networks with bundled links
Article Publication Date
15-Feb-2024




