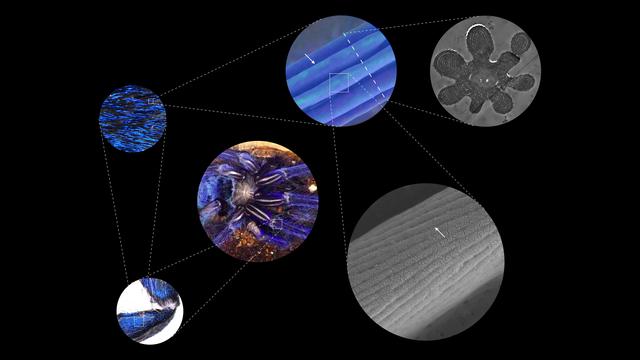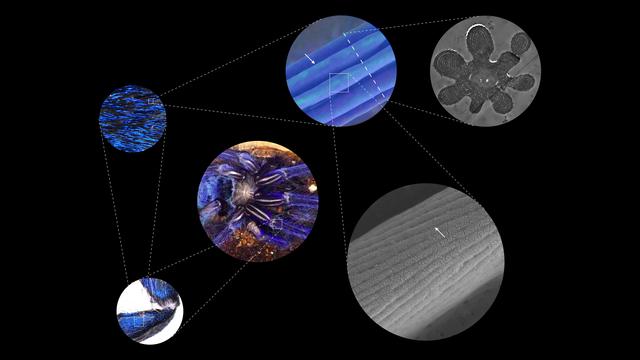
Credit: The University of Akron
Inspired by the hair of blue tarantulas, researchers from The University of Akron lead a team that made a structural-colored material that shows consistent color from all viewing directions. This finding overturns the conventional wisdom that long-range order photonic structures are always iridescent, opening new potential to mass produce structural colors because highly ordered designs are easy to scale-up and manufacture. Bor-Kai (Bill) Hsiung and his colleagues at UA, Ghent University, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln published their research, which is featured on the cover of the January 2017 journal of Advanced Optical Materials.
"Structural colors are more vibrant and durable than the pigments used in most human-made products," explained Hsiung, the lead author of this research and a Biomimicry Fellow in the Integrated Bioscience Ph.D. program at The University of Akron. "They are produced by optical effects when light interacts with nanostructures that are about the same size as the wavelength of light." Think of a peacock, or a butterfly. The problem is that most structural colors are strongly iridescent, changing color when viewed from different angles. It's beautiful out in nature, but not very functional when we're watching television and we move to a new seat."
The team first discovered that many vibrant blue tarantulas do not show iridescence even though the spiders use nanostructures to produce those colors. Since the spider's blue color is not iridescent, Hsiung's team suggested that the same process could be applied to make pigment replacements that never fade, as well as to help reduce glare on wide-angle viewing systems in phones, televisions and other devices.
As they dug deeper, they found that the hairs of some species of blue tarantulas show a special flower-like shape that they hypothesized reduced the iridescent effect resulting from periodic structures. Then, thanks to the crowdfunding push they received earlier, they were able to test this hypothesis using a series of computer simulations and physical prototypes built using cutting-edge nano-3D printing technology.
Their color produced by the 3D printed structures has a viewing angle of 160 degrees, the largest viewing angle of any synthetic structural colors demonstrated.
"These structural colorants could be used as pigment replacements – many of which are toxic – in materials such as plastics, metal, textiles and paper, and for producing color for wide-angle viewing systems such as phones and televisions," Hsiung said.
###
Media Contact
Lisa Craig
[email protected]
330-972-7429
@UAkronNews
http://www.uakron.edu/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag