This study is led by Prof. Ji Qian and Prof. Renjie Chen (Department of Energy and Environmental Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology). In this work, fluorinated cyclic carbonate (DFEC) is introduced into ether electrolyte as a SEI-forming additive. The modified electrolyte can improve the interface of Li metal anode and achieve high efficiency and long cycling stability of LMBs.
Credit: ©Science China Press
This study is led by Prof. Ji Qian and Prof. Renjie Chen (Department of Energy and Environmental Materials, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology). In this work, fluorinated cyclic carbonate (DFEC) is introduced into ether electrolyte as a SEI-forming additive. The modified electrolyte can improve the interface of Li metal anode and achieve high efficiency and long cycling stability of LMBs.
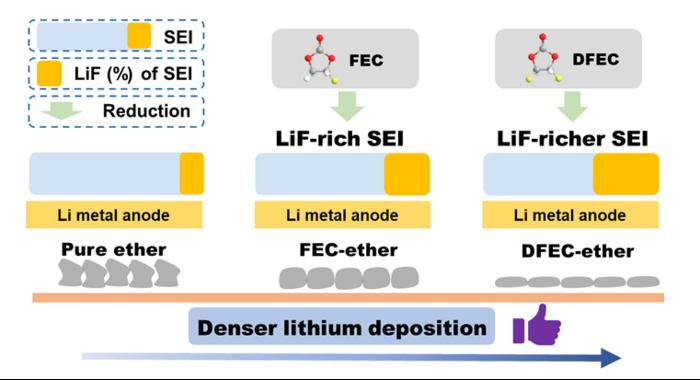
LMBs are regarded as the most promising next-generation battery system due to the high specific capacity (3860 mAh g−1) and low electrode potential (-3.04 V vs. SHE) of the Li metal anode. However, there are many limiting factors which limit the development of LMBs, as follows: side reaction between Li anode and electrolyte, Li dendrite growth and serious volume effect of Li anode, etc., which lead to low coulombic efficiency (CE) and poor cycle life. Stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) is the key to achieve high efficiency and long cycling stability of LMBs. Adjusting SEI through electrolyte optimization is regard as a low-cost and efficient way to improve Li metal anode interface. So, it is critical to design an electrolyte formulation which can form a stable SEI, the key is the choice of solvents and film-forming additive.
Recently, Prof. Renjie Chen and Prof. Ji Qian proposed an ether-ester mixed electrolyte in which trans-difluoroethylene carbonate (DFEC) was introduced into the ether electrolyte as a film-forming additive. Firstly, ether electrolyte has good anti-reduction stability with Li metal. Secondly, due to the lower LUMO level of DFEC, it can be preferentially reduced during the initial cycle, forming LiF-rich SEI on the Li metal anode. LiF-rich SEI can inhibit the growth of lithium dendrite, alleviate side reactions, and induce dense lithium deposition. Thanks to the above advantages, the LMBs using modified electrolyte show high efficiency and stable cycling performance. The first author of this paper is Tianyang Xue, a graduate student at Beijing Institute of Technology, and the corresponding authors are Prof. Renjie Chen, Prof. Ji Qian, and Prof. Xingming Guo.
A few implications thus emerge for designing an electrolyte to boost high efficiency and long cycling stability of LMBs. This work explores the interphase chemistry of LMBs, and provides important insights for further study on the novel electrolyte system for LMBs.
See the article:
Tailoring fluorine-rich solid electrolyte interphase to boost high efficiency and long cycling stability of lithium metal batteries.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-022-1623-2
Journal
Science China Chemistry
DOI
10.1007/s11426-022-1623-2




