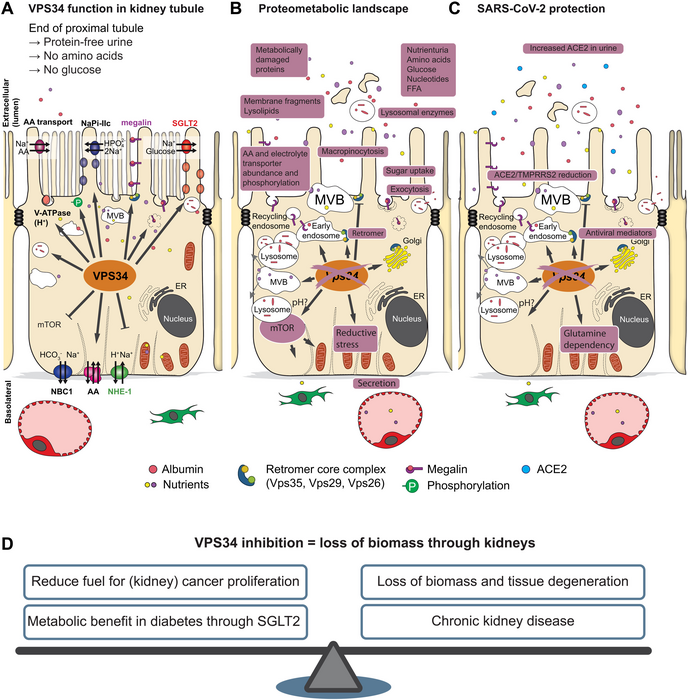
Our kidney filters 180 liters of blood every day and retains nutrients through a process called ‘endocytosis’ and through active transport in the kidney cells. In a new international study, an international team of researchers, led by Markus Rinschen from Aarhus Institute of Advanced Studies and the Department of Biomedicine at Aarhus University, investigated how this process of ‘endocytosis’ is regulated by a very central enzyme, the ‘lipid kinase’ VPS34, in mice. This lipid kinase is involved in vesicular trafficking and endocytic sorting of membrane proteins. A process that is crucial for the body to obtain the right nutrients, but also to block out the unhealthy ones, such a viruses.
Credit: Science Signaling: DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.abo7940
Our kidney filters 180 liters of blood every day and retains nutrients through a process called ‘endocytosis’ and through active transport in the kidney cells. In a new international study, an international team of researchers, led by Markus Rinschen from Aarhus Institute of Advanced Studies and the Department of Biomedicine at Aarhus University, investigated how this process of ‘endocytosis’ is regulated by a very central enzyme, the ‘lipid kinase’ VPS34, in mice. This lipid kinase is involved in vesicular trafficking and endocytic sorting of membrane proteins. A process that is crucial for the body to obtain the right nutrients, but also to block out the unhealthy ones, such a viruses.
Multiomics – combining multiple datasets
The researchers have applied a new method of ‘multiomics,’ an approach where multiple data sets are combined during analysis to provide a comprehensive view of cell physiology. This approach is hypothesis-free but can quantify the functions of many transporters and enzymes as well as their interactions – the entire system. This multiomics analysis of the study showed that a lack of lipid kinase in proximal tubule cells in mice lowered the abundance of nutrient transporters on the cell surface, which was associated with increased urinary loss of lipids, amino acids, sugars and proteins. In addition, the number of viral entry receptors on the cell surface was reduced. Accordingly, treatment with a lipid kinase inhibitor reduced the entry of the virus SARS-CoV-2 in cultured proximal tubular cells and human kidney organoids.
A gatekeeper for viral infections – Lipid kinase
The results of the study show that blocking of the enzyme lipid kinase could be used to treat diseases in which limiting the retention of nutrients gives clinical benefit, such as kidney cancer or diabetes, or to block a viral infection of the kidney.
‘Our primary goal in this study was to gather and organize novel knowledge of the fundamental processes of cell physiology. Although this is hypothesis-free, these comprehensive large-scale datasets can be central to understand medical problems. In this case, we ultimately improved targeted drug treatment for instance for kidney related diseases or infections,’ said Markus Rinschen, first-author of the study and Associate Professor at the Aarhus Institute of Advanced Studies and the Department of Biomedicine at Aarhus University. ‘Of course, more knowledge needs to be gathered before any conclusions regarding human relevance can be made.’
The study was a collaboration between researchers at Aarhus University, the University Hospital Hamburg Eppendorf, University of Kiel and University of Michigan.
Journal
Science Signaling
DOI
10.1126/scisignal.abo7940
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
VPS34-dependent control of apical membrane function of proximal tubule cells and nutrient recovery by the kidney
Article Publication Date
29-Nov-2022




