Credit: IEE
Regional severe haze in northern China is characterized by exceedingly high concentrations of fine particulate matter and exhibits extensive temporal and spatial coverage, thus influencing air quality, human health, and ecosystems. The causes of these severe haze events, however, are very complex and still debated.
A study led by AN Zhisheng from the Institute of Earth Environment (IEE), Chinese Academy of Sciences, published online in PNAS on April 15, reviews and synthesizes recent advances in the causes and formation mechanisms of severe haze pollution in northern China.
“The severe haze events in northern China can be regarded as synergetic effects from the interactions between anthropogenic emissions and atmospheric processes,” said AN.
Researchers found that the seasonally enhanced emissions of pollutants from residential heating and efficient secondary aerosol formation and transformation could cause severe haze.
Unfavorable meteorological conditions, for example, enhanced air static stability and shallow planetary boundary layer due to aerosol-radiation and aerosol-cloud interactions could also exacerbate the formation of severe haze, according to AN.
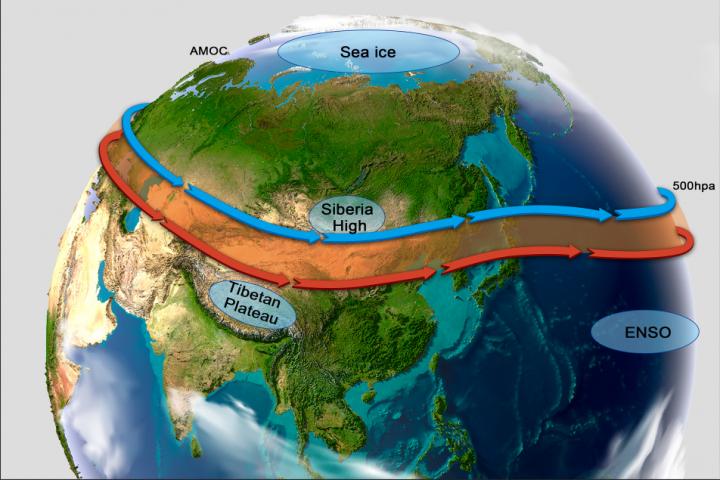
“In addition, the regional East Asian winter monsoon and westerly circulation, which are influenced by various factors, including variations of Arctic sea ice and the Siberian High, the topography of the Tibetan Plateau, and El Niño – Southern Oscillation, may also have significant influence on the formation of severe haze in northern China,” AN said.
Severe haze pollution in northern China provides a unique scientific platform for gaining insights into many aspects of the relevant atmospheric chemistry and physics.
The scientists call for additional research, including on the mechanisms leading to secondary aerosol formation and the chemical/physical transformation of primary and secondary aerosols during haze development as well as the interactions and feedback cycles between haze and meteorological/climatic conditions.
###
This work was supported by the National Research Program for Key Issues in Air Pollution Control, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, and the Robert A. Welch Foundation.
Media Contact
AN Zhisheng
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




