Researchers from Osaka University have described the link between accurate protein folding and misfolding that can lead to the formation of amyloid fibers, which are implicated in neurodegenerative diseases
Credit: Osaka University
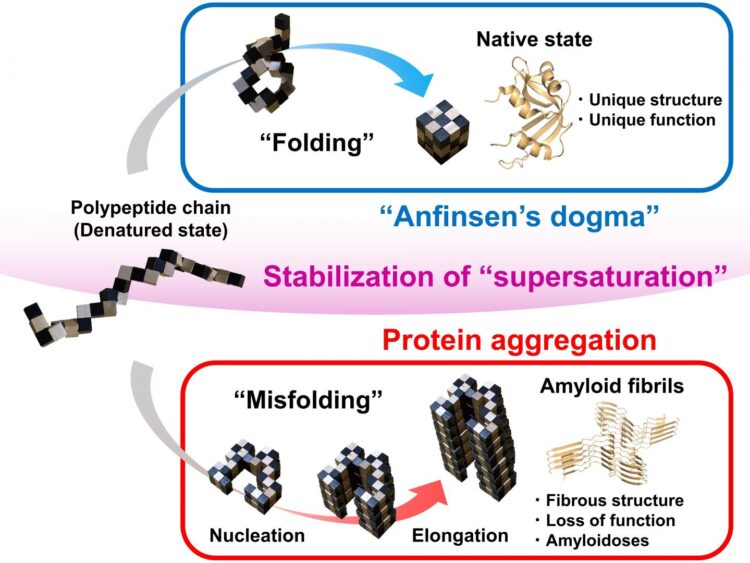
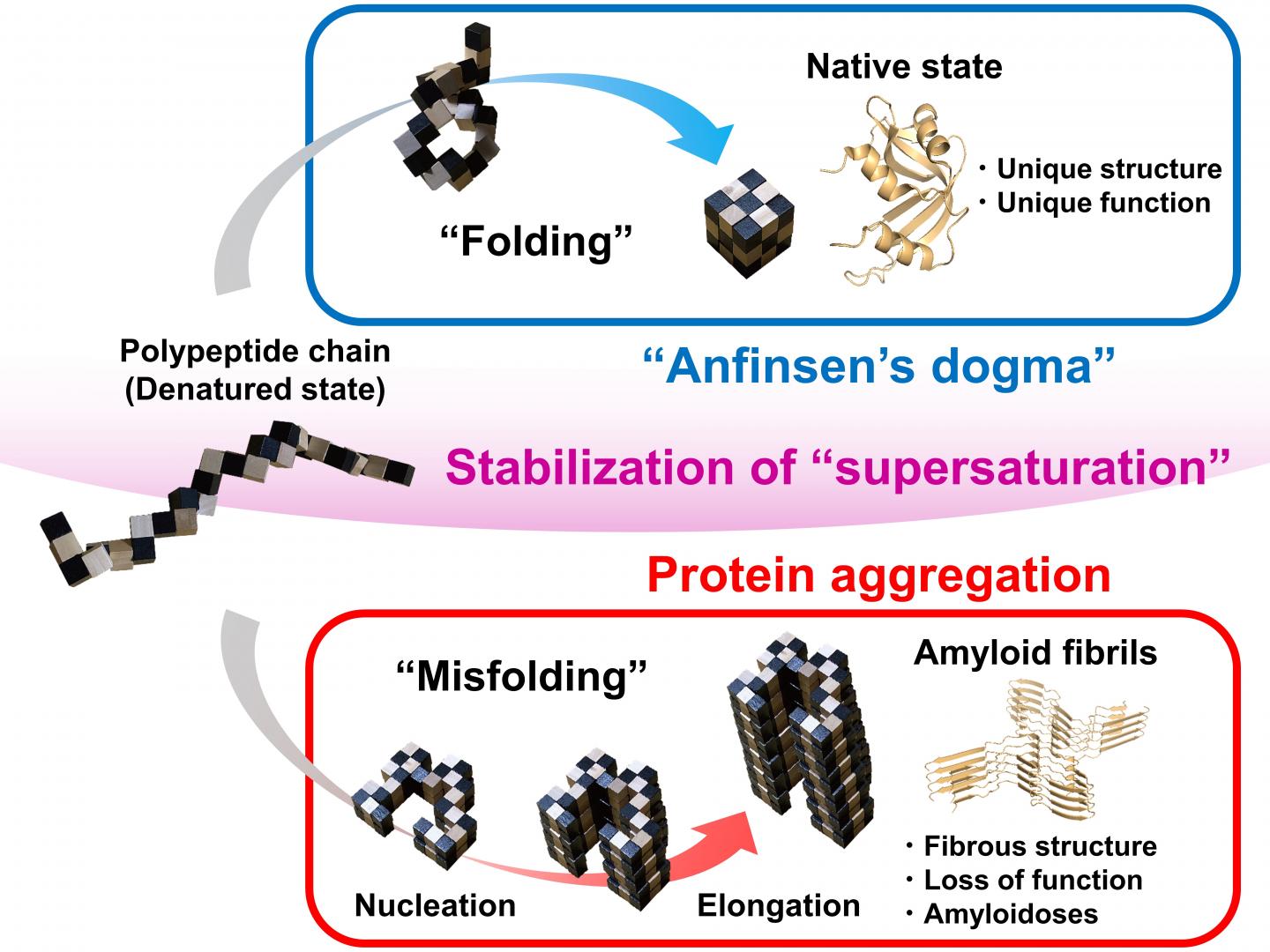
Correct, or native, protein folding is essential for correct protein function. Protein misfolding can lead to the formation of amyloid fibrils, and amyloidosis, which is implicated in various human neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s diseases. In this study Yuji Goto and colleagues describe, for the first time, a dynamic link between protein folding and misfolding, and the threshold that must be overcome for the formation of amyloid fibrils.
Technological advances are at the forefront of many scientific discoveries. The atomic structures of some amyloid fibrils were recently revealed as a result of advances in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance and cryogenic electron microscopy. While an important step forward for the field, this development does not fully explain the determining factors of protein misfolding. How are folding and misfolding related? Can folding/unfolding and amyloid polymerization/depolymerization be explained by a single mechanism, and if so what might this look like? These are the questions that researchers at Osaka University sought to answer.
Summarizing their motivation for this work, senior author Masahiro Noji explains: “The thermodynamic hypothesis of protein folding, known as the ‘Anfinsen’s dogma’ describes that the native structure of a protein represents a free energy minimum determined by the amino acid sequence. However, this is not consistent with the misfolding of globular proteins to form amyloid fibrils.” Therefore, Yuji Goto and colleagues set out to explore the link between protein folding and misfolding.
Although proteins perform their functions by folding to their native structures, as represented by Anfinsen’s dogma, proteins often misfold to form amyloid fibrils, leading to amyloidosis. In their paper, the research team from Osaka University describe a general concept for the link between protein folding and misfolding.
“The supersaturation barrier of a denatured protein separates protein folding and amyloid formation, and misfolding occurs when this barrier breaks down” corresponding author Yuji Goto says. “Our results show a clear link between correct protein folding, as defined by Anfinsen’s dogma, and protein misfolding.”
Supersaturation can be observed throughout nature in the formation of crystals, including those involved in ice formation. Here, the team at Osaka University show that supersaturation is fundamental to correct protein folding. The supersaturation barrier represents a novel concept that will advance the field of protein folding and contribute to the development of therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat amyloidosis, including those involved in neurodegenerative diseases.
###
The article, “Breakdown of supersaturation barrier links protein folding to amyloid formation,” was published in Communications Biology at DOI: https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan’s most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.