Credit: IBS
Climate scientists from the IBS Center for Climate Physics discover that, contrary to previously held beliefs, Neanderthal extinction was neither caused by abrupt glacial climate shifts, nor by interbreeding with Homo sapiens. According to new supercomputer model simulations, only competition between Neanderthals and Homo sapiens can explain the rapid demise of Neanderthals around 43 to 38 thousand years ago.
Neanderthals lived in Eurasia for at least 300,000 years. Then, around 43 to 38 thousand years ago they quickly disappeared off the face of the earth, leaving only weak genetic traces in present-day Homo sapiens populations. It is well established that their extinction coincided with a period of rapidly fluctuating climatic conditions, as well as with the arrival of Homo sapiens in Europe. However, determining which of these factors was the dominant cause, has remained one of the biggest challenges of evolutionary anthropology.
To quantify which processes played a major role in the collapse of Neanderthal populations one needs to use mathematical models that can realistically simulate the migration of Neanderthals and Homo sapiens, their interactions, competition and interbreeding in a changing climatic environment. Such models did not exist previously.
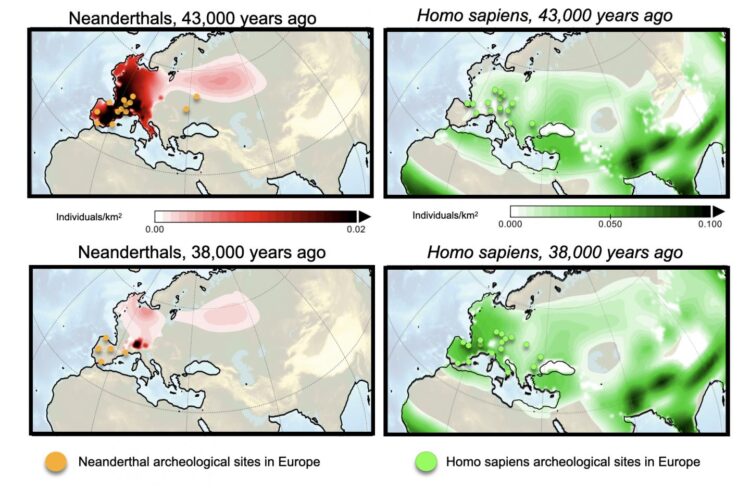
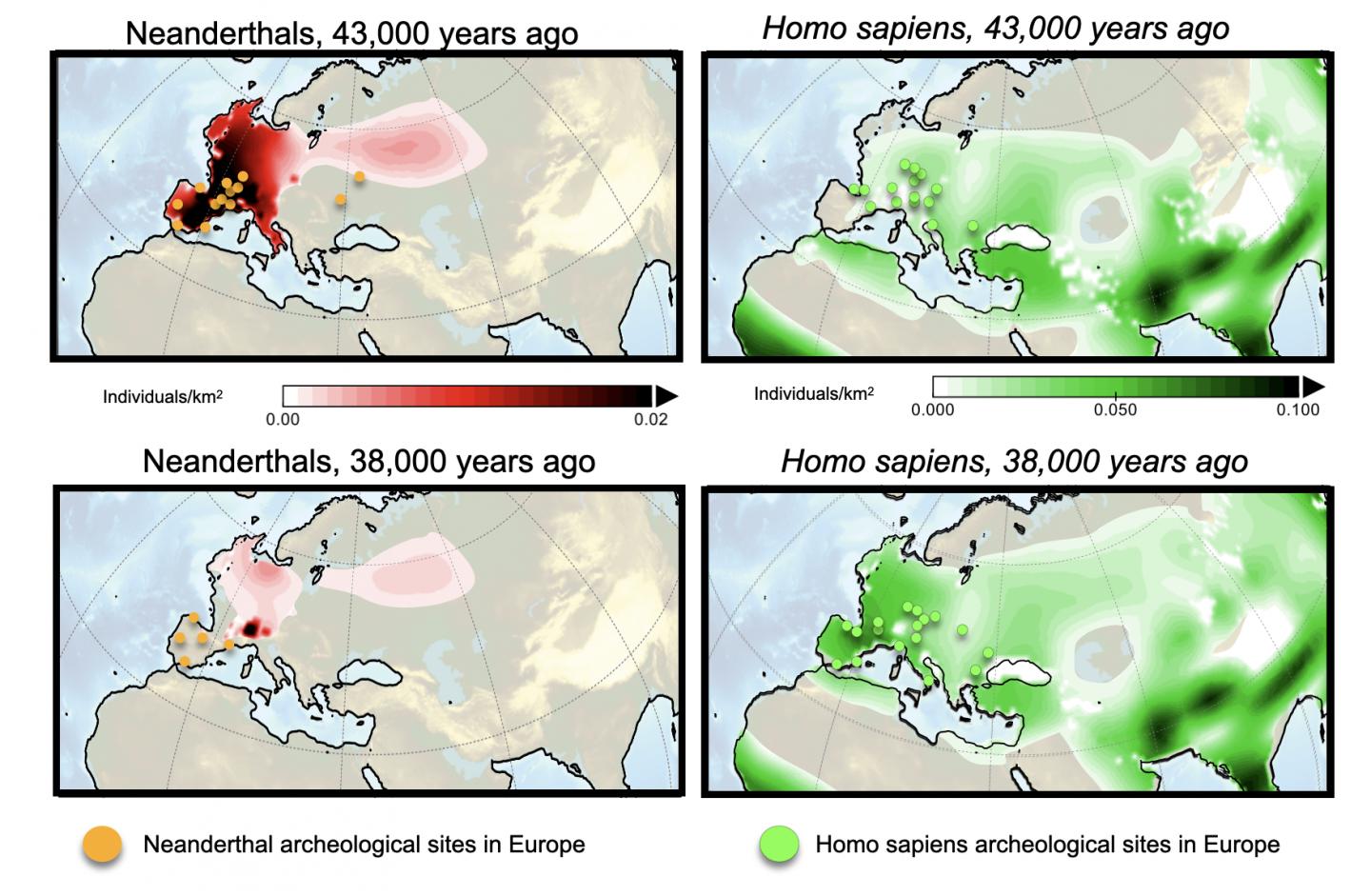
In a new paper published in the journal Quaternary Science Review, Axel Timmermann, Director of the IBS Center for Climate Physics at Pusan National University, presents the first realistic computer model simulation of the extinction of Neanderthals across Eurasia (Figure 1). The model which is comprised of several thousands of lines of computer code and is run on the IBS supercomputer Aleph, solves a series of mathematical equations that describe how Neanderthals and Homo sapiens moved in a time-varying glacial landscape and under shifting temperature, rainfall and vegetation patterns. In the model both hominin groups compete for the same food resources and a small fraction is allowed to interbreed. The key parameters of the model are obtained from realistic climate computer model simulations, genetic and demographic data.
“This is the first time we can quantify the drivers of Neanderthal extinction,” said Timmermann. “In the computer model I can turn on and off different processes, such as abrupt climate change, interbreeding or competition” he said. By comparing the results with existing paleo-anthropological, genetic and archeological data (e.g. Figure 1), Timmermann demonstrated that a realistic extinction in the computer model is only possible, if Homo sapiens had significant advantages over Neanderthals in terms of exploiting existing food resources. Even though the model does not specify the details, possible reasons for the superiority of Homo sapiens could have been associated with better hunting techniques, stronger resistance to pathogens or higher level of fecundity.
What exactly caused the rapid Neanderthal demise has remained elusive for a long time. This new computer modeling approach identifies competitive exclusion as the likely reason for the disappearance of our cousins. “Neanderthals lived in Eurasia for the last 300,000 years and experienced and adapted to abrupt climate shifts, that were even more dramatic than those that occurred during the time of Neanderthal disappearance. It is not a coincidence that Neanderthals vanished just at the time, when Homo sapiens started to spread into Europe” says Timmermann. He adds “The new computer model simulations show clearly that this event was the first major extinction caused by our own species”.
A research team at the IBS Center for Climate Physics is now improving the computer model to also include megafauna and implement more realistic climate forcings. “This is a new field of research in which climate scientists can interact with mathematicians, geneticists, archeologists and anthropologists”, said Axel Timmermann.
###
Media Contact
Axel Timmermann
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.