Credit: David Hunt/University of Rochester
Teenage girls who were maltreated as children are more likely to entertain suicidal thoughts if the relationship with their mother is poor and the degree of conflict between the two of them high.
Researchers at the University of Rochester's Mt. Hope Family Center found that the quality of the mother-daughter relationship and their level of conflict are two direct mechanisms underlying the association between child maltreatment and suicidal thoughts during adolescence.
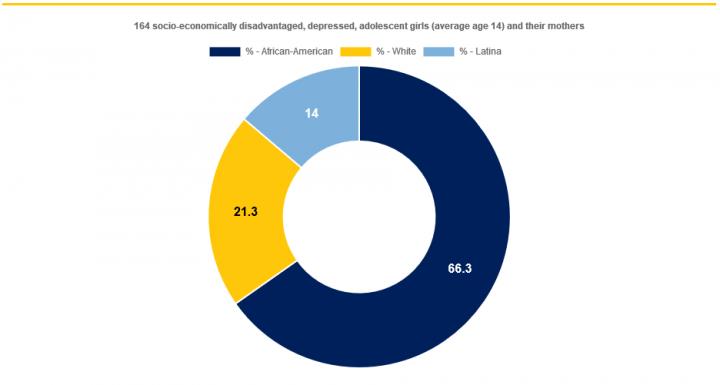
Their study, published in the journal Suicide and Life Threatening Behavior, included 164 socio-economically disadvantaged, depressed, adolescent girls (average age 14) and their mothers. Of the adolescents, 66.3 percent were African-American, 21.3 percent white, and 14 percent Latina.
The team, led by Mt. Hope research assistant professor Elizabeth Handley, used structural equation modeling to test three distinct mediating pathways that linked earlier maltreatment in childhood to suicidal thoughts for adolescent girls: 1) mother-daughter relationship quality, 2) mother-daughter conflict, and 3) adolescent depressive symptoms.
"Our findings suggest that disruptions to a positive mother-teen relationship are one reason why children who experienced abuse or neglect are at risk for suicide as teens," says lead author Handley.
According to Handley, the findings highlight how important relationship-based interventions are for vulnerable youths.
The researchers assessed child maltreatment and mother-daughter relationship quality by looking at the teens' responses to a series of questions. Mother-daughter conflict was measured by using their mothers' answers to another questionnaire.
"We know from decades of research that a warm, nurturing, and consistent relationship between mothers and their children is critical for many aspects of healthy development. This continues to be true even in adolescence, when teens spend more time with their friends and less time at home with family," says Handley.
Maltreatment includes emotional, physical, and sexual abuse, and emotional and physical neglect. Among the study participants 51.8% of adolescents indicated a history of at least one form of maltreatment.
As expected, the researchers found that rates of suicidal thoughts and recurrent thoughts of death were higher among teenage girls with a history of maltreatment than those without: 11.7 percent of non-maltreated, depressed adolescents indicated suicidal ideation, compared to 26.8 percent of maltreated, depressed adolescents.
Child maltreatment is associated with poorer mother-daughter relationship quality and increased mother-daughter conflict, both of which are linked with higher levels of suicidal thoughts among teenagers.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), suicide is the second leading cause of death among adolescents aged 10 to 24 in the United States (accidental death is the leading cause). Adolescent girls in general are more likely than their male counterparts to have suicidal thoughts.
Given the scientific evidence that the more severe and pervasive the suicidal thoughts, the greater the likelihood of suicide attempt, understanding the cause of suicidal thoughts is critical for effective youth suicide prevention and intervention design.
According to the Rochester researchers, relationship-based interventions are a promising approach to depression treatment for maltreated youth, such as interpersonal psychotherapy for adolescents, which focuses on the interpersonal context of depression. Attachment-based family therapy has also proven useful in reducing suicidal thoughts among teenagers by strengthening the functioning of the family and the parent-adolescent attachment relationship.
The Mt. Hope study, which received funding from the National Institute on Mental Health (NIMH), was conducted by researchers at the University of Rochester's Mt. Hope Family Center and the University of Minnesota: lead author Handley was joined by Mt. Hope's Tangeria Adams, Jody Todd Manly, and Sheree Toth, and Minnesota's Dante Cicchetti.
###
Media Contact
Sandra Knispel
[email protected]
585-200-7571
@UofR
http://www.rochester.edu
Original Source
http://www.rochester.edu/newscenter/suicide-risk-in-abused-teen-girls-correlates-directly-with-mother-daughter-relationship-344512/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/sltb.12522