Ikoma, Japan – Scientists from the Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute international, and Tamagawa University have demonstrated that obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) can be understood as a result of imbalanced learning between reinforcement and punishment. On the basis of empirical tests of their theoretical model, they showed that asymmetries in brain calculations that link current results to past actions can lead to disordered behavior. Specifically, this can happen when the memory trace signal for past actions decays differently for good and bad outcomes. In this case, “good” means the result was better than expected, and “bad” means that it was worse than expected. This work helps to explain how OCD develops.
Credit: Saori C. Tanaka
Ikoma, Japan – Scientists from the Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Advanced Telecommunications Research Institute international, and Tamagawa University have demonstrated that obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) can be understood as a result of imbalanced learning between reinforcement and punishment. On the basis of empirical tests of their theoretical model, they showed that asymmetries in brain calculations that link current results to past actions can lead to disordered behavior. Specifically, this can happen when the memory trace signal for past actions decays differently for good and bad outcomes. In this case, “good” means the result was better than expected, and “bad” means that it was worse than expected. This work helps to explain how OCD develops.
OCD is a mental illness involving anxiety, characterized by intrusive and repetitious thoughts, called obsessions, coupled with certain repeated actions, known as compulsions. Patients with OCD often feel unable to change behavior even when they know that the obsessions or compulsions are not reasonable. In severe cases, these may render the person incapable of leading a normal life. Compulsive behaviors, such as washing hands excessively or repeatedly checking whether doors are locked before leaving the house, are attempts to temporarily relieve anxiety caused by obsessions. However, hitherto, the means by which the cycle of obsessions and compulsions becomes strengthened was not well understood.
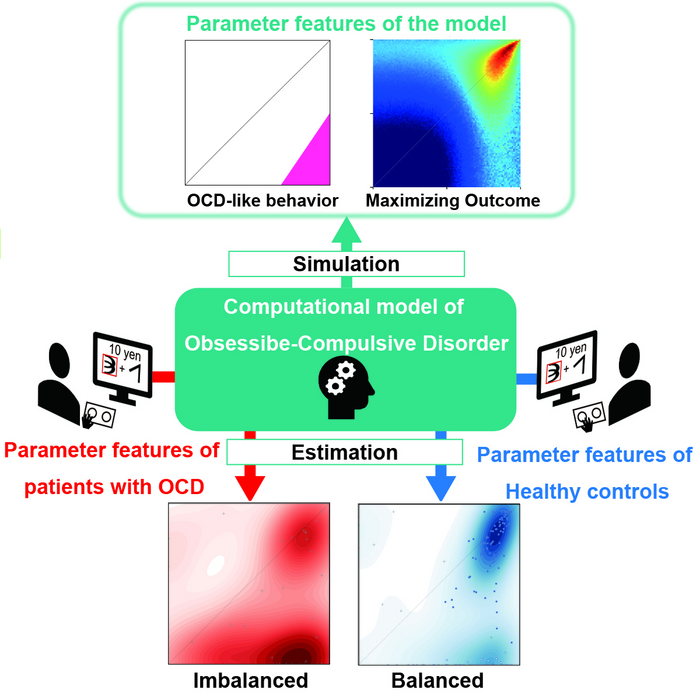
Now, a team led by researchers at NAIST has used reinforcement learning theory to model the disordered cycle associated with OCD. In this framework, an outcome that is better than predicted becomes more likely (positive prediction error), while a result that is worse than expected is suppressed (negative prediction error). In implementation of reinforcement learning, it is also important to consider delays, as well as positive/negative prediction errors. In general, the outcome of a certain choice is available after a certain delay. Therefore, reinforcement and punishment should be assigned to recent choices within a certain time frame. This is called credit assignment, which is implemented as a memory trace in reinforcement learning theory. Ideally, memory trace signals for past actions decay at equal speed for both positive and negative prediction errors. However, this cannot be completely realized in discrete neural systems. Using simulations, NAIST scientists found that agents implicitly learn obsessive-compulsive behavior when the trace decay factor for memory traces of past actions related to negative prediction errors (–) is much smaller than that related to positive prediction errors (+). This means that, from the opposite perspective, the view of past actions is much narrower for negative prediction errors than for positive prediction errors. “Our model, with imbalanced trace decay factors (+ > –) successfully represents the vicious circle of obsession and compulsion characteristic of OCD”, say co-first authors Yuki Sakai and Yutaka Sakai.
To test this prediction, the researchers had 45 patients with OCD and 168 healthy control subjects play a computer-based game with monetary rewards and penalties. Patients with OCD showed much smaller – compared with +, as predicted by computational characteristics of OCD. In addition, this imbalanced setting of trace decay factors (+ > –) was normalized by serotonin enhancers, which are first-line medications for treatment of OCD. “Although we think that we always make rational decisions, our computational model proves that we sometimes implicitly reinforce maladaptive behaviors,” says corresponding author, Saori C. Tanaka.
Although it is currently difficult to identify treatment-resistant patients based upon their clinical symptoms, this computational model suggests that patients with highly imbalanced trace decay factors may not respond to behavioral therapy alone. These findings may one day be used to determine which patients are likely to be resistant to behavioral therapy before commencement of treatment.
###
Resource
Title: Memory trace imbalance in reinforcement and punishment systems can reinforce implicit choices leading to obsessive-compulsive behavior
Authors: Yuki Sakai*, Yutaka Sakai*, Yoshinari Abe, Jin Narumoto & Saori C. Tanaka (*co-first authors)
Journal: Cell Reports
Information about the Computational Behavioral Neuroscience Laboratory can be found at the following website: http://isw3.naist.jp/Research/ai-cbn-en.html
Journal
Cell Reports
DOI
10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111275
Article Title
Memory trace imbalance in reinforcement and punishment systems can reinforce implicit choices leading to obsessive-compulsive behavior




