Credit: Sonia Jancar / University of São Paulo
Whenever an organism is damaged, the cells surrounding the wound receive signals to proliferate more intensely so as to regenerate the injured tissue. Same goes with cancer — tumor cells may be all but eliminated by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy, only to return even more aggressively some time later.
The phenomenon of tumor repopulation is explained by a protein called PAF-R (platelet activating factor receptor), which plays a key role in the process, according to a project by a group of researchers at the University of São Paulo's Biomedical Science Institute (ICB-USP) — supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) — headed by principal investigator, Professor Sonia Jancar.
Jancar pointed the doctorate thesis by Ildefonso Alves da Silva-Junior which showed that — at least for the types of cancer studied by the ICB-USP group — radiation led to the production of molecules similar to PAF, which activated PAF-R in tumor cells, driving increased expression of PAF-R and tumor cell proliferation.
"So this activation promoted tumor repopulation. Using more sensitive methods, the study also confirmed that when the macrophages (a type of defense cell) present in the tumor microenvironment were treated with PAF-R-blocking drugs, they were reprogrammed to combat the disease more effectively."
The experiments that proved the involvement of PAF-R in tumor repopulation were performed with human oral cancer cells and murine cervical cancer cells, in which radiotherapy is usually preferred. However, scientists found that large numbers of molecules similar to PAF-R were produced in the cultures shortly after irradiating the cells in a radiotherapy simulation. "PAF is actually a phospholipid produced mainly in inflammatory and cell death processes," Silva-Junior explained.
The researchers then treated some of the cultured cells with PAF-R-blocking drugs. Various molecules were tested, including some that were already commercially available but had never been used against cancer.
Analysis performed shortly afterwards showed up one-third more death from radiotherapy among the cells exposed to PAF-R antagonists than among untreated cells. Another analysis performed nine days later showed a much higher rate of cell proliferation in untreated lines, which multiplied about 1.5 times as much as cells treated with PAF-R antagonists.
"In experiments with tumor cell lines and mice, we found that PAF-R-blocking drugs significantly inhibited tumor growth and repopulation after radiotherapy," Jancar said. "We therefore suggested associating radiotherapy with antagonists of this receptor as a promising new therapeutic strategy."
Proliferation rate in PAF-R-expressing tumor cells
Next they injected under the skin of mice irradiated tumor cells of two lines of genetically modified tumor cells: one that overexpressed PAF-R and other that didn't express PAF-R at all, with the aim of observing the phenomenon of tumor repopulation in vivo. Researchers measured tumor volume at about 30 days after the cells were injected.
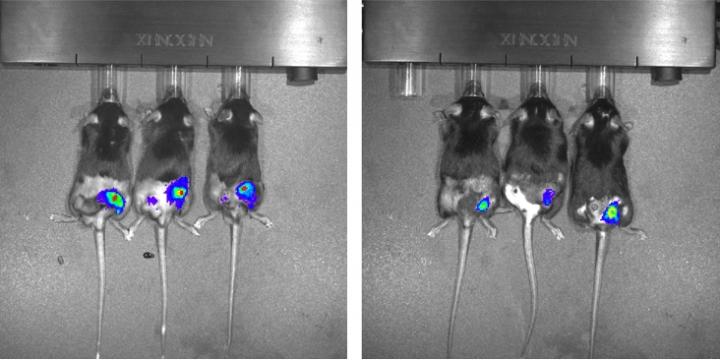
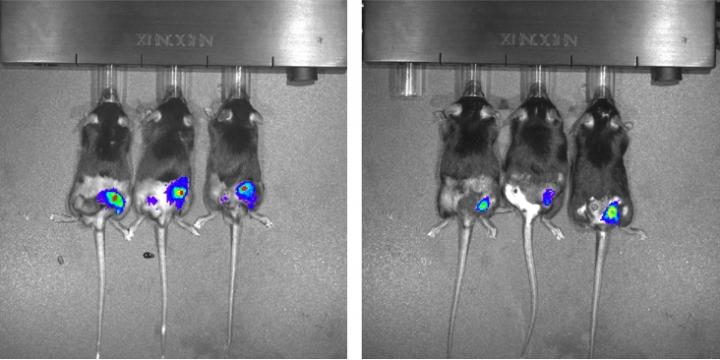
Then, mice were injected with tumor cells and a type of control cell genetically modified to express a light-emitting enzyme that served as a marker inside tumors. "The control cells were not irradiated, but they were exposed to the same environment and received the signals produced by the tumor to stimulate cell proliferation," Silva-Junior said.
"We used an in vivo imaging system, or IVIS, to measure the proliferation of these luminescent cells and calculate the extent to which irradiation was inducing tumor repopulation." The results showed that the proliferation rate in the animals injected with irradiated cells that overexpressed PAF-R was 30 times higher than in those injected with non-irradiated cells of the same line.
Some of their results were published in January in Nature's outlet Oncogenesis.
Clinical trials
Sonia Jancar added that the ideal approach would be to return to clinical trials of PAF-R antagonists performed in the 1980s with patients with asthma or pancreatitis.
"For these diseases, the trials were negative, but they could be positive against cancer. I hope our publications alert other researchers in the same field so that they can take this step. Meanwhile, we're evaluating ways of protecting our findings," she said.
To find out whether the results were specific to the tumor cell lines studied to date, the researchers at ICB-USP are now replicating the experiments with ten other kinds of human tumor and performing trials in which PAF-R antagonists are tested in combination with chemotherapy drugs.
The researchers are also testing new kinds of PAF-R inhibitors on the tumor cell lines, including a group of molecules isolated from a marine fungus by Professor Roberto Berlinck and his team at the São Carlos Chemistry Institute in the interior of São Paulo State.
"Several of these molecules have proved to be powerful PAF-R antagonists and capable of inhibiting tumor repopulation," Jancar said. "Although the discovery is important, the road to validation and use in clinical trials is long and requires collaboration among researchers in basic science like us, chemists to synthesize molecules, and clinicians to test them in healthy subjects and in patients."
###
According to Jancar, this line of research began in the 1990s during Denise Fecchio's PhD studies, when the group showed that tumors induced in the peritoneal cavity of mice grew significantly less when PAF-R was blocked. In that project, the researchers found that treatment with PAF-R antagonists activated macrophages and inhibited tumor growth. The results were published in Inflammation.
Some years later, during Soraya Imon de Oliveira's PhD research in collaboration with Roger Chammas, a professor in the University of São Paulo's Medical School (FM-USP), the group showed that tumors also grew less in mice treated with PAF-R antagonists. The results were published in BMC Cancer.
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known by the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. For more information: http://www.fapesp.br/en.
Media Contact
Heitor Shimizu
[email protected]
55-113-838-4223
@AgencyFAPESP
http://www.fapesp.br
Original Source
http://agencia.fapesp.br/brazilian_researchers_propose_new_strategy_to_treat_cancer/25955/