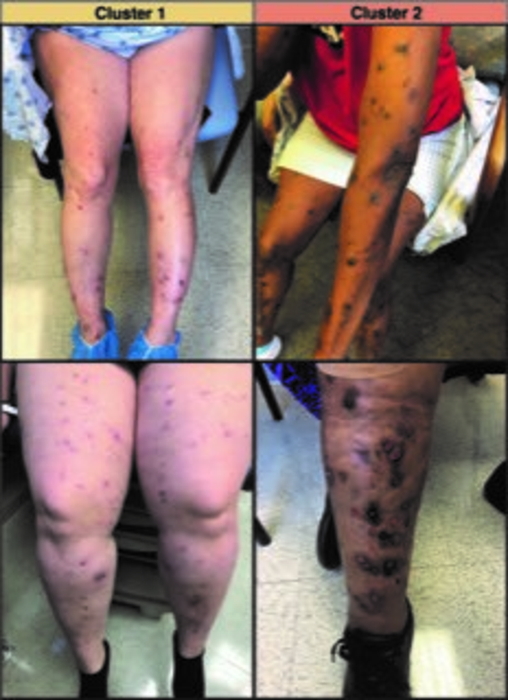
Prurigo nodularis (PN) is a chronic skin disease that affects an estimated 72 out of 100,000 people in the U.S. The disease disproportionately affects Black patients and other minority groups. Patients with PN have intensely itchy nodules on their arms and legs, which greatly impact their quality of life. Johns Hopkins researchers identified two distinct clusters of patients with PN: those who had increased inflammation in the blood, and those who did not but were more likely to have a history of spinal disease, which may sensitize the nerves. Identifying those with unique types of inflammation may help doctors provide more precise and personalized treatment for the disorder.
In a study published Oct. 27 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, Shawn Kwatra, M.D., an assistant professor of dermatology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and his colleagues determined there are patients who have differences in their bodies’ inflammation profiles.
Credit: Shawn Kwatra
Prurigo nodularis (PN) is a chronic skin disease that affects an estimated 72 out of 100,000 people in the U.S. The disease disproportionately affects Black patients and other minority groups. Patients with PN have intensely itchy nodules on their arms and legs, which greatly impact their quality of life. Johns Hopkins researchers identified two distinct clusters of patients with PN: those who had increased inflammation in the blood, and those who did not but were more likely to have a history of spinal disease, which may sensitize the nerves. Identifying those with unique types of inflammation may help doctors provide more precise and personalized treatment for the disorder.
In a study published Oct. 27 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, Shawn Kwatra, M.D., an assistant professor of dermatology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and his colleagues determined there are patients who have differences in their bodies’ inflammation profiles.
“In Black patients with PN, we have noticed thicker, more fibrotic nodules, so we hypothesized that there would be a unique inflammatory signature in the blood,” Kwatra says. “We also have noticed that some patients respond very well to immune modulating therapies while some patients do not, so this study shows there are patients who have varying degrees of immune and neural dysregulation that have implications for personalized treatment.”
Using algorithms on a broad panel of patients’ bloodwork, Kwatra and his colleagues were able to characterize different patterns of cytokines — small proteins in the blood that regulate inflammation in the body and help control the immune system.
They found two distinct clusters: noninflammatory plasma profiles, in which patients had a greater likelihood of spinal disease (Cluster 1), and inflammatory plasma profiles (Cluster 2). Cluster 1 included fewer minority patients who had a higher rate of myelopathy (an injury to the spinal cord due to severe compression). Cluster 2 included more Black patients who had a higher severity of itch.
By identifying these clusters, doctors gain better insight into selecting appropriate treatments that are personalized for PN patients with medications that primarily treat inflammation versus medications that treat those with myelopathy.
“We’ve known that therapy cannot be a one-size-fits-all approach,” says Kwatra. “The goal is to understand what is unique to every patient so we can use precision medicine to tailor treatment, and this data reinforces why this is so important.”
Kwatra hopes to next study a larger cohort of patients to gather more information and build on this research.
Kwatra is available for interviews.
Journal
Journal of Investigative Dermatology




