Overview:
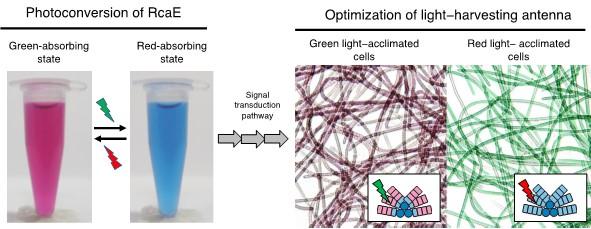
Certain cyanobacteria can change the absorbing light colors for photosynthesis using a green- and red-light sensing photosensor protein. A Japanese research group elucidated the molecular structure of RcaE, a representative member of the photosensors. They revealed the unique conformation of the bilin chromophore and the unique protein structure that potentially functions as a proton transfer route to bilin. They also demonstrated that RcaE undergoes protonation and deprotonation of the bilin chromophore during the green and red photoconversion. These results provide insights into how cyanobacteria evolved photosensors with diverse spectral sensitivities and contribute to the development of new photoswitches of gene expression.
Details:
Certain cyanobacteria can utilize both green and red lights for photosynthesis by using their light-harvesting antenna supercomplex called phycobilisome. They can control the absorptive maxima of phycobilisome, which results in remarkable changes in cell color. This phenomenon is regulated by RcaE that belongs to cyanobacteriochrome family of photosensors. RcaE harbors a bilin chromophore and photoconverts green- and red-absorbing states to sense ambient light colors. Although the green and red photoconversion is involved in bilin photoisomerization and subsequent change in bilin protonation state, the structural basis of this photoconversion remains unknown.
The research group demonstrated by molecular dynamic simulations that the water molecules in the cavity were exchanged with the solvent water. They also demonstrated by 15N NMR spectroscopy that four pyrrole nitrogen atoms of bilin are fully protonated in the red-absorbing state, whereas one nitrogen atom is deprotonated in the green-absorbing state. They assume that the unique porous cavity functioned as a proton exit or inlet pathway during the green and red photoconversion. Considering previous study reports on Raman spectroscopy of RcaE, they proposed that bilin deprotonation occurred in the B-ring nitrogen with the C15-Z,anti structure. They are currently working on the crystallization of the green-absorbing state of RcaE to confirm this model.
Elucidating the structure and spectral tuning mechanisms of RcaE provides insights into how cyanobacteria have evolved diverse cyanobacterial subfamilies to acclimate to different light environments. Green and red light-sensing cyanobacteriochromes have been utilized in synthetic biology as sophisticated photoswitches that control gene expression. Amino acid residue modification based on RcaE structure will contribute to the development of new photoswitches with desirable photosensitivities.
###
Reference:
Structural basis of the protochromic green/red photocycle of the chromatic acclimation sensor RcaE.
Nagae T, Unno M, Koizumi T, Miyanoiri Y, Fujisawa T, Masui K, Kamo T, Wada K, Eki T, Ito Y, Hirose Y, Mishima M. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 118(20), e2024583118, (2021) doi: 10.1073/pnas.2024583118.
Media Contact
Yuko Ito
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.