NEW YORK, January 12, 2024 — Proteins do the heavy lifting of performing biochemical functions in our bodies by binding to metabolites or other proteins to complete tasks. To do this successfully, protein molecules often shape-shift to allow specific binding interactions that are needed to perform complex, precise chemical processes.
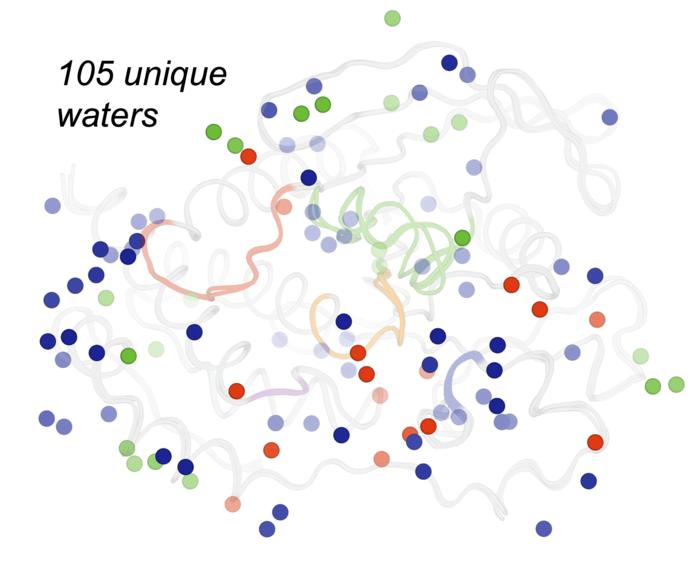
Credit: Ali Ebrahim & Liliana Guerrero
NEW YORK, January 12, 2024 — Proteins do the heavy lifting of performing biochemical functions in our bodies by binding to metabolites or other proteins to complete tasks. To do this successfully, protein molecules often shape-shift to allow specific binding interactions that are needed to perform complex, precise chemical processes.
A better understanding of the shapes proteins take on would give researchers important insight into stopping or treating diseases, but current methods for revealing these dynamic, three-dimensional forms offer scientists limited information. To address this knowledge gap, a team from the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) designed an experiment to test whether performing X-ray crystallography imaging using elevated temperature versus elevated pressure would reveal distinct shapes. The results of the team’s work appear in the journal Communications Biology.
“Protein structures don’t sit still; they shift between several similar shapes much like a dancer,” said the study’s principal investigator Daniel Keedy, Ph.D., a professor with the CUNY ASRC’s Structural Biology Initiative and a chemistry and biochemistry professor at The City College of New York and the CUNY Graduate Center. “Unfortunately, existing approaches for viewing proteins only reveal one shape, or suggest the presence of multiple shapes without providing specific details. We wanted to see if different ways of poking at a protein could give a us a more detailed view of how it shape-shifts.”
For their experiment, the team obtained crystals of STEP, also known as PTPN5—a drug target protein for the treatment of several diseases, including Alzheimer’s—and agitated them using either high pressure (2,000 times the Earth’s atmospheric pressure) or high temperature (body temperature), both of which are very different from typical crystallography experiments at atmospheric pressure and cryogenic temperature (-280 F, -173 C). The researchers viewed the samples using X-ray crystallography and observed that high temperature and high pressure had different effects on the protein, revealing distinct shapes.
While high pressure isn’t a condition that proteins experience inside the body, Keedy said the agitation method exposed different structural states of the protein that may be relevant to its activity in human cells.
“Having the ability to use perturbations such as heat and pressure to elucidate these different states could give drug developers tools for determining how they can trap a protein in a particular shape using a small-molecule drug to diminish its function,” Keedy added.
About the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center
The Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) is a world-leading center of scientific excellence that elevates STEM inquiry and education at CUNY and beyond. The CUNY ASRC’s research initiatives span five distinctive, but broadly interconnected disciplines: nanoscience, photonics, neuroscience, structural biology, and environmental sciences. The center promotes a collaborative, interdisciplinary research culture where renowned and emerging scientists advance their discoveries using state-of-the-art equipment and cutting-edge core facilities.
Journal
Communications Biology
DOI
10.1038/s42003-023-05609-0
Method of Research
Imaging analysis
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Pushed to extremes: distinct effects of high temperature versus pressure on the structure of STEP
Article Publication Date
12-Jan-2024




