For the sake of the environment and our quality of life, effective treatment of wastewater plays a vital role. A biological method to treat sewage using moving, biofilm-covered plastic items known as carriers has been gaining prominence, and an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has found ways to make the process more efficient.
For the sake of the environment and our quality of life, effective treatment of wastewater plays a vital role. A biological method to treat sewage using moving, biofilm-covered plastic items known as carriers has been gaining prominence, and an Osaka Metropolitan University-led team has found ways to make the process more efficient.
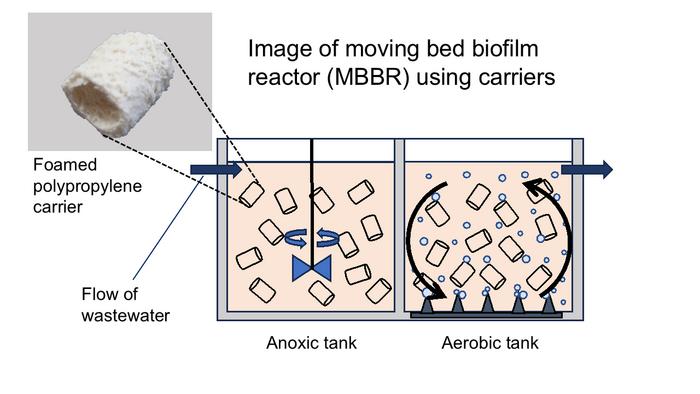
The moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) process purifies wastewater by putting these carriers in motion to get the biofilm’s microorganisms into greater contact with organic matter and other impurities. The more biofilm that can be attached to the plastic carriers, the more microorganisms that are available to clean the wastewater.
OMU Professor Masayuki Azuma and Associate Professor Yoshihiro Ojima of the Graduate School of Engineering worked with a team from Kansaikako Co., an Osaka-based company specializing in water treatment-related products, and found that polypropylene carriers foamed to create uneven surfaces and more surface area allowed 44 times more biofilm formation than smooth plastic carriers.
Moreover, adding waste biomass such as composted seaweed when foaming further enhanced the performance of the foamed plastic carriers, especially in terms of nitrate removal during the MBBR process.
“Since there is a wide variety of wastewater, it will be necessary to prove that these foamed carriers also have superior suitability to various wastewater,” stated Professor Azuma. “It is clear that the addition of waste biomass improves the performance of the carriers, so we expect that further performance enhancement can be achieved depending on the additive.”
The findings were published in Environmental Technology & Innovation.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
Journal
Environmental Technology & Innovation
DOI
10.1016/j.eti.2024.103747
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Nitrogen conversion performance of a polypropylene carrier designed to promote biofilm formation through foaming
Article Publication Date
10-Jul-2024
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.