This study is led by Dr. Cunrui Huang (Vanke School of Public Health, Tsinghua University). Heatwaves impose heavy disease burden by increasing the risk of mortality and morbidity, which has been exacerbated worldwide under climate change. “In China, evidence documenting the impact of heatwaves on the number of attributable deaths, spatiotemporal variations and their driving factors is still limited, hindering the understanding of dangerous heatwaves. ” Huang says.
Credit: ©Science China Press
This study is led by Dr. Cunrui Huang (Vanke School of Public Health, Tsinghua University). Heatwaves impose heavy disease burden by increasing the risk of mortality and morbidity, which has been exacerbated worldwide under climate change. “In China, evidence documenting the impact of heatwaves on the number of attributable deaths, spatiotemporal variations and their driving factors is still limited, hindering the understanding of dangerous heatwaves. ” Huang says.
Huang, together with his group member Chen and meteorological expert Zhao, sought to identify what was the spatial and temporal trends of heatwave-attributable deaths in China over the past four decades. The team performed event-based attributable loss estimation to quantify the gridded attributable deaths.
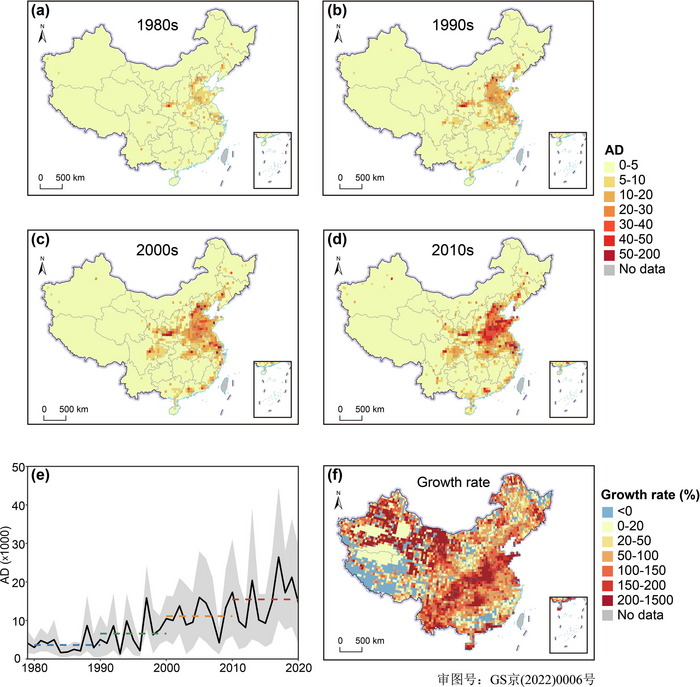
The team found that health risks of climate change were characterized by rapid growth, nonlinear evolution and extremity. The attributable deaths to heatwaves in China have increased dramatically by four times in the past four decades, with the rising trends becoming more apparent in the recent decade but some fluctuations among individual years. Regionally, east and central China had the largest number of attributable deaths in general, accounting for more than 50% of deaths nationwide. Among the provinces, deaths ascribed to heatwaves were highest in Shandong, followed by Henan, Hebei and Jiangsu.
The researchers also decomposed the driving factors to changes in attributable deaths. The increase in attributable deaths to heatwaves in China over time was primarily due to increased heatwave exposure, followed by population growth, population aging and the mounting baseline mortality. Notably, population aging has played an increasingly important role in attributable deaths over time. This work could serve important information for policy-makers to develop effective climate mitigation and adaptation measures in response to increasing heatwaves, especially for the most vulnerable elderly populations.
See the article:
Spatiotemporal Variation of Mortality Burden Attributable to Heatwaves in China, 1979-2020
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2022.05.006
Journal
Science Bulletin
DOI
10.1016/j.scib.2022.05.006




