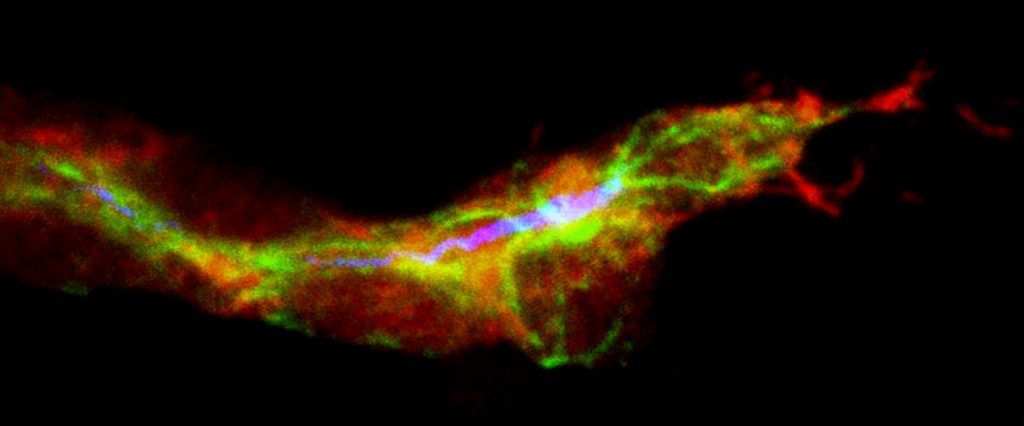
One of the major causes of hearing loss in mammals is damage to the sound-sensing hair cells in the inner ear. For years, scientists have thought that these cells are not replaced once they’re lost, but new research appearing online February 20 in the journal Stem Cell Reports reveals that supporting cells in the ear can turn into hair cells in newborn mice. If the findings can be applied to older animals, they may lead to ways to help stimulate cell replacement in adults and to the design of new treatment strategies for people suffering from deafness due to hair cell loss.
Whereas previous research indicated that hair cells are not replaced, this latest study found that replacement does indeed occur, but at very low levels. “The finding that newborn hair cells regenerate spontaneously is novel,” says senior author Dr. Albert Edge of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.
The team’s previous research revealed that inhibition of the Notch signaling pathway increases hair cell differentiation and can help restore hearing to mice with noise-induced deafness. In their latest work, the investigators found that blocking the Notch pathway increases the formation of new hair cells not from remaining hair cells but from certain nearby supporting cells that express a protein called Lgr5.
“By using an inhibitor of Notch signaling, we could push even more cells to differentiate into hair cells,” says Dr. Edge. “It was surprising that the Lgr5-expressing cells were the only supporting cells that differentiated under these conditions.”
Combining this new knowledge about Lgr5-expressing cells with the previous finding that Notch inhibition can regenerate hair cells will allow the scientists to design new hair cell regeneration strategies to treat hearing loss and deafness.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Cell Press via eurekalert.