Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new strategy for the treatment of coronary artery disease.
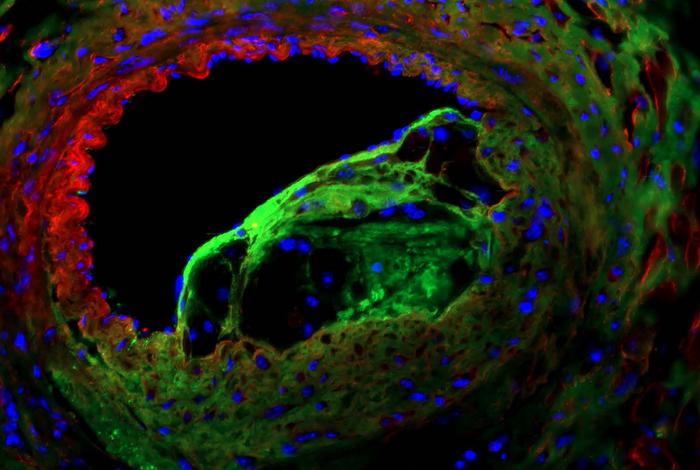
Credit: Credit: Dr. Onorina Manzo.
Solving the Riddle of the Sphingolipids in Coronary Artery Disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new strategy for the treatment of coronary artery disease.
In the study, published March 8 in Circulation Research, the researchers showed that boosting levels of a sphingolipid called S1P in artery-lining endothelial cells slows the development and progression of coronary artery disease in an animal model. The lead author was Dr. Onorina Laura Manzo, a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Dr. Annarita Di Lorenzo, an associate professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine.
Sphingolipids are named for the enigmatic sphinx of ancient mythology because their functions in biology traditionally have been somewhat mysterious. In recent years, there has been increasing evidence of their relevance in coronary artery disease; bloodstream levels of S1P, for example, are lower in patients with this condition. But the precise roles of these lipids have remained unclear.
In the new study, the researchers sought a better understanding of those roles—and of sphingolipids’ potential as therapeutic targets. Despite the availability of cholesterol-lowering drugs and other interventions, coronary artery disease—the underlying cause of most heart attacks and many strokes—continues to be the world’s leading cause of mortality, affecting more than 20 million people in the United States alone.
Using a novel mouse model developed by the same group, the researchers found that blood pressure-related stress on arteries—which eventually will induce coronary artery disease—triggers an increase in S1P production in endothelial cells, as part of a protective response. This response normally is only temporary, but deleting a protein called NOGO-B, which inhibits S1P production, allows the rise in endothelial S1P production to be sustained—and made the animals much more resistant to coronary artery disease and associated mortality.
Another key finding is related to a different group of sphingolipids called ceramides. Prior studies have linked coronary artery disease to high bloodstream levels of some ceramides, and their causative role in the disease has been widely assumed. In their model, however, the researchers observed that while ceramide levels were high in the bloodstream, levels in artery-lining endothelial cells remained about the same regardless of coronary artery disease status. This suggests that the current view of ceramides’ role in the disease should be revised.
All in all, the findings lay the foundation for the development of drugs that boost S1P to treat or prevent coronary artery disease, the researchers concluded.
The work reported in this story was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, through grant numbers R01HL126913 and R01HL152195 and a Harold S. Geneen Charitable Trust Award for Coronary Heart Disease Research.
Journal
Circulation Research




