Multicomponent ultra-high temperature ceramic (UHTC) has attracted much attention in research due to its superior high-temperature mechanical properties, lower thermal conductivity and enhanced oxidation resistance. Multiphase design is a promising approach to achieve improved ablation resistance of multicomponent UHTC, potentially meeting the stringent demands for thermal protection materials (TPMs) for aerospace. However, understanding the ablation mechanism of multiphase multicomponent ceramic is foundational.
Credit: Ziming Ye, et al.
Multicomponent ultra-high temperature ceramic (UHTC) has attracted much attention in research due to its superior high-temperature mechanical properties, lower thermal conductivity and enhanced oxidation resistance. Multiphase design is a promising approach to achieve improved ablation resistance of multicomponent UHTC, potentially meeting the stringent demands for thermal protection materials (TPMs) for aerospace. However, understanding the ablation mechanism of multiphase multicomponent ceramic is foundational.
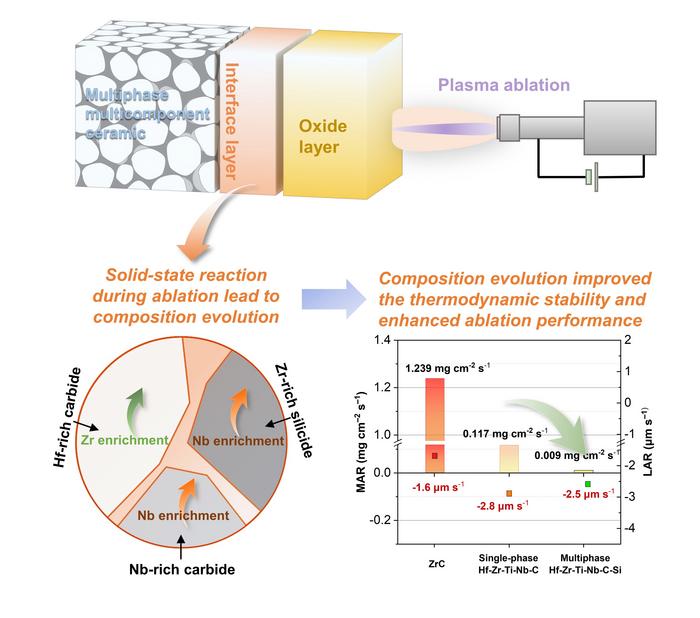
In the past, it is generally believed that the constituent phases among the multiphase multicomponent UHTC would not react with each other during ablation. However, a team of researchers led by Xiang Xiong and Yi Zeng at the Central South University in China reported a new solid-state reaction process between different multicomponent phases during ablation. Their investigation focused on a three-phase multicomponent ceramic consisting of Hf-rich carbide, Nb-rich carbide and Zr-rich silicide phases. More importantly, they found the ablation performance was also affectsed by this solid-state reaction.
Specifically, this solid-state reaction occurred in the matrix/oxide scale interface region. During this process, metal cations counter-diffused between the multicomponent phases, resulting in their composition evolution.
“The composition evolution allowed the underlying multicomponent phases to remain stable even under a higher oxygen partial pressure, which led to the improvement of thermodynamic stability of three-phase multicomponent ceramic,” explains Xiong. “Moreover, this solid-state reaction process appeared synergistic with the preferential oxidation behavior among the oxide scale in enhancing of the ablation performance within a specific temperature range.”
“The present findings proved that multiphase design allows the multicomponent ceramic to achieve even better ablation performance. The obtained results may also provide a preliminary basis for the future development of multiphase multicomponent UHTCs,” Zeng adds.
###
Contact the author: Yi Zeng, State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha, P.R. China, [email protected].
Xiang Xiong, State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha, P.R. China, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Advanced Powder Materials
DOI
10.1016/j.apmate.2024.100189
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Revealing the solid-state reaction process among multiphase multicomponent ceramic during ablation
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper




