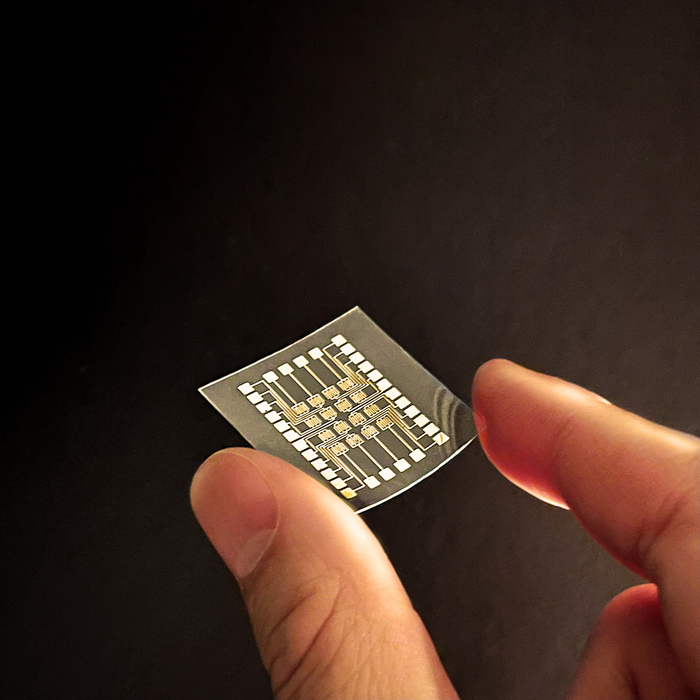
A soft and flexible electronic “e-skin,” so sensitive it can detect the minute temperature difference between an inhaled and an exhaled breath, could form the basis of a new form of on-skin biosensor. The ultrathin material is also sensitive to touch and body motion, suggesting a wide array of potential applications.
Credit: © 2022 KAUST; Vincent Tung
A soft and flexible electronic “e-skin,” so sensitive it can detect the minute temperature difference between an inhaled and an exhaled breath, could form the basis of a new form of on-skin biosensor. The ultrathin material is also sensitive to touch and body motion, suggesting a wide array of potential applications.
“The skin plays a vital role in our interactions with the world,” says Vincent Tung from KAUST, who led the work. “Recreating its properties in an e-skin could have profound implications for wearable electronics, as well as for sensory prosthetics, soft robotics and human-machine interfaces,” he says. Despite considerable research effort, however, it has been very challenging to create suitable materials, which must be strong and highly sensitive, yet imperceptible when applied to the skin.
A carbon nanomaterial called hydrogen-substituted graphdiyne (HsGDY) could be ideal for the task, Tung and his collaborators have shown. This two-dimensional sheet of carbon atoms has similarities to graphene in its strength and electrical conductivity, but also has key differences, Tung notes. Graphene’s tight honeycomb-like carbon structure lends the material rigidity. In contrast, HsGDY’s “island-bridge” atomic structure of rigid regions connected by thin polymer bridges in theory should provide an inherent softness and flexibility that is ideal for on-skin applications.
“The implementation of HsGDY into e-skin has long been touted by theorists, but had yet to be demonstrated experimentally,” Tung says. The team first developed a novel synthetic strategy to form large uniform HsGDY sheets. “The key was our use of an atomically structured, single-crystal copper catalyst to couple the molecular building blocks of the material,” Tung explains.
The team were able to show what the theory had predicted: the resulting material was highly twistable, stretchable and mechanically durable. “At around 18 nanometers thick, our e-skin is a fraction of the thickness of human skin, enabling conformal contact and long-term adhesion to the body with maximum flexibility and comfort,” Tung says.
The material’s island-bridge atomic structure not only contributes to HsGDY’s soft and flexible nature but is also key to its electronic properties, Tung adds. The bridges form ultrathin conduction channels that are easily deformed, resulting in significant changes in electrical signal when the material is stretched by a gentle touch or even by a temperature change. “The excellent sensitivity and conformability make it possible to visualize the tiny deformation caused by the temperature difference between inhalation and exhalation, showing promising potential for practical clinical applications,” Tung says.
Journal
ACS Nano
DOI
10.1021/acsnano.2c06169
Article Title
Graphdiyne-Based Nanofilms for Compliant On-Skin Sensing
Article Publication Date
20-Sep-2022




