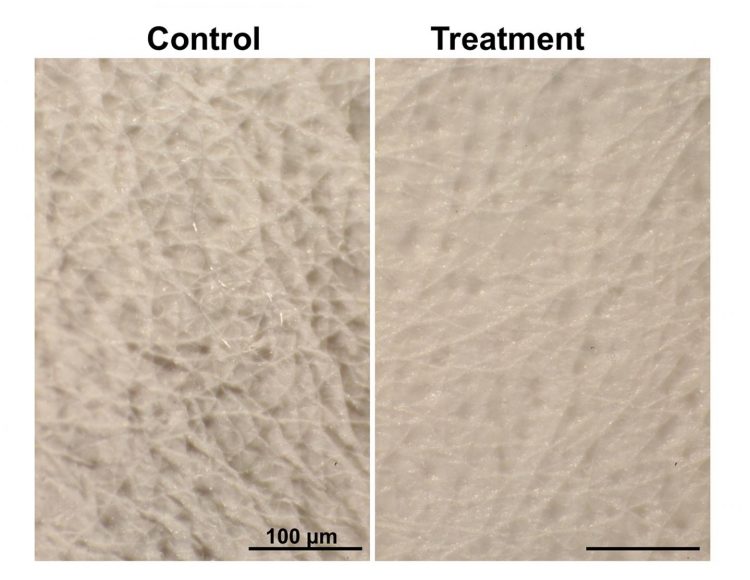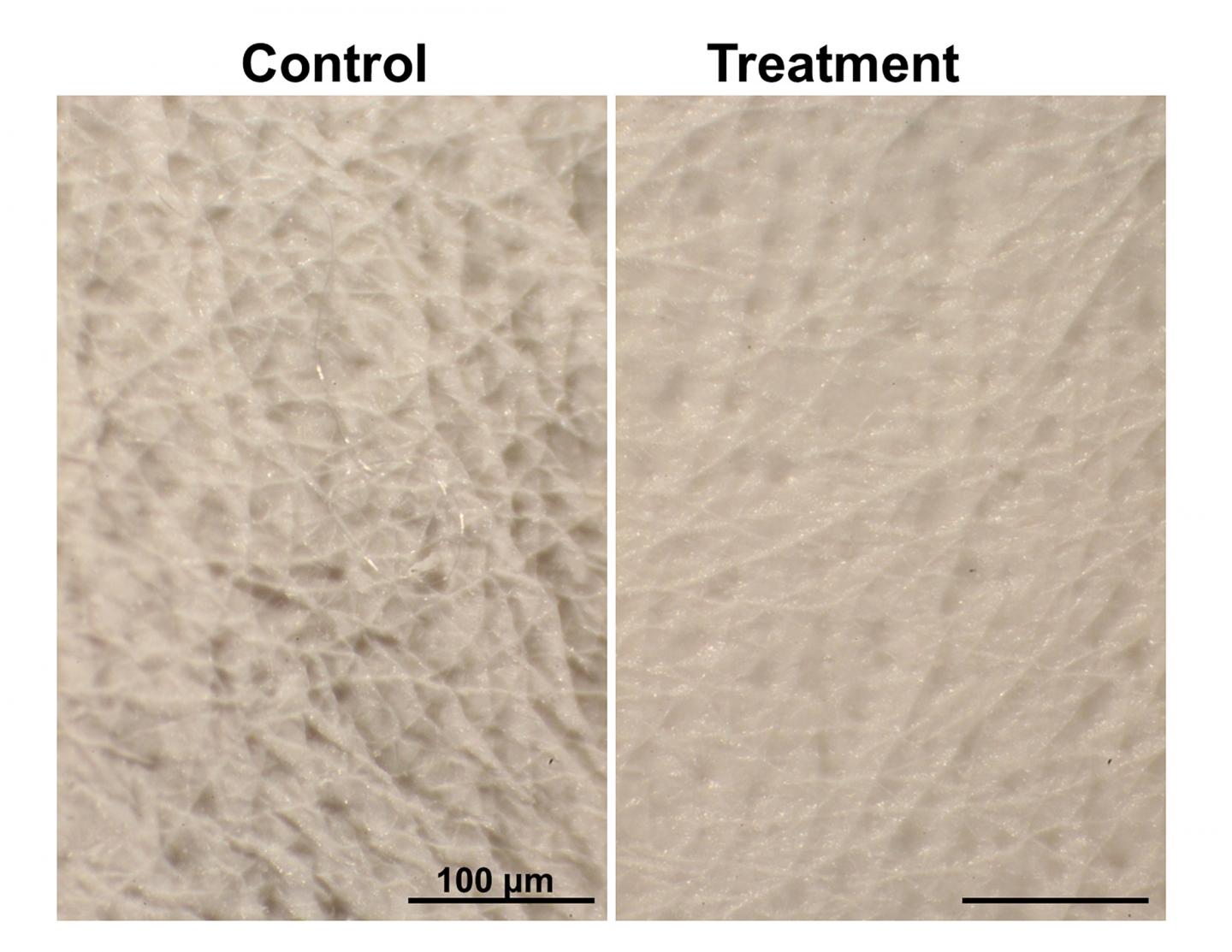
Credit: Adapted from ACS Nano 2019, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.9b0438
In the quest for a more youthful appearance, many people slather ointments on their skin or undergo injections of dermal fillers. But topical treatments often aren’t very effective because they don’t penetrate deep within the skin, whereas the results from injections typically last for only a few months and can be painful. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have developed a needle-free “exosome” treatment that reduces wrinkles in UV-exposed mice.
As skin cells age, they lose their ability to multiply and to produce collagen, which is the main structural protein in skin. Recently, scientists discovered that treating human skin cells in a dish with exosomes from stem cells boosted the amount of collagen and caused other youthful changes. Exosomes are membranous vesicles containing protein and RNA that cells release to communicate with each other. Ke Cheng and colleagues wondered if treating mouse skin with exosomes from human dermal fibroblasts could reduce wrinkles and restore youthful characteristics. To avoid having to inject the exosomes, the researchers tested a needle-free device that uses a jet of air to deliver medications deep into the skin.
The researchers exposed mice to ultraviolet B (UVB) light, which accelerates aging and causes wrinkles to form. After 8 weeks of UVB exposure, the researchers administered exosomes from human dermal fibroblasts to some of the mice with the needle-free injector. Three weeks later, the treated mice showed significantly thinner and more superficial wrinkles than untreated mice or those that received topical retinoic acid, a standard anti-aging medication. Skin from the exosome-treated mice was thicker and showed reduced inflammation and enhanced collagen synthesis compared with skin from untreated mice.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association.
The abstract that accompanies this study is available here.
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, is a not-for-profit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us on Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.