A new study in Nature Communications unveils the hidden world of sensory evolution in fruit flies. By delving into the genes and cells behind their delicate noses and tongues, researchers have discovered surprising secrets about how these tiny insects adapt their senses to different environments.
Credit: Gwénaëlle Bontonou et. al./Nature Communications
A new study in Nature Communications unveils the hidden world of sensory evolution in fruit flies. By delving into the genes and cells behind their delicate noses and tongues, researchers have discovered surprising secrets about how these tiny insects adapt their senses to different environments.
“Imagine a world where a ripe peach tastes and smells like tangy vinegar to one fly, but like a burst of summer to another,” explains principal author of the study Dr Roman Arguello, a Lecturer in Genetics, Genomics and Fundamental Cell Biology at Queen Mary University of London. “Our study shows that this is not just possible, but it’s actually quite common.”
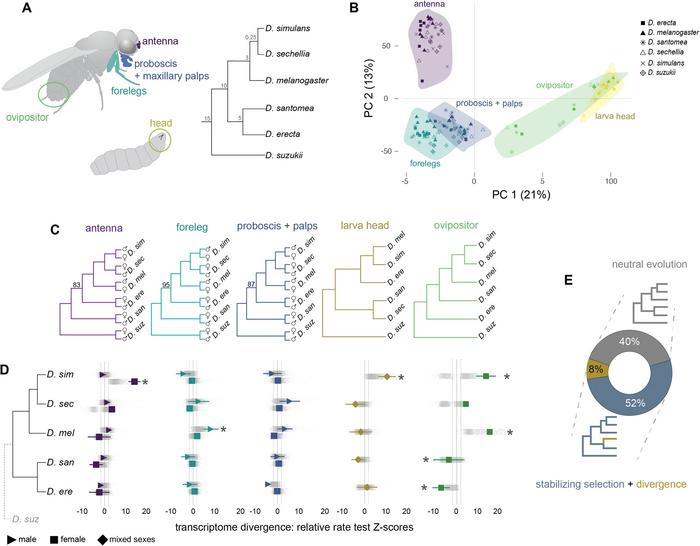
The research team analysed the gene expression patterns in five key scent-detecting tissues across six different Drosophila species. This comprehensive approach allowed them to delve deeper than ever before into the molecular underpinnings of smell.
One surprising discovery was the prevalence of “stabilising selection,” a force that keeps most genes expressed at the same levels across generations. However, within this sea of stability, the researchers found thousands of genes that had undergone significant changes in expression, shaping the unique olfactory landscapes of different fly species.
“It’s like finding hidden islands of diversity within a vast ocean of uniformity,” says Dr Arguello. “These changes in gene expression tell us about the evolution of new smells, new sensitivities, and even new ways of using scent to navigate the world.”
The study also reveals intriguing differences between the sexes. In fruit flies, as in many other animals, males and females often experience the world through different olfactory lenses. The researchers identified a surprising excess of male-biased gene expression in the front legs of D. melanogaster, suggesting that these limbs play a crucial role in male-specific scent detection.
“These findings open up exciting new avenues for understanding how sex differences evolve and how they impact animal behavior,” says Dr Arguello.
The study’s implications extend beyond the fascinating world of flies. It provides valuable insights into the general principles of how sensory systems evolve, offering clues to understanding how other animals, including humans, perceive their chemical environments.
Journal
Nature Communications
Article Title
Evolution of chemosensory tissues and cells across ecologically diverse Drosophilids
Article Publication Date
5-Feb-2024




