The development of various hypoxia-activated prodrugs (HAPs) has made considerable advances in the last few decades; however, cancer therapy using HAPs is still hindered by problems such as poor therapeutic outcomes due to difficulty in reaching the hypoxic region and metastasis resulting from hypoxia.
Credit: The authors
The development of various hypoxia-activated prodrugs (HAPs) has made considerable advances in the last few decades; however, cancer therapy using HAPs is still hindered by problems such as poor therapeutic outcomes due to difficulty in reaching the hypoxic region and metastasis resulting from hypoxia.
To that end, a team of researchers in China proposed a novel treatment approach capable of enhancing HAP-based chemotherapy and suppress tumor metastasis.
Hangrong Chen, a professor at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and one of the lead authors of the study, explained that solid tumours often contain areas with low oxygen concentration (hypoxia) near areas of necrosis. These hypoxic regions are resistant to both radiotherapy and chemotherapy, providing an opportunity for selective therapy such as prodrugs activated by hypoxia.
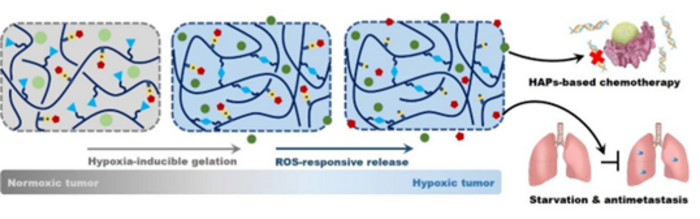
“HAPs, also known as bioreductive prodrugs, which can become toxic drugs in a hypoxia-dependent manner, are non-toxic in normoxic regions,” added Chen. “However, one major hindrance for the clinical translations of HAPs is the inability to reach hypoxic regions that are distant from blood vessel network, which results in inadequate exposure to antitumor HAPs and contributes to low efficient chemotherapy.”
The team created a novel hypoxia-inducible chitosan polymer that can be combined with antiangiogenic Pazopanib to form an injectable hydrogel that is sensitive to oxygen. Enzyme-mediated chemical reactions enable the polymers to react to oxygen and cause gelation. By administering this oxygen scavenging hydrogel with HAPs, it is possible to improve the hypoxic environment of tumors, leading to heightened toxicity of HAP for selective chemotherapy. Furthermore, when exposed to elevated ROS in tumor regions, the responsive linkages within the hydrogel are broken, allowing sustained release of Pazopanib and inhibiting pulmonary metastasis.
The team’s findings are published in the KeAi journal Bioactive Materials.
In the study the oxygen elimination within the tumor was visualized in real-time with a micro-PET imaging technique provided by Professor Shaoli Song, a co-supervisor the study.
“This novel hydrogel can significantly remodel tumor hypoxic microenvironment as a kind of engineered niche,” said Song. “We hope that our results will encourage scientists to continue investigating the use of HAP-based chemotherapy to combat cancer.”
###
Contact the corresponding author: Hangrong Chen, [email protected] / Shaoli Song, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Bioactive Materials
DOI
10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.08.002
Article Title
In Situ forming oxygen/ROS-responsive niche-like hydrogel enabling gelation-triggered chemotherapy and inhibition of metastasis




